Related Research Articles
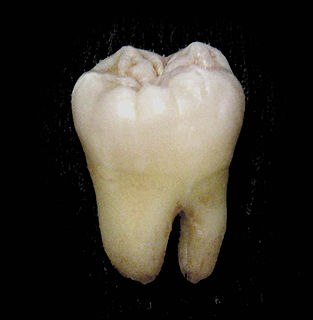
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name molar derives from Latin, molaris dens, meaning "millstone tooth", from mola, millstone and dens, tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across mammal groups.

Chiniquodon is an extinct genus of carnivorous cynodonts, which lived during the Late Triassic (Carnian) in South America and Africa. Chiniquodon is closely related to a contemporary genus, Probelesodon, and close to the ancestry of mammals.
The Middle Jurassic is the second epoch of the Jurassic Period. It lasted from about 174.1 to 163.5 million years ago. Fossils of land-dwelling animals, such as dinosaurs, from the Middle Jurassic are relatively rare, but geological formations containing land animal fossils include the Forest Marble Formation in England, the Kilmaluag Formation in Scotland, the Daohugou Beds in China, the Itat Formation in Russia, and the Isalo III Formation of western Madagascar.

Peltephilus, the horned armadillo, is an extinct genus of dog-sized, armadillo xenarthran mammals which first inhabited Argentina during the Oligocene epoch, and became extinct in the Miocene epoch. Notably, the scutes on its head were so developed that they formed horns. Aside from the horned gophers of North America, it is the only known fossorial horned mammal.
The fossil Tinguiririca fauna, entombed in volcanic mudflows and ash layers at the onset of the Oligocene, about 33-31.5 million years ago, represents a unique snapshot of the history of South America's endemic fauna, which was extinguished when the former island continent was joined to North America by the rising Isthmus of Panama. The fossil-bearing sedimentary layers of the Abanico Formation were first discovered in the valley of the Tinguiririca River, high in the Andes of central Chile. The faunal assemblage lends its name to the Tinguirirican stage in the South American land mammal age (SALMA) classification.

The Isalo III Formation is a geological formation in Madagascar, off the eastern coast of Africa. It dates back to the Middle Jurassic. The use of the term "Isalo III" is somewhat controversial as the two prior units Isalo I and II are Triassic cross-bedded sandstone units that form a continuous depositional sequence, while the "Isalo III" sandstones are not part of the same depositional sequence, and were deposited considerably later. and are perhaps better treated as part of several separate formations. It is traditionally divided into two subunits the lower, Bajocian aged Isalo IIIa unit also known as the Beronono Formation and the upper, Bathonian aged Isalo IIIb unit also known as the Sakaraha Formation. The Sakaraha Formation consists of sandstones, marls and carbonates and represents a coastal plain environment, and is laterally equivalent to the predomiantly carbonate Bemaraha Formation, which represents a coastal barrier lagoon complex. The formation is found in the northwest and in the southeast of the country and has provided a variety of fossils.
The Casamayoran age is a period of geologic time within the Early Eocene epoch of the Paleogene, used more specifically within the South American land mammal age (SALMA) classification. It follows the Riochican and precedes the Mustersan age.
The Mustersan age is a period of geologic time within the Eocene epoch of the Paleogene, used more specifically within the South American land mammal age (SALMA) classification. It follows the Casamayoran and precedes the Divisaderan age.
The Divisaderan age is a South American land mammal age, covering a period of geologic time within the Late Eocene epoch of the Paleogene. It follows the Mustersan age and is followed by the Tinguirirican age.
The Tinguirirican age is a period of geologic time within the Late Eocene and Early Oligocene epochs of the Paleogene, used more specifically within the SALMA classification in South America. It follows the Divisaderan and precedes the Deseadan age.
The Deseadan age is a period of geologic time within the Oligocene epoch of the Paleogene to the Early Miocene epoch of the Neogene, used more specifically within the SALMA classification of South America. It follows the Tinguirirican and precedes the Colhuehuapian age.
The Colhuehuapian age is a period of geologic time within the Early Miocene epoch of the Neogene, used more specifically within the SALMA classification in South America. It follows the Deseadan and precedes the Santacrucian age.

