
A circular saw is a power-saw using a toothed or abrasive disc or blade to cut different materials using a rotary motion spinning around an arbor. A hole saw and ring saw also use a rotary motion but are different from a circular saw. Circular saws may also be loosely used for the blade itself. Circular saws were invented in the late 18th century and were in common use in sawmills in the United States by the middle of the 19th century.

Continuous track is a system of vehicle propulsion used in tracked vehicles, running on a continuous band of treads or track plates driven by two or more wheels. The large surface area of the tracks distributes the weight of the vehicle better than steel or rubber tyres on an equivalent vehicle, enabling continuous tracked vehicles to traverse soft ground with less likelihood of becoming stuck due to sinking.
Portable sawmills are sawmills small enough to be moved easily and set up in the field. They have existed for over 100 years but grew in popularity in the United States starting in the 1970s, when the 1973 oil crisis and the back-to-the-land movement had led to renewed interest in small woodlots and in self-sufficiency. Their popularity has grown exponentially since 1982, when the portable bandsaw mill was first commercialized.

A sawmill or lumber mill is a facility where logs are cut into lumber. Modern sawmills use a motorized saw to cut logs lengthwise to make long pieces, and crosswise to length depending on standard or custom sizes. The "portable" sawmill is simple to operate. The log lies flat on a steel bed, and the motorized saw cuts the log horizontally along the length of the bed, by the operator manually pushing the saw. The most basic kind of sawmill consists of a chainsaw and a customized jig, with similar horizontal operation.

A half-track is a civilian or military vehicle with regular wheels at the front for steering and continuous tracks at the back to propel the vehicle and carry most of the load. The purpose of this combination is to produce a vehicle with the cross-country capabilities of a tank and the handling of a wheeled vehicle.

A bandsaw is a power saw with a long, sharp blade consisting of a continuous band of toothed metal stretched between two or more wheels to cut material. They are used principally in woodworking, metalworking, and lumbering, but may cut a variety of materials. Advantages include uniform cutting action as a result of an evenly distributed tooth load, and the ability to cut irregular or curved shapes like a jigsaw. The minimum radius of a curve is determined by the width of the band and its kerf. Most bandsaws have two wheels rotating in the same plane, one of which is powered, although some may have three or four to distribute the load. The blade itself can come in a variety of sizes and tooth pitches, which enables the machine to be highly versatile and able to cut a wide variety of materials including wood, metal and plastic.

A skidder is any type of heavy vehicle used in a logging operation for pulling cut trees out of a forest in a process called "skidding", in which the logs are transported from the cutting site to a landing. There they are loaded onto trucks, and sent to the mill. One exception is that in the early days of logging, when distances from the timberline to the mill were shorter, the landing stage was omitted altogether, and the "skidder" would have been used as the main road vehicle, in place of the trucks, railroad, or flume. Modern forms of skidders can pull trees with a cable and winch, just like the old steam donkeys, or with a hydraulic grapple either on boom or on the back of the frame (clambunk skidder).

Benjamin Leroy Holt was an American businessman and inventor who patented and manufactured the first practical crawler-type tread tractor. The continuous-type track is used for heavy agricultural and engineering vehicles to spread the weight over a large area to prevent the vehicle from sinking into soft ground. He founded with his brothers the Holt Manufacturing Company.

The Sandy River and Rangeley Lakes Railroad (SR&RL) was a 2 ft narrow gauge common carrier railroad that operated approximately 112 miles (180 km) of track in Franklin County, Maine. The former equipment from the SR&RL continues to operate in the present day on a revived, short segment of the railway in Phillips, Maine.
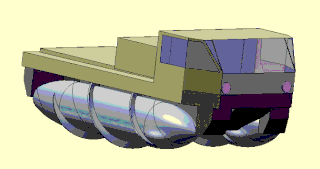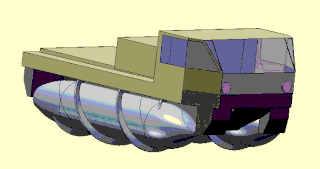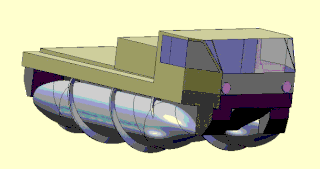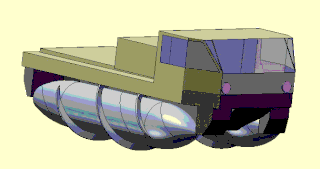
A screw-propelled vehicle is a land or amphibious vehicle designed to cope with difficult terrain, such as snow, ice, mud, and swamp. Such vehicles are distinguished by being moved by the rotation of one or more auger-like cylinders fitted with a helical flange that engages with the medium through or over which the vehicle is moving. They have been called Archimedes screw vehicles by the US military, where they are classified as a type of marginal terrain vehicle (MTV). Modern vehicles called Amphirols and other similar vehicles have specialised uses.

