
Harvey Williams Cushing was an American neurosurgeon, pathologist, writer, and draftsman. A pioneer of brain surgery, he was the first exclusive neurosurgeon and the first person to describe Cushing's disease. He wrote a biography of physician William Osler in three volumes.

The 39th Infantry Division was an infantry formation of the Army National Guard, originally formed as the 18th Division in 1917. The division consisted of troops from Arkansas, Louisiana, and Mississippi. After training at Camp Beauregard, Louisiana, the division was deployed to France but did not see combat before the end of World War I. In July 1923 the division was re-designated as the 31st Infantry Division. The 39th Infantry Division was reactivated after World War II with troops from Louisiana and Arkansas and its headquarters in Louisiana. In 1967, the 39th Infantry Division was reorganized to become the 39th Infantry Brigade (Separate). Its headquarters was in Little Rock and the unit consisted entirely of troops from Arkansas.

The 109th Airlift Squadron is a unit of the Minnesota Air National Guard 133d Airlift Wing located at Minneapolis–Saint Paul Joint Air Reserve Station, Minnesota. The squadron is equipped with the C-130H Hercules.

Elliot Carr Cutler was an American surgeon, military physician, and medical educator. He was Moseley Professor of Surgery at Harvard Medical School, surgeon-in-chief at Peter Bent Brigham Hospital from 1932 to 1947, and a brigadier general in the U.S. Army Medical Corps.

Harper University Hospital is one of eight hospitals and institutes that compose the Detroit Medical Center. Harper offers services in a broad range of clinical areas, including cardiology, neurology, neurosurgery, organ transplant, plastic surgery, general surgery, bariatric endocrinology and sleep disorders.

The United States Army Ambulance Service (USAAS) was a unit of the United States Army established by the United States Department of War during World War I. It was established by General Order No. 75 of the War Department in May 1917 and was headquartered in Allentown, Pennsylvania.
Camp Fremont was a World War I-era military base located near Palo Alto, California. Construction started in July 1917 and the post closed in September, 1919. The post was named for John C. Frémont, a US Army officer and government official who was prominent in California during the 1850s.

Sir Cuthbert Sidney Wallace, 1st Baronet was a British surgeon.

Camp Crane was a World War I United States Army Ambulance Service (USAAS) training camp, located in Allentown, Pennsylvania. Its mission was to train ambulance drivers to evacuate casualties on the Western Front in France. It was named for Brigadier General Charles Henry Crane, surgeon general of the Army in 1882-83.

Sir James Berry FRCS FSA was a Canadian-born British surgeon.

The Siamese Expeditionary Forces consisted of the Royal Siamese Army sent to Europe under the command of Major General Phraya Pichai Charnyarit in 1917 to help the Triple Entente fight in World War I.

Base Hospital No. 20, located in Châtel-Guyon, France, was one of the hundreds of Base Hospitals created to treat soldiers wounded during the First World War. It was created in 1916 by the University of Pennsylvania and served the American Expeditionary Forces (A.E.F.) until 1919.

Base Hospital No. 5 was organized by Harvard University and was one of six American Expeditionary Forces (AEF) Base Hospitals loaned to the British Expeditionary Forces (BEF) during the First World War. The personnel started in Camiers at General Hospital No. 11 in June 1917 and then moved to General Hospital No. 13, at Boulogne-sur-Mer to finish out the war.

Mary Hannah Frances Ivens CBE FRCOG was an obstetrician and gynaecologist who was the first woman appointed to a hospital consultant post in Liverpool. During the First World War she was chief medical officer at the Scottish Women's Hospital at Royaumont, northeast of Paris. For her services to the French forces she was awarded a knighthood in France's Legion of Honour and the Croix de Guerre.

American Base Hospital No. 1 was an American military hospital formed in Bellevue Hospital, New York City, United States. During the First World War the hospital moved to Vichy, France where it was set up to deal with war casualties.
American Base Hospital No. 238 was an American military hospital formed in Rimaucourt, Department Haute Marne, France. This was the last hospital to be created during the First World War.
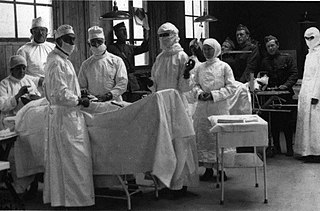
American Base Hospital No. 116 was an American military hospital formed in New York City, United States. During the First World War the hospital moved to Bazoilles-sur-Meuse, Department Vosges, in the advance section, France where it was set up to deal with war casualties.

Norman T. Kirk was a surgeon who specialized in bone and joint surgery during World War 1 and was Surgeon General of the Army from 1943 to 1947 during the height of the second World War.

American Base Hospital No. 36 was an American military hospital formed in Detroit, Michigan. During the First World War, the hospital moved to Vittel in northeastern France where it was set up to deal with war casualties.



















