
A tokamak is a device which uses a powerful magnetic field generated by external magnets to confine plasma in the shape of an axially symmetrical torus. The tokamak is one of several types of magnetic confinement devices being developed to produce controlled thermonuclear fusion power. The tokamak concept is currently one of the leading candidates for a practical fusion reactor.

Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) is a United States Department of Energy national laboratory for plasma physics and nuclear fusion science. Its primary mission is research into and development of fusion as an energy source. It is known for the development of the stellarator and tokamak designs, along with numerous fundamental advances in plasma physics and the exploration of many other plasma confinement concepts.

Fusion power is a proposed form of power generation that would generate electricity by using heat from nuclear fusion reactions. In a fusion process, two lighter atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, while releasing energy. Devices designed to harness this energy are known as fusion reactors. Research into fusion reactors began in the 1940s, but as of 2024, no device has reached net power, although net positive reactions have been achieved.
This timeline of nuclear fusion is an incomplete chronological summary of significant events in the study and use of nuclear fusion.

The Joint European Torus (JET) was a magnetically confined plasma physics experiment, located at Culham Centre for Fusion Energy in Oxfordshire, UK. Based on a tokamak design, the fusion research facility was a joint European project with the main purpose of opening the way to future nuclear fusion grid energy. At the time of its design JET was larger than any comparable machine.
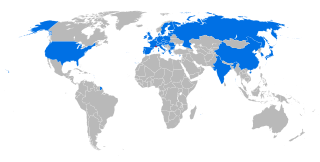
ITER is an international nuclear fusion research and engineering megaproject aimed at creating energy through a fusion process similar to that of the Sun. It is being built next to the Cadarache facility in southern France. Upon completion of construction of the main reactor and first plasma, planned for 2033–2034, ITER will be the largest of more than 100 fusion reactors built since the 1950s, with six times the plasma volume of JT-60SA in Japan, the largest tokamak operating today.

Magnetic confinement fusion (MCF) is an approach to generate thermonuclear fusion power that uses magnetic fields to confine fusion fuel in the form of a plasma. Magnetic confinement is one of two major branches of controlled fusion research, along with inertial confinement fusion.

DEMO, or a demonstration power plant, refers to a proposed class of nuclear fusion experimental reactors that are intended to demonstrate the net production of electric power from nuclear fusion. Most of the ITER partners have plans for their own DEMO-class reactors. With the possible exception of the EU and Japan, there are no plans for international collaboration as there was with ITER.

The Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST), internal designation HT-7U, is an experimental superconducting tokamak magnetic fusion energy reactor in Hefei, China. The Hefei Institutes of Physical Science is conducting the experiment for the Chinese Academy of Sciences. It has operated since 2006.

Minh-Quảng Trần is a professor at the EPFL.
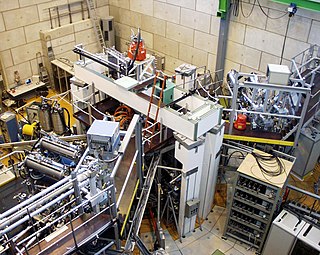
The tokamak à configuration variable is an experimental tokamak located at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) Swiss Plasma Center (SPC) in Lausanne, Switzerland. As the largest experimental facility of the Swiss Plasma Center, the TCV tokamak explores the physics of magnetic confinement fusion. It distinguishes itself from other tokamaks with its specialized plasma shaping capability, which can produce diverse plasma shapes without requiring hardware modifications.
Ignitor is the Italian name for a proposed tokamak device, developed by ENEA. The project was abandoned in 2022.

The Culham Centre for Fusion Energy (CCFE) is the UK's national laboratory for fusion research. It is located at the Culham Science Centre, near Culham, Oxfordshire, and is the site of the Joint European Torus (JET), Mega Ampere Spherical Tokamak (MAST) and the now closed Small Tight Aspect Ratio Tokamak (START).

In nuclear fusion power research, the plasma-facing material (PFM) is any material used to construct the plasma-facing components (PFC), those components exposed to the plasma within which nuclear fusion occurs, and particularly the material used for the lining the first wall or divertor region of the reactor vessel.

In magnetic confinement fusion, a divertor or diverted configuration is a magnetic field configuration of a tokamak or a stellarator which separates the confined plasma from the material surface of the device. The plasma particles which diffuse across the boundary of the confined region are diverted by the open, wall-intersecting magnetic field lines to wall structures which are called the divertor targets, usually remote from the confined plasma. The magnetic divertor extracts heat and ash produced by the fusion reaction, minimizes plasma contamination, and protects the surrounding walls from thermal and neutronic loads.

Sir Steven Charles Cowley is a British theoretical physicist and international authority on nuclear fusion and astrophysical plasmas. He has served as director of the United States Department of Energy (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) since 1 July 2018. Previously he served as president of Corpus Christi College, Oxford, since October 2016. and head of the EURATOM / CCFE Fusion Association and chief executive officer of the United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority (UKAEA).
Hartmut Zohm is a German plasma physicist who is known for his work on the ASDEX Upgrade machine. He received the 2014 John Dawson Award and the 2016 Hannes Alfvén Prize for successfully demonstrating that neoclassical tearing modes in tokamaks can be stabilized by electron cyclotron resonance heating, which is an important design consideration for pushing the performance limit of the ITER.
Donato Palumbo was an Italian physicist best known as the leader of the European Atomic Energy Community (Euratom) fusion research program from its formation in 1958 to his retirement in 1986. He was a key force in the development of the tokamak during the 1970s and 80s, contributing several papers on plasma confinement in these devices and leading the JET fusion reactor program, which as of 2021, retains the record for the closest approach to breakeven, the ratio between the produced fusion power and the power used to heat it. He is referred to as the founding father of the European fusion program.
The history of nuclear fusion began early in the 20th century as an inquiry into how stars powered themselves and expanded to incorporate a broad inquiry into the nature of matter and energy, as potential applications expanded to include warfare, energy production and rocket propulsion.