The Linn tractor is a heavy duty civilian half-track or crawler tractor invented by Holman Harry Linn. Approximately 2500 units were built in Morris, New York, USA from 1916 to 1952.

A saw pit or sawpit is a pit over which timber is positioned to be sawed with a long two-handled saw, usually a whipsaw, by two people, one standing above the timber and the other below. It was used for producing sawn planks from tree trunks, which could then be cut down into boards, pales, posts, etc. Many towns, villages and country estates had their own saw pits. The greatest user of sawn timber in past centuries was the shipbuilding industry. After falling, without bark, in smaller and more standardized sizes, and not intended as primary members in shipbuilding, the term 'timber' is often replaced by the term 'lumber'.

The Holt Manufacturing Company began with the 1883 founding of Stockton Wheel Service in Stockton, California, United States. Benjamin Holt, later credited with patenting the first workable crawler ("caterpillar") tractor design, incorporated the Holt Manufacturing Company in 1892. Holt Manufacturing Company was the first company to successfully manufacture a continuous track tractor By the early 20th century, Holt Manufacturing Company was the leading manufacturer of combine harvesters in the US, and the leading California-based manufacturer of steam traction engines.

The Lombard Steam Log Hauler, patented 21 May 1901, was the first successful commercial application of a continuous track for vehicle propulsion. The concept was later used for military tanks during World War I and for agricultural tractors and construction equipment following the war.
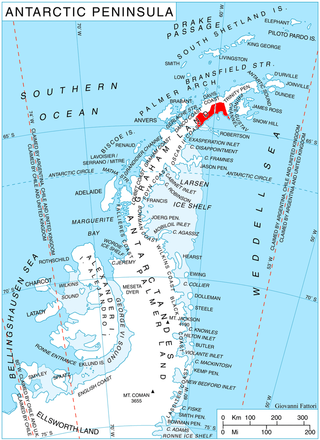
Mount Lombard is the highest peak dominating the mountain mass whose southern extremity is Cape Sobral, Graham Land, Antarctica, and surmounting Mundraga Bay to the west. It was mapped from surveys by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (1960–61), and was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for American engineer Alvin O. Lombard of the Lombard Steam Log Hauler Company, Waterville, Maine, who designed some of the earliest successful over-snow tractors, the first application of knowledge of snow mechanics to trafficability, 1901–13.
The Maine Forest and Logging Museum is a non-profit historical museum located in Bradley, Maine. It was founded in 1960 to preserve the history of forestry and logging in the state. Leonard's Mills is the centerpiece of the 1790s living history site which is home to the only operational water wheel powered, up-and-down sawmill in Maine. The museum also has a period blacksmith's shop, stone dam, saw pit, settler's cottage, smokehouse, trapper's hut, log cabin, batteau, hovel, rotary saw mill, shingle machine, clapboard mill, covered bridge, and gift shop. The museum is open daily for self-guided tours, during organized weekend events it is staffed by volunteers dressing in period clothes. It is adjacent to a forest and the Blackman Stream. The museum recently completed restoring a circa 1910 Lombard Steam Log Hauler. This 20 ton steam traction engine runs several times a year at museum events.
The Seboomook Lake and Saint John Railroad was a forest railway built to transfer pulpwood between drainage basins in the Maine North Woods. The railroad was built slowly in preparation for anticipated pulpwood harvesting, but onset of the Great Depression caused the railroad to be dismantled when harvesting plans were delayed.

The Phoenix Manufacturing Company, later the Phoenix Steel Company, was one of Eau Claire, Wisconsin's oldest manufacturing firms. It manufactured equipment predominantly for the sawmill and logging equipment industries, which were vital to the establishment and growth of Eau Claire.

The Alvin O. Lombard House is a historic house at 65 Elm Street in Waterville, Maine. Built in 1908, it is a distinctive local example of late Shingle style architecture. It is further notable as the home of inventor Alvin O. Lombard, who developed the Lombard Steam Log Hauler, an early commercial use of track-propelled vehicles. The house was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1982.
















