Related Research Articles

Endocytosis is a cellular process in which substances are brought into the cell. The material to be internalized is surrounded by an area of cell membrane, which then buds off inside the cell to form a vesicle containing the ingested material. Endocytosis includes pinocytosis and phagocytosis. It is a form of active transport.
In biology, caveolae, which are a special type of lipid raft, are small invaginations of the plasma membrane in the cells of many vertebrates. They are the most abundant surface feature of many vertebrate cell types, especially endothelial cells, adipocytes and embryonic notochord cells. They were originally discovered by E. Yamada in 1955.

A steroid hormone is a steroid that acts as a hormone. Steroid hormones can be grouped into two classes: corticosteroids and sex steroids. Within those two classes are five types according to the receptors to which they bind: glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids and androgens, estrogens, and progestogens. Vitamin D derivatives are a sixth closely related hormone system with homologous receptors. They have some of the characteristics of true steroids as receptor ligands.
Transferrins are glycoproteins found in vertebrates which bind to and consequently mediate the transport of iron (Fe) through blood plasma. They are produced in the liver and contain binding sites for two Fe3+ ions. Human transferrin is encoded by the TF gene and produced as a 76 kDa glycoprotein.
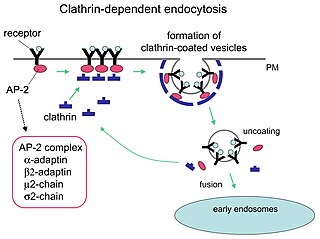
Receptor-mediated endocytosis (RME), also called clathrin-mediated endocytosis, is a process by which cells absorb metabolites, hormones, proteins – and in some cases viruses – by the inward budding of the plasma membrane (invagination). This process forms vesicles containing the absorbed substances and is strictly mediated by receptors on the surface of the cell. Only the receptor-specific substances can enter the cell through this process.
Vascular endothelial growth factor, originally known as vascular permeability factor (VPF), is a signal protein produced by many cells that stimulates the formation of blood vessels. To be specific, VEGF is a sub-family of growth factors, the platelet-derived growth factor family of cystine-knot growth factors. They are important signaling proteins involved in both vasculogenesis and angiogenesis.

Human serum albumin is the serum albumin found in human blood. It is the most abundant protein in human blood plasma; it constitutes about half of serum protein. It is produced in the liver. It is soluble in water, and it is monomeric.
Transcytosis is a type of transcellular transport in which various macromolecules are transported across the interior of a cell. Macromolecules are captured in vesicles on one side of the cell, drawn across the cell, and ejected on the other side. Examples of macromolecules transported include IgA, transferrin, and insulin. While transcytosis is most commonly observed in epithelial cells, the process is also present elsewhere. Blood capillaries are a well-known site for transcytosis, though it occurs in other cells, including neurons, osteoclasts and M cells of the intestine.

Angiopoietin is part of a family of vascular growth factors that play a role in embryonic and postnatal angiogenesis. Angiopoietin signaling most directly corresponds with angiogenesis, the process by which new arteries and veins form from preexisting blood vessels. Angiogenesis proceeds through sprouting, endothelial cell migration, proliferation, and vessel destabilization and stabilization. They are responsible for assembling and disassembling the endothelial lining of blood vessels. Angiopoietin cytokines are involved with controlling microvascular permeability, vasodilation, and vasoconstriction by signaling smooth muscle cells surrounding vessels. There are now four identified angiopoietins: ANGPT1, ANGPT2, ANGPTL3, ANGPT4.
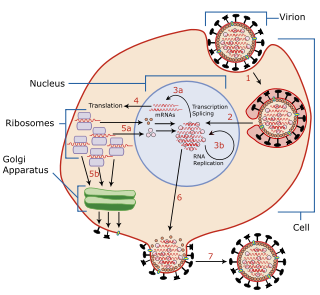
Viral entry is the earliest stage of infection in the viral life cycle, as the virus comes into contact with the host cell and introduces viral material into the cell. The major steps involved in viral entry are shown below. Despite the variation among viruses, there are several shared generalities concerning viral entry.

Transferrin receptor (TfR) is a carrier protein for transferrin. It is needed for the import of iron into the cell and is regulated in response to intracellular iron concentration. It imports iron by internalizing the transferrin-iron complex through receptor-mediated endocytosis. The existence of a receptor for transferrin iron uptake has been recognized since the late 1950s. Earlier two transferrin receptors in humans, transferrin receptor 1 and transferrin receptor 2 had been characterized and until recently cellular iron uptake was believed to occur chiefly via these two well documented transferrin receptors. Both these receptors are transmembrane glycoproteins. TfR1 is a high affinity ubiquitously expressed receptor while expression of TfR2 is restricted to certain cell types and is unaffected by intracellular iron concentrations. TfR2 binds to transferrin with a 25-30 fold lower affinity than TfR1. Although TfR1 mediated iron uptake is the major pathway for iron acquisition by most cells and especially developing erythrocytes, several studies have indicated that the uptake mechanism varies depending upon the cell type. It is also reported that Tf uptake exists independent of these TfRs although the mechanisms are not well characterized. The multifunctional glycolytic enzyme glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase has been shown to utilize post translational modifications to exhibit higher order moonlighting behavior wherein it switches its function as a holo or apo transferrin receptor leading to either iron delivery or iron export respectively.
The mannose receptor is a C-type lectin primarily present on the surface of macrophages, immature dendritic cells and liver sinusoidal endothelial cells, but is also expressed on the surface of skin cells such as human dermal fibroblasts and keratinocytes. It is the first member of a family of endocytic receptors that includes Endo180 (CD280), M-type PLA2R, and DEC-205 (CD205).
The neonatal Fc receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FCGRT gene. It is an IgG Fc receptor which is similar in structure to the MHC class I molecule and also associates with beta-2-microglobulin. In rodents, FcRn was originally identified as the receptor that transports maternal immunoglobulin G (IgG) from mother to neonatal offspring via mother's milk, leading to its name as the neonatal Fc receptor. In humans, FcRn is present in the placenta where it transports mother's IgG to the growing fetus. FcRn has also been shown to play a role in regulating IgG and serum albumin turnover. Neonatal Fc receptor expression is up-regulated by the proinflammatory cytokine, TNF, and down-regulated by IFN-γ.

Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 2 also known as LRP-2 or megalin is a protein which in humans is encoded by the LRP2 gene.

The CLCN5 gene encodes the chloride channel Cl-/H+ exchanger ClC-5. ClC-5 is mainly expressed in the kidney, in particular in proximal tubules where it participates to the uptake of albumin and low-molecular-weight proteins, which is one of the principal physiological role of proximal tubular cells. Mutations in the CLCN5 gene cause an X-linked recessive nephropathy named Dent disease characterized by excessive urinary loss of low-molecular-weight proteins and of calcium (hypercalciuria), nephrocalcinosis and nephrolithiasis.

Transferrin receptor protein 1 (TfR1), also known as Cluster of Differentiation 71 (CD71), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TFRC gene. TfR1 is required for iron import from transferrin into cells by endocytosis.
The endocannabinoid transporters (eCBTs) are transport proteins for the endocannabinoids. Most neurotransmitters are water-soluble and require transmembrane proteins to transport them across the cell membrane. The endocannabinoids on the other hand, are non-charged lipids that readily cross lipid membranes. However, since the endocannabinoids are water immiscible, protein transporters have been described that act as carriers to solubilize and transport the endocannabinoids through the aqueous cytoplasm. These include the heat shock proteins (Hsp70s) and fatty acid-binding proteins for anandamide (FABPs). FABPs such as FABP1, FABP3, FABP5, and FABP7 have been shown to bind endocannabinoids. FABP inhibitors attenuate the breakdown of anandamide by the enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) in cell culture. One of these inhibitors (SB-FI-26), isolated from a virtual library of a million compounds, belongs to a class of compounds that act as an anti-nociceptive agent with mild anti-inflammatory activity in mice. These truxillic acids and their derivatives have been known to have anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive effects in mice and are active components of a Chinese herbal medicine used to treat rheumatism and pain in human. The blockade of anandamide transport may, at least in part, be the mechanism through which these compounds exert their anti-nociceptive effects.
Nanoparticles for drug delivery to the brain is a method for transporting drug molecules across the blood–brain barrier (BBB) using nanoparticles. These drugs cross the BBB and deliver pharmaceuticals to the brain for therapeutic treatment of neurological disorders. These disorders include Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, schizophrenia, depression, and brain tumors. Part of the difficulty in finding cures for these central nervous system (CNS) disorders is that there is yet no truly efficient delivery method for drugs to cross the BBB. Antibiotics, antineoplastic agents, and a variety of CNS-active drugs, especially neuropeptides, are a few examples of molecules that cannot pass the BBB alone. With the aid of nanoparticle delivery systems, however, studies have shown that some drugs can now cross the BBB, and even exhibit lower toxicity and decrease adverse effects throughout the body. Toxicity is an important concept for pharmacology because high toxicity levels in the body could be detrimental to the patient by affecting other organs and disrupting their function. Further, the BBB is not the only physiological barrier for drug delivery to the brain. Other biological factors influence how drugs are transported throughout the body and how they target specific locations for action. Some of these pathophysiological factors include blood flow alterations, edema and increased intracranial pressure, metabolic perturbations, and altered gene expression and protein synthesis. Though there exist many obstacles that make developing a robust delivery system difficult, nanoparticles provide a promising mechanism for drug transport to the CNS.
Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs) form the lining of the smallest blood vessels in the liver, also called the hepatic sinusoids. LSECs are highly specialized endothelial cells with characteristic morphology and function. They constitute an important part of the reticuloendothelial system (RES).
Endothelial cell tropism or endotheliotropism is a type of tissue tropism or host tropism that characterizes an pathogen's ability to recognize and infect an endothelial cell. Pathogens, such as viruses, can target a specific tissue type or multiple tissue types. Like other cells, the endothelial cell possesses several features that supports a productive viral infection a cell including, cell surface receptors, immune responses, and other virulence factors. Endothelial cells are found in various tissue types such as in the capillaries, veins, and arteries in the human body. As endothelial cells line these blood vessels and critical networks that extend access to various human organ systems, the virus entry into these cells can be detrimental to virus spread across the host system and affect clinical course of disease. Understanding the mechanisms of how viruses attach, enter, and control endothelial functions and host responses inform infectious disease understanding and medical countermeasures.
References
- ↑ Schnitzer, J. E.; Oh, P. (1994). "Albondin-mediated capillary permeability to albumin. Differential role of receptors in endothelial transcytosis and endocytosis of native and modified albumins". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 269 (8): 6072–6082. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(17)37571-3 . PMID 8119952.
- ↑ Merlot, AM; Kalinowski, DS; Richardson, DR (2014). "Unraveling the mysteries of serum albumin-more than just a serum protein". Frontiers in Physiology. 5: 299. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00299 . PMC 4129365 . PMID 25161624.