Related Research Articles

Ludwig Karl Martin Leonhard Albrecht Kossel was a German biochemist and pioneer in the study of genetics. He was awarded the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine in 1910 for his work in determining the chemical composition of nucleic acids, the genetic substance of biological cells.
The University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center is a public academic health science center in Dallas, Texas. With approximately 18,800 employees, more than 2,900 full-time faculty, and nearly 4 million outpatient visits per year, UT Southwestern is the largest medical school in the University of Texas System and state of Texas.

The University of Rostock is a public university located in Rostock, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. Founded in 1419, it is the third-oldest university in Germany. It is the oldest university in continental northern Europe and the Baltic Sea area, and 8th oldest in Central Europe. It was the 5th university established in the Holy Roman Empire.
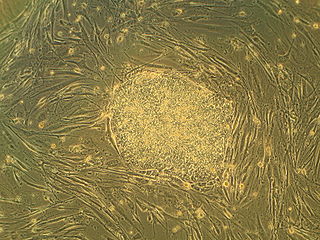
Regenerative medicine deals with the "process of replacing, engineering or regenerating human or animal cells, tissues or organs to restore or establish normal function". This field holds the promise of engineering damaged tissues and organs by stimulating the body's own repair mechanisms to functionally heal previously irreparable tissues or organs.

Proposition 71 of 2004 is a law enacted by California voters to support stem cell research in the state. It was proposed by means of the initiative process and approved in the 2004 state elections on November 2. The Act amended both the Constitution of California and the Health and Safety Code.

Anthony Atala, M.D., is an American bioengineer, urologist, and pediatric surgeon. He is the W.H. Boyce professor of urology, the founding director of the Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine, and the chair of the Department of Urology at Wake Forest School of Medicine in North Carolina. His work focuses on the science of regenerative medicine: "a practice that aims to refurbish diseased or damaged tissue using the body's own healthy cells".
The Australian Regenerative Medicine Institute (ARMI) is an Australian medical research institute. Opened in April 2009, the institute is based at the Clayton campus of Monash University, in the Monash Science Technology Research and Innovation Precinct.
Sifap is a Pan-European study dedicated to investigating the correlation of juvenile stroke and a genetic disorder known as Fabry's disease. It was initiated by University of Rostock, Germany. In recruiting 5,000 patients aged 18 to 55 it will be the largest study on stroke in the young. Approximately 50 study centres from about 15 European countries are participating in the project. The study is divided into two parts: sifap1 and sifap2. Whereas sifap1 analyses the frequency of Fabry disease within the patient cohort, sifap2 controls and investigates the rehabilitation phase of diagnosed Fabry patients.

The Paracelsus Medical University is a private university located in Salzburg municipality, Austria and Nuremberg, Germany.

The International Clinical Research Centre at St. Anne’s University Hospital in Brno (FNUSA-ICRC) is a next-generation research and development center that focuses on finding new methods, technologies and medicines used to prevent, diagnose and treat cardiovascular and neurological diseases and disorders such as heart failure, coronary syndromes, hypertension, cardiac arrhythmia, sleep apnea, stroke, dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Such diseases are among the leading diseases and causes of death in modern society.
ReNeuron is a UK-based stem cell research company whose shares are listed on the Alternative Investment Market. Its focus is on the development of stem-cell therapies targeting areas of poorly-met medical need, including peripheral arterial disease, strokes, and retinal diseases.
MIRA is a multidisciplinary and complementary method for treating many chronic diseases. The MIRA Procedure is a result of combining efforts from different medical fields developed in the University of Chicago in 1992. It basically consists in medically grafting live rejuvenated tissue in the form of autologous adipose adult stem cells to a damaged organ in order to restore it and improve its function. This method is currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Neural Regeneration Research is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research on neuroregeneration and stem cells. Topics covered include neural stem cells, neural tissue engineering, gene therapy, and minimally-invasive treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. It was established in 2006 and the editors in chief are Kwok-Fai So and Xiao-Ming Xu. The journal publishes the following types of papers: research and reports, techniques and methods, investigation and analysis, meta-analyses and reviews, evidence-based case reports, and perspectives.
Adult mesenchymal stem cells are being used by researchers in the fields of regenerative medicine and tissue engineering to artificially reconstruct human tissue which has been previously damaged. Mesenchymal stem cells are able to differentiate, or mature from a less specialized cell to a more specialized cell type, to replace damaged tissues in various organs.

Jan A. Nolta is an American scientist and the director of the stem cell program at the UC Davis School of Medicine and Institute for Regenerative Cures. She is Scientific Director for the UC Davis Good Manufacturing Practice and editor of the journal Stem Cells. Nolta is known for her work with stem cell-related regenerative medicine. Nolta's current research focuses on treatment of Huntington's disease using mesenchymal stem cells. She was elected a AAAS Fellow in 2013.
The Max Delbrück Medal has been awarded annually from 1992 to 2013 by the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine. Named after the German biophysicist Max Delbrück, it is presented in Berlin to an outstanding scientist on the occasion of the annual "Berlin Lecture on Molecular Medicine", which the MDC organizes together with other Berlin research institutions and Bayer HealthCare. The award recipient usually delivers a lecture after the award.
Stephen H. Tsang is an American ophthalmologist and geneticist. He is currently a Professor of Ophthalmology, and Pathology and Cell Biology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center in New York.
Kameshwar Prasad is an Indian neurologist, medical researcher, academic and the head of the department of Neurology at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Delhi (AIIMS), known as a proponent of Evidence-based medicine (EBM) and Evidence-based Healthcare (EBHC). The Government of India awarded him the fourth highest civilian honour of the Padma Shri in 1991.
Jeffrey D. Macklis is an American neuroscientist. He is the Max and Anne Wien Professor of Life Sciences in the Department of Stem Cell and Regenerative Biology and Center for Brain Science at Harvard University, Professor of Neurology and of Neurosurgery at Harvard Medical School, and Principal Faculty of the Neuroscience / Nervous System Diseases Program at the Harvard Stem Cell Institute.
James Affram Adjaye is a Ghanaian British Stem cell scientist. He is the Director of the Institute for Stem Cell Research and Regenerative Medicine at the Heinrich Heine University's faculty of medicine. He also led the Molecular Embryology and Aging Group of the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics situated in Berlin, Germany.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Albrecht-Kossel-Insitut für Neuroregeneration". University of Rostock. 2011. Archived from the original on 2011-04-20. Retrieved 13 August 2011.
- ↑ "Universitätsklinikum Rostock". University of Rostock. 2011. Archived from the original on 2011-07-24. Retrieved 13 August 2011.
- ↑ "Stroke In Young Fabry Patients". University of Rostock. 2011. Archived from the original on 19 July 2011. Retrieved 13 August 2011.
- ↑ "5th International Stem Cell School in Regenerative Medicine in Berlin and Rostock". Eurostemcell.org. 2011. Archived from the original on 5 October 2011. Retrieved 13 August 2011.