Related Research Articles
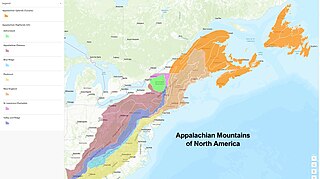
The geology of the Appalachians dates back more than 1.2 billion years to the Mesoproterozoic era when two continental cratons collided to form the supercontinent Rodinia, 500 million years prior to the development of the range during the formation of Pangea. The rocks exposed in today's Appalachian Mountains reveal elongate belts of folded and thrust faulted marine sedimentary rocks, volcanic rocks, and slivers of ancient ocean floor—strong evidences that these rocks were deformed during plate collision. The birth of the Appalachian ranges marks the first of several mountain building plate collisions that culminated in the construction of Pangea with the Appalachians and neighboring Anti-Atlas mountains near the center. These mountain ranges likely once reached elevations similar to those of the Alps and the Rocky Mountains before they were eroded.

The Permian Basin is a large sedimentary basin in the southwestern part of the United States. It is the highest producing oil field in the United States, producing an average of 4.2 million barrels of crude oil per day in 2019. This sedimentary basin is located in western Texas and southeastern New Mexico. It reaches from just south of Lubbock, past Midland and Odessa, south nearly to the Rio Grande River in southern West Central Texas, and extending westward into the southeastern part of New Mexico. It is so named because it has one of the world's thickest deposits of rocks from the Permian geologic period. The greater Permian Basin comprises several component basins; of these, the Midland Basin is the largest, Delaware Basin is the second largest, and Marfa Basin is the smallest. The Permian Basin covers more than 86,000 square miles (220,000 km2), and extends across an area approximately 250 miles (400 km) wide and 300 miles (480 km) long.

The Mackenzie River is a river in the Canadian boreal forest. It forms, along with the Slave, Peace, and Finlay, the longest river system in Canada, and includes the second largest drainage basin of any North American river after the Mississippi.

The Front Range is a mountain range of the Southern Rocky Mountains of North America located in the central portion of the U.S. State of Colorado, and southeastern portion of the U.S. State of Wyoming. It is the first mountain range encountered as one goes westbound along the 40th parallel north across the Great Plains of North America.

The richly textured landscape of the United States is a product of the dueling forces of plate tectonics, weathering and erosion. Over the 4.5 billion-year history of the Earth, tectonic upheavals and colliding plates have raised great mountain ranges while the forces of erosion and weathering worked to tear them down. Even after many millions of years, records of Earth's great upheavals remain imprinted as textural variations and surface patterns that define distinctive landscapes or provinces.

The Colorado Plateau, also known as the Colorado Plateau Province, is a physiographic and desert region of the Intermontane Plateaus, roughly centered on the Four Corners region of the southwestern United States. This province covers an area of 336,700 km2 (130,000 mi2) within western Colorado, northwestern New Mexico, southern and eastern Utah, northern Arizona, and a tiny fraction in the extreme southeast of Nevada. About 90% of the area is drained by the Colorado River and its main tributaries: the Green, San Juan, and Little Colorado. Most of the remainder of the plateau is drained by the Rio Grande and its tributaries.

The geology of the Grand Teton area consists of some of the oldest rocks and one of the youngest mountain ranges in North America. The Teton Range, partly located in Grand Teton National Park, started to grow some 9 million years ago. An older feature, Jackson Hole, is a basin that sits aside the range.

The exposed geology of the Death Valley area presents a diverse and complex set of at least 23 formations of sedimentary units, two major gaps in the geologic record called unconformities, and at least one distinct set of related formations geologists call a group. The oldest rocks in the area that now includes Death Valley National Park are extensively metamorphosed by intense heat and pressure and are at least 1700 million years old. These rocks were intruded by a mass of granite 1400 Ma and later uplifted and exposed to nearly 500 million years of erosion.
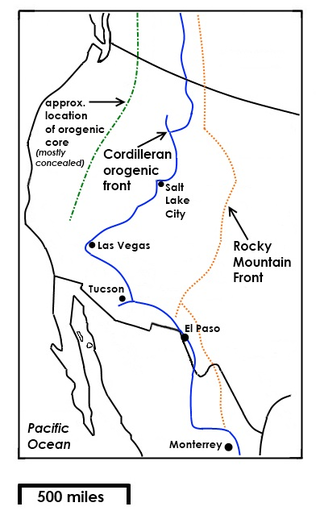
The Rocky Mountain Front is a somewhat unified geologic and ecosystem area in North America where the eastern slopes of the Rocky Mountains meet the plains. In 1983, the Bureau of Land Management called the Rocky Mountain Front "a nationally significant area because of its high wildlife, recreation, and scenic values". Conservationists Gregory Neudecker, Alison Duvall, and James Stutzman have described the Rocky Mountain Front as an area that warrants "the highest of conservation priorities" because it is largely unaltered by development and contains "unparalleled" numbers of wildlife.

Sponge reefs are reefs produced by sea sponges. All modern sponge reefs are formed by hexactinellid sponges, which have an endoskeleton made of silica spicules and are often referred to as "glass sponges", while historically the non-spiculed, calcite-skeletoned archaeocyathid and stromatoporoid sponges were the primariy reef-builders.

The geology of Saskatchewan can be divided into two main geological regions, the Precambrian Canadian Shield and the Phanerozoic Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin. Within the Precambrian shield exists the Athabasca sedimentary basin. Meteorite impacts have altered the natural geological formation processes. The prairies were most recently affected by glacial events in the Quaternary period.

The geology of North America is a subject of regional geology and covers the North American continent, the third-largest in the world. Geologic units and processes are investigated on a large scale to reach a synthesized picture of the geological development of the continent.
The geology of Ohio formed beginning more than one billion years ago in the Proterozoic eon of the Precambrian. The igneous and metamorphic crystalline basement rock is poorly understood except through deep boreholes and does not outcrop at the surface. The basement rock is divided between the Grenville Province and Superior Province. When the Grenville Province crust collided with Proto-North America, it launched the Grenville orogeny, a major mountain building event. The Grenville mountains eroded, filling in rift basins and Ohio was flooded and periodically exposed as dry land throughout the Paleozoic. In addition to marine carbonates such as limestone and dolomite, large deposits of shale and sandstone formed as subsequent mountain building events such as the Taconic orogeny and Acadian orogeny led to additional sediment deposition. Ohio transitioned to dryland conditions in the Pennsylvanian, forming large coal swamps and the region has been dryland ever since. Until the Pleistocene glaciations erased these features, the landscape was cut with deep stream valleys, which scoured away hundreds of meters of rock leaving little trace of geologic history in the Mesozoic and Cenozoic.

The geology of South Dakota began to form more than 2.5 billion years ago in the Archean eon of the Precambrian. Igneous crystalline basement rock continued to emplace through the Proterozoic, interspersed with sediments and volcanic materials. Large limestone and shale deposits formed during the Paleozoic, during prevalent shallow marine conditions, followed by red beds during terrestrial conditions in the Triassic. The Western Interior Seaway flooded the region, creating vast shale, chalk and coal beds in the Cretaceous as the Laramide orogeny began to form the Rocky Mountains. The Black Hills were uplifted in the early Cenozoic, followed by long-running periods of erosion, sediment deposition and volcanic ash fall, forming the Badlands and storing marine and mammal fossils. Much of the state's landscape was reworked during several phases of glaciation in the Pleistocene. South Dakota has extensive mineral resources in the Black Hills and some oil and gas extraction in the Williston Basin. The Homestake Mine, active until 2002, was a major gold mine that reached up to 8000 feet underground and is now used for dark matter and neutrino research.
The geology of Austria consists of Precambrian rocks and minerals together with younger marine sedimentary rocks uplifted by the Alpine orogeny.
The geology of Alberta encompasses parts of the Canadian Rockies and thick sedimentary sequences, bearing coal, oil and natural gas, atop complex Precambrian crystalline basement rock.

The geology of Utah, in the western United States, includes rocks formed at the edge of the proto-North American continent during the Precambrian. A shallow marine sedimentary environment covered the region for much of the Paleozoic and Mesozoic, followed by dryland conditions, volcanism, and the formation of the basin and range terrain in the Cenozoic.

The bedrock under the U.S. State of Colorado was assembled from island arcs accreted onto the edge of the ancient Wyoming Craton. The Sonoma orogeny uplifted the ancestral Rocky Mountains in parallel with the diversification of multicellular life. Shallow seas covered the regions, followed by the uplift current Rocky Mountains and intense volcanic activity. Colorado has thick sedimentary sequences with oil, gas and coal deposits, as well as base metals and other minerals.

The geology of North Dakota includes thick sequences oil and coal bearing sedimentary rocks formed in shallow seas in the Paleozoic and Mesozoic, as well as terrestrial deposits from the Cenozoic on top of ancient Precambrian crystalline basement rocks. The state has extensive oil and gas, sand and gravel, coal, groundwater and other natural resources.
The geology of Montana includes thick sequences of Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic sedimentary rocks overlying ancient Archean and Proterozoic crystalline basement rock. Eastern Montana has considerable oil and gas resources, while the uplifted Rocky Mountains in the west, which resulted from the Laramide orogeny and other tectonic events have locations with metal ore.
References
- ↑ "Alberta Basin | depression, Alberta, Canada". Britannica.com. Retrieved 2016-05-03.
- ↑ Alberta Environment and Sustainable Resource Development Retrieved 25 May 2015.
- ↑ Alberta Geological Survey Archived 2008-12-26 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 5 May 2015.
- ↑ Deep Basin - Canada Retrieved 25 May 2015.