Ambondro mahabo is a mammal from the Middle Jurassic (Bathonian) Isalo III Formation of Madagascar. The only described species of the genus Ambondro, it is known from a fragmentary lower jaw with three teeth, interpreted as the last premolar and the first two molars. The premolar consists of a central cusp with one or two smaller cusps and a cingulum (shelf) on the inner, or lingual, side of the tooth. The molars also have such a lingual cingulum. They consist of two groups of cusps: a trigonid of three cusps at the front and a talonid with a main cusp, a smaller cusp, and a crest at the back. Features of the talonid suggest that Ambondro had tribosphenic molars, the basic arrangement of molar features also present in marsupial and placental mammals. It is the oldest known mammal with putatively tribosphenic teeth; at the time of its discovery it antedated the second oldest example by about 25 million years.

Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 2010.

Dadadon is an extinct genus of traversodontid cynodonts which existed in Madagascar during the late Middle Triassic. The only species in the genus is Dadadon isaloi.
Several mammals are known from the Mesozoic of Madagascar. The Bathonian Ambondro, known from a piece of jaw with three teeth, is the earliest known mammal with molars showing the modern, tribosphenic pattern that is characteristic of marsupial and placental mammals. Interpretations of its affinities have differed; one proposal places it in a group known as Australosphenida with other Mesozoic tribosphenic mammals from the southern continents (Gondwana) as well as the monotremes, while others favor closer affinities with northern (Laurasian) tribosphenic mammals or specifically with placentals. At least five species are known from the Maastrichtian, including a yet undescribed species known from a nearly complete skeleton that may represent a completely new group of mammals. The gondwanathere Lavanify, known from two teeth, is most closely related to other gondwanatheres found in India and Argentina. Two other teeth may represent another gondwanathere or a different kind of mammal. One molar fragment is one of the few known remains of a multituberculate mammal from Gondwana and another has been interpreted as either a marsupial or a placental.

Gomphodontosuchinae is a subfamily of Triassic traversodontid cynodonts. It includes the genera Gomphodontosuchus, Exaeretodon, Menadon, Protuberum, Ruberodon and Scalenodontoides.

The geology of Madagascar comprises a variety of rocks of Precambrian age which make up the larger part of the east and centre of the island. They are intruded by basalts and rhyolites of Mesozoic to Cenozoic age. In contrast, the western part of the island is formed from sedimentary rocks of Carboniferous to Quaternary age. Archean rocks occur from the northeast portion of the island down to the south in the Ranotsara shear zone. Rocks in the northern portion of Madagascar are greenstone belts, from the Archean or Paleoproterozoic age.

Abanico Formation is a 3 kilometres (9,800 ft) thick sedimentary formation exposed in the Andes of Central Chile. The formation has been deposited in a timespan from the Eocene to the Miocene. Abanico Formation's contact with the overlying Miocene Farellones Formation has been the subject of differing interpretations since the 1960s. A small part of the formation crops out in the Mendoza Province of western Argentina.

Cura-Mallín Group is a heterogeneous group of volcano-sedimentary formations of Oligocene-Miocene age, Colhuehuapian to Laventan in the SALMA classification, in south-central Chile and nearby parts of Argentina. The sediments belonging to the group were deposited in a lacustrine environment and alongside rivers in an intra-arc basin. Southeast of Laguna del Laja Cura-Mallín Group has a thickness of more than 1,800 metres (5,900 ft). The sediments making up the group deposited in an interval between 22 and 8 million years ago.
References
- 1 2 Flynn, John J.; Parrish, J. Michael; Rakotosamimanana, Berthe; Simpson, William F.; Wyss, André R. (September 1999). "A Middle Jurassic mammal from Madagascar". Nature. 401 (6748): 57–60. doi:10.1038/43420.
- ↑ Flynn, John J.; Wyss, André R. (February 2002). "Madagascar's Mesozoic secrets". Scientific American. 286 (2): 62.
| This Madagascar location article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |