
The Rheingold ('Rhinegold') was a named train that operated between Hook of Holland, near Rotterdam, and Geneva, Switzerland, a distance of 1,067 kilometres (663 mi), until 1987. Another section of the train started in Amsterdam and was coupled to the Hoek cars in Utrecht. The Rheingold ran along the Rhine River via Arnhem, Netherlands, and Cologne, Germany, using special luxury coaches. It was named after Richard Wagner's Das Rheingold opera, which romanticized the Rhine. From 1965 until the train's discontinuation in 1987, the Rheingold was a first-class-only Trans Europ Express (TEE) train.

The ETR 300, also known as "Settebello-type" for its use on the former Settebello train service, is a type of Italian fast electric multiple unit (EMU) trainset formerly operated by Ferrovie dello Stato. The letters ETR stood for elettrotreno rapido. Thanks to its aerodynamically low-drag profile, it boasted a maximum speed of 200 km/h (124 mph), with a power output of 2600 kW. Manufactured for FS by Breda, a total of only three trainsets were built, numbered ETR 301–303.

The Bavaria was an express train that linked München Hbf in Munich, Germany, with Zürich HB in Zurich, Switzerland. Introduced in the 1950s, it ran through to Geneva until 1969, when it was cut back to Zurich. The train was named on the basis that Bavaria is the Latin equivalent to the German word Bayern, the official name of the federal state of Bavaria, of which Munich is the capital. It was operated by the Deutsche Bundesbahn / Deutsche Bahn (DB) and the Swiss Federal Railways (SBB-CFF-FFS). The route also included a single stop in Austria, at Bregenz. The 24 km (15 mi) section between Lindau, Germany, and St. Margrethen, Switzerland, is located mostly in Austria, but Swiss locomotives hauled the train over this section, most of which is part of the Vorarlberg line of Austrian Federal Railways.

The Arbalète was an express train that linked Paris-Est in Paris, France, with Zürich HB in Zurich, Switzerland. Introduced in 1957, it was operated by the SNCF and the Swiss Federal Railways (SBB-CFF-FFS).

The Cisalpin was an express train that linked Paris-Gare de Lyon in Paris, France, with Milano Centrale in Milan, Italy. Introduced in 1961, it was operated by the SNCF, the Swiss Federal Railways (SBB-CFF-FFS) and the Italian State Railways (FS).

The Iris was an express train that linked Brussels Midi/Zuid in Brussels, Belgium, with Chur station in Chur, Switzerland.

The Helvetia was an express train that, for most of its existence, linked Hamburg-Altona station in Hamburg, Germany, with Zürich HB in Zurich, Switzerland. Introduced in 1952, it was operated by the Deutsche Bundesbahn / Deutsche Bahn (DB) and the Swiss Federal Railways (SBB-CFF-FFS). The train's name, Helvetia, is the Latin word for "Switzerland".

The Goethe was an express train that, for most of its existence, linked Paris-Est in Paris, France, with Frankfurt Hbf in Frankfurt, Germany. Introduced in 1970, it was operated by the SNCF and the Deutsche Bundesbahn / Deutsche Bahn (DB).

The Edelweiss was an international express train. For most of its existence, it linked the Netherlands with Switzerland, via Belgium, Luxembourg and France. Introduced in 1928, it was named after a mountain flower, the Edelweiss, which is associated with alpinism and the Alps, and regarded as a symbol of Switzerland.

The Settebello was a famous Italian high-speed express train that linked Milano Centrale in Milan with Roma Termini station in Rome, via Bologna and Florence. Introduced in 1953, it was operated by the Italian State Railways (FS) and used the distinctive ETR 300-type electric multiple unit trainsets, featuring observation lounges at the front and rear of the train. When introduced, it "set a standard of speed and luxurious travelling accommodation previously unknown in Italy [and] rivalling anything else on European rails." It was a Trans Europ Express (TEE) from 1974 until its withdrawal, in 1984.
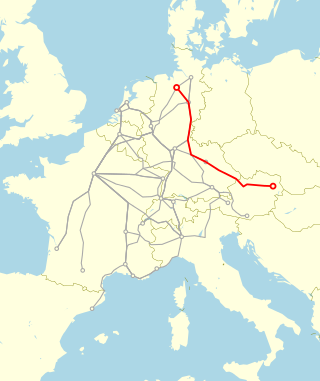
The Prinz Eugen was an express train that linked northern Germany with Wien Westbf in Vienna, Austria. Introduced in 1971, it was operated by the Deutsche Bundesbahn / Deutsche Bahn (DB) and the Austrian Federal Railways (ÖBB).

The Roland was an express train that ran in Germany. For part of its existence, it was also an international train. Introduced in 1939, suspended during World War II, and reintroduced in 1952, it was operated in Germany by the Deutsche Reichsbahn Gesellschaft (DRG), the Deutsche Bundesbahn (DB) and the Deutsche Bahn (DB), respectively.

Le Capitole was an express train between Paris and Toulouse in France. Introduced in 1960, it was operated by the Société Nationale des Chemins de fer français (SNCF). It was also the SNCF's first foray into high-speed commercial service above 160 km/h (99 mph).

The Étoile du Nord was an international express train. It linked Paris Nord in Paris, France, with Brussels, Belgium, and, for most of its existence, also with Amsterdam CS in Amsterdam, the Netherlands. Its name meant literally "Star of the North", and alluded not only to its route heading north from Paris, but also to one of its original operators, the Chemin de Fer du Nord.

The Gottardo was an express train that, for most of its existence, linked Zurich, Switzerland, with Milan, Italy. Introduced in 1961, it was a first-class-only Trans Europ Express (TEE) until 1988, then becoming a EuroCity service and finally a EuroNight service – on a longer route, to Rome – before being discontinued in 2002. The train followed the Gotthard railway and was named for the line, using the Italian spelling for it, Ferrovia del Gottardo.

The word Mediolanum has been used to name three distinct international express trains that have run to and from Milano Centrale in Milan, Italy since 1957. The focus of these trains on the city now known as Milan reflects the fact that Mediolanum is the Latin word for ancient Milan.

Stanislas was an express train that linked Paris and Strasbourg in France. Introduced in 1971, it was operated by the Société Nationale des Chemins de fer français (SNCF).

The Saphir was an express train operated by the Deutsche Bundesbahn linking the port of Ostend with Dortmund as part of a link between London and the Ruhr. The name Saphir, German for sapphire, refers to the Belgian gemstone industry.

The Ticino was an express train that linked Milan in Italy, with Zürich, Switzerland and for some years even to Munich, Germany. The train was named after the Canton of Ticino in the south of Switzerland. Introduced in 1961, it was a first-class-only Trans Europ Express (TEE) service until 1974. Later, it was a EuroCity service.

The Rembrandt was an express train that linked Amsterdam in the Netherlands, with Munich in Germany and later Chur in Switzerland. The train was named after the renowned Dutch painter Rembrandt. For its first 16 years it was a first-class-only Trans Europ Express, becoming a two-class InterCity in 1983 and finally a EuroCity in 1987.





















