
The American Expeditionary Forces (AEF) was a formation of the United States Armed Forces on the Western Front during World War I, comprised mostly of units from the U.S. Army. The AEF was established on July 5, 1917, in France under the command of then-Major General John J. Pershing. It fought alongside French Army, British Army, Canadian Army, British Indian Army, New Zealand Army and Australian Army units against the Imperial German Army. A small number of AEF troops also fought alongside Italian Army units in 1918 against the Austro-Hungarian Army. The AEF helped the French Army on the Western Front during the Aisne Offensive in the summer of 1918, and fought its major actions in the Battle of Saint-Mihiel and the Meuse-Argonne Offensive in the latter part of 1918.

Mobile Army Surgical Hospitals (MASH) were U.S. Army field hospital units conceptualized in 1946 as replacements for the obsolete World War II-era Auxiliary Surgical Group hospital units. MASH units were in operation from the Korean War to the Gulf War before being phased out in the early 2000s. Each MASH unit had 60 beds, as well as surgical, nursing, and other enlisted and officer staff available at all times. MASH units filled a vital role in military medicine by providing support to army units upwards of 10,000 to 20,000 soldiers. These units had a low mortality rate compared to others, as the transportation time to hospitals was shorter, resulting in fewer patients dying within the "Golden Hour", the first hour after an injury is first sustained, which is referred to in trauma as the "most important hour". The U.S. Army deactivated the last MASH unit on February 16, 2006, and the successors to Mobile Army Surgical Hospitals are combat support hospitals.

The 86th Infantry Division, also known as the Blackhawk Division, was a unit of the United States Army in World War I and World War II. Currently called the 86th Training Division, based at Fort McCoy, Wisconsin, members of the division now work with Active Army, Reserve, and National Guard units to provide them with a Decisive Action Training Environment on a yearly basis.

The 92nd Infantry Division was an African-American, later mixed, infantry division of the United States Army that served in World War I, World War II, and the Korean War. The military was racially segregated during the World Wars. The division was organized in October 1917, after the U.S. entry into World War I, at Camp Funston, Kansas, with African-American soldiers from all states. In 1918, before leaving for France, the American buffalo was selected as the divisional insignia due to the "Buffalo Soldiers" nickname, given to African-American cavalrymen in the 19th century. The divisional nickname, "Buffalo Soldiers Division", was inherited from the 366th Infantry, one of the first units organized in the division.
Bellevue Hospital is a hospital in New York City and the oldest public hospital in the United States. One of the largest hospitals in the United States by number of beds, it is located at 462 First Avenue in the Kips Bay neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City. Bellevue is also home to FDNY EMS Station 08, formerly NYC EMS Station 13.

The 39th Infantry Division was an infantry formation of the Army National Guard, originally formed as the 18th Division in 1917. The division consisted of troops from Arkansas, Louisiana, and Mississippi. After training at Camp Beauregard, Louisiana, the division was deployed to France but did not see combat before the end of World War I. In July 1923 the division was re-designated as the 31st Infantry Division. The 39th Infantry Division was reactivated after World War II with troops from Louisiana and Arkansas and its headquarters in Louisiana. In 1967, the 39th Infantry Division was reorganized to become the 39th Infantry Brigade (Separate). Its headquarters was in Little Rock and the unit consisted entirely of troops from Arkansas.

Harper University Hospital is one of eight hospitals and institutes that compose the Detroit Medical Center. Harper offers services in a broad range of clinical areas, including cardiology, neurology, neurosurgery, organ transplant, plastic surgery, general surgery, bariatric endocrinology and sleep disorders.

The 49th Aero Squadron was a United States Army Air Service unit that fought on the Western Front during World War I.

The 103rd Aero Squadron was an aviation pursuit squadron of the U.S. Air Service that served in combat in France during World War I. Its original complement included pilots from the disbanded Lafayette Escadrille and Lafayette Flying Corps. One of those pilots, Paul F. Baer, became the first ace of an American unit in World War I.

The 139th Aero Squadron was a United States Army Air Service unit that fought on the Western Front during World War I.

The 22nd Aero Squadron was a United States Army Air Service unit that fought on the Western Front during World War I.

The 339th Infantry Regiment is an infantry regiment of the United States Army, raised for service in World War I, that served in the North Russia Intervention and World War II.

The 186th Aero Squadron was a United States Army Air Service unit that fought on the Western Front during World War I.

Base Hospital No. 20, located in Châtel-Guyon, France, was one of the hundreds of Base Hospitals created to treat soldiers wounded during the First World War. It was created in 1916 by the University of Pennsylvania and served the American Expeditionary Forces (A.E.F.) until 1919.

Base Hospital No. 5 was organized by Harvard University and was one of six American Expeditionary Forces (AEF) Base Hospitals loaned to the British Expeditionary Forces (BEF) during the First World War. The personnel started in Camiers at General Hospital No. 11 in June 1917 and then moved to General Hospital No. 13, at Boulogne-sur-Mer to finish out the war.

American Base Hospital No. 57 was an American military hospital formed in Georgia, United States. During the First World War the hospital moved to Paris, where a 1,800-bed hospital was set up to deal with war casualties.
American Base Hospital No. 238 was an American military hospital formed in Rimaucourt, Department Haute Marne, France. This was the last hospital to be created during the First World War.
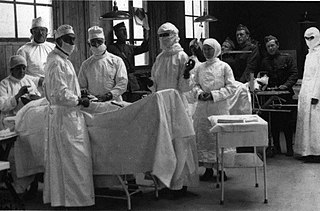
American Base Hospital No. 116 was an American military hospital formed in New York City, United States. During the First World War the hospital moved to Bazoilles-sur-Meuse, Department Vosges, in the advance section, France where it was set up to deal with war casualties.

American Base Hospital No. 36 was an American military hospital formed in Detroit, Michigan. During the First World War, the hospital moved to Vittel in northeastern France where it was set up to deal with war casualties.


















