
Albert Cohen (born 29 June 1965 in Paris) is a French mathematician, specializing in approximation theory, numerical analysis, and digital signal processing.

Albert Cohen (born 29 June 1965 in Paris) is a French mathematician, specializing in approximation theory, numerical analysis, and digital signal processing.
He is, through maternal descent, the grand-nephew of the physicist Jacques Solomon. From 1984 to 1987 Albert Cohen was a student at the École Polytechnique. In 1990 he defended his doctoral thesis at Paris Dauphine University. His thesis, written under the supervision of Yves Meyer, is entitled Ondelettes, analyse multi résolution et traitement numérique du signal (Wavelets, multiresolution analysis and digital signal analysis) [1] From 1990 to 1991 Cohen was a postdoc at Bell Laboratories at Murray Hill. He completed his habilitation in 1992 at Paris Dauphine University. From 1993 to 1995 he worked at ENSTA Paris. Since 1995 he has been a professor at the Laboratoire Jacques-Louis Lions of Pierre and Marie Curie University (Paris 6), [2] which is a component of Sorbonne University. He is the author of 3 books and the author of co-author of over 100 research articles. [3]
Cohen developed in 1990, with Ingrid Daubechies and Jean-Christophe Feauveau, the first biorthogonal bases for wavelets; [4] this research has an important application in the image compression standard JPEG-2000. With Wolfgang Dahmen and Ronald DeVore, Cohen then worked on the analysis of nonlinear and adaptive approximation methods, with a view to applications in learning theory and in numerical analysis of partial differential equations. He is interested in algorithmic problems involving a very large number of variables, which cause a prohibitive increase in the complexity of calculations. These problems arise in statistical learning theory, in the treatment of parametric and stochastic partial differential equations, and in the development of response surfaces from computer software involving adaptive numerical methods. [2]
In 2000 Cohen received the grand prix Jacques Herbrand from the French Academy of Sciences. In 1995 he won the V. A. Popov Prize in approximation theory from the University of South Carolina and in 2004 the prix Blaise Pascal from the French Academy of Sciences. He was elected in 1998 a junior member and in 2013 a senior member of the Institut Universitaire de France. [5] He was an invited speaker at the International Congress of Mathematicians (ICM) in Beijing in 2002, [6] a plenary speaker at the International Congress on Industrial and Applied Mathematics (ICIAM) in Zurich in 2007, and an invited speaker at the conference Dynamics, Equations and Applications in Kraków in 2019. [7]
In 2013 Cohen was awarded an ERC Advanced Grant for a project called BREAD (Breaking the curse of dimensionality in analysis and simulation ).
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link){{cite book}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link){{cite book}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link)Cohen, A. (13 May 2003). 2003 hbk edition. ISBN 978-0-444-51124-9.
A wavelet is a wave-like oscillation with an amplitude that begins at zero, increases or decreases, and then returns to zero one or more times. Wavelets are termed a "brief oscillation". A taxonomy of wavelets has been established, based on the number and direction of its pulses. Wavelets are imbued with specific properties that make them useful for signal processing.
In digital signal processing, a quadrature mirror filter is a filter whose magnitude response is the mirror image around of that of another filter. Together these filters, first introduced by Croisier et al., are known as the quadrature mirror filter pair.
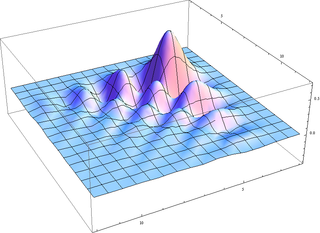
The Daubechies wavelets, based on the work of Ingrid Daubechies, are a family of orthogonal wavelets defining a discrete wavelet transform and characterized by a maximal number of vanishing moments for some given support. With each wavelet type of this class, there is a scaling function which generates an orthogonal multiresolution analysis.

In numerical analysis and functional analysis, a discrete wavelet transform (DWT) is any wavelet transform for which the wavelets are discretely sampled. As with other wavelet transforms, a key advantage it has over Fourier transforms is temporal resolution: it captures both frequency and location information.

Baroness Ingrid Daubechies is a Belgian physicist and mathematician. She is best known for her work with wavelets in image compression.

Yves F. Meyer is a French mathematician. He is among the progenitors of wavelet theory, having proposed the Meyer wavelet. Meyer was awarded the Abel Prize in 2017.

Cohen–Daubechies–Feauveau wavelets are a family of biorthogonal wavelets that was made popular by Ingrid Daubechies. These are not the same as the orthogonal Daubechies wavelets, and also not very similar in shape and properties. However, their construction idea is the same.
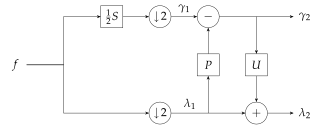
The lifting scheme is a technique for both designing wavelets and performing the discrete wavelet transform (DWT). In an implementation, it is often worthwhile to merge these steps and design the wavelet filters while performing the wavelet transform. This is then called the second-generation wavelet transform. The technique was introduced by Wim Sweldens.

Emmanuel Jean Candès is a French statistician. He is a professor of statistics and electrical engineering at Stanford University, where he is also the Barnum-Simons Chair in Mathematics and Statistics. Candès is a 2017 MacArthur Fellow.

Wolfgang Dahmen is a German mathematician working in approximation theory, numerical analysis, and partial differential equations. In 2002, he was awarded the Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Prize and in 2011 the Gauss Lectureship. He was also a taekwondo athlete. He has been the Chair of the Society for the Foundations of Computational Mathematics (2014–).
István Gyöngy is a Hungarian mathematician working in the fields of stochastic differential equations, stochastic partial differential equations and their applications to nonlinear filtering and stochastic control. Recently, he has focused his attention on numerical analysis and especially accelerated numerical methods, making use of Richardson extrapolation.

Foundations of Computational Mathematics (FoCM) is an international nonprofit organization that supports and promotes research at the interface of mathematics and computation. It fosters interaction among mathematics, computer science, and other areas of computational science through conferences, events and publications.
Christine Bernardi was a French mathematician known for her research on numerical analysis of partial differential equations.
Weizhu Bao is a Chinese mathematician at the National University of Singapore (NUS). He is known for his work in applied mathematics with applications in quantum physics and chemistry and materials science, especially Bose-Einstein condensation (BEC) and highly oscillatory partial differential equations.

Rolf Rannacher is a German mathematician and a professor of numerical analysis at Heidelberg University.
Yvan Martel is a French mathematician.
Christoph Schwab is a German applied mathematician, specializing in numerical analysis of partial differential equations and boundary integral equations.
Zuowei Shen is a Chinese mathematician, and Tan Chin Tuan Centennial Professor at the National University of Singapore (NUS). Shen received his BSc in 1982 from Hohai University (China), MSc in 1987 and PhD in 1991 from University of Alberta. He first joined NUS as a lecturer at the Department of Mathematics in 1993; was promoted to professor in 2002 and distinguished professor in 2009. Shen was Head of Department of Mathematics from 2012 to 2014 and was appointed Dean of Science in 2014.
Charles Anthony Micchelli is an American mathematician, with an international reputation in numerical analysis, approximation theory, and machine learning.
Probabilistic numerics is a scientific field at the intersection of statistics, machine learning and applied mathematics, where tasks in numerical analysis including finding numerical solutions for integration, linear algebra, optimisation and differential equations are seen as problems of statistical, probabilistic, or Bayesian inference.