Related Research Articles

In finance, a holdout problem occurs when a bond issuer is in default or nears default, and launches an exchange offer in an attempt to restructure debt held by existing bond holders. Such exchange offers typically require the consent of holders of some minimum portion of the total outstanding debt, often in excess of 90%, because, unless the terms of the bond provide otherwise, non-consenting bondholders will retain their legal right to demand repayment of their bonds at par. Bondholders who withhold their consent and retain their right to seek the full repayment of original bonds, may disrupt the restructuring process, creating a situation known as the holdout problem.

The Argentine Navy is the navy of Argentina. It is one of the three branches of the Armed Forces of the Argentine Republic, together with the Army and the Air Force.
The debt of developing countries usually refers to the external debt incurred by governments of developing countries.

The 1998–2002 Argentine great depression was an economic depression in Argentina, which began in the third quarter of 1998 and lasted until the second quarter of 2002. It followed fifteen years of stagnation and a brief period of free-market reforms. The depression, which began after the Russian and Brazilian financial crises, caused widespread unemployment, riots, the fall of the government, a default on the country's foreign debt, the rise of alternative currencies and the end of the peso's fixed exchange rate to the US dollar. The economy shrank by 28 per cent from 1998 to 2002. In terms of income, over 50 per cent of Argentines lived below the official poverty line and 25 per cent were indigent ; seven out of ten Argentine children were poor at the depth of the crisis in 2002.

The Argentine Air Force is the air force of Argentina and one of three branches of the Armed Forces of the Argentine Republic. In 2018, it had 13,837 military and 6,900 civilian personnel. FAA commander in chief is Brigadier Gustavo Valverde.
In corporate finance, distressed securities are securities over companies or government entities that are experiencing financial or operational distress, default, or are under bankruptcy. As far as debt securities, this is called distressed debt. Purchasing or holding such distressed-debt creates significant risk due to the possibility that bankruptcy may render such securities worthless.

The Argentine debt restructuring is a process of debt restructuring by Argentina that began on January 14, 2005, and allowed it to resume payment on 76% of the US$82 billion in sovereign bonds that defaulted in 2001 at the depth of the worst economic crisis in the nation's history. A second debt restructuring in 2010 brought the percentage of bonds under some form of repayment to 93%, though ongoing disputes with holdouts remained. Bondholders who participated in the restructuring settled for repayments of around 30% of face value and deferred payment terms, as well as warrants that paid investors based on annual economic growth as part of the same offer, and began to be paid punctually; the value of their nearly worthless bonds also began to rise. The remaining 7% of bondholders were later repaid 25% less than they were demanding, after centre-right and US-aligned leader Mauricio Macri came to power in 2015.

The Central Bank of the Argentine Republic is the central bank of Argentina, being an autarchic entity.
David Martínez Guzmán is a Mexican investor who is the founder and managing partner of Fintech Advisory. This firm specializes in corporate and sovereign debt. Fintech Advisory has offices in London and New York City, and he currently divides his time between those two cities.

Paul Elliott Singer is an American hedge fund manager, activist investor, and the founder, president, and co-CEO of Elliott Management. As of March 2024, Forbes estimated his net worth at US$6.1 billion. Fortune described Singer as one of the "smartest and toughest money managers" in the hedge fund industry. A number of sources have branded him a vulture capitalist, largely on account of his role at Elliott Management, which is a vulture fund. The Independent has described him as "a pioneer in the business of buying up sovereign bonds on the cheap, and then going after countries for unpaid debts".

Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of 2,780,400 km2 (1,073,500 sq mi), making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourth-largest country in the Americas, and the eighth-largest country in the world. It shares the bulk of the Southern Cone with Chile to the west, and is also bordered by Bolivia and Paraguay to the north, Brazil to the northeast, Uruguay and the South Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Drake Passage to the south. Argentina is a federal state subdivided into twenty-three provinces, and one autonomous city, which is the federal capital and largest city of the nation, Buenos Aires. The provinces and the capital have their own constitutions, but exist under a federal system. Argentina claims sovereignty over the Falkland Islands, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, the Southern Patagonian Ice Field, and a part of Antarctica.

Amado Boudou is an Argentine economist and politician who served as the Vice President of Argentina from 2011 to 2015. He previously served as Minister of Economy from 2009 to 2011.

The economy of Argentina is the second-largest national economy in South America, behind Brazil. Argentina is a developing country with a highly literate population, an export-oriented agricultural sector, and a diversified industrial base.

The Argentine Naval Aviation is the naval aviation branch of the Argentine Navy and one of its four operational commands. Argentina, along with Brazil is one of two South American countries to have operated two aircraft carriers.

The Presidency of Cristina Fernández de Kirchner began on 10 December 2007, when she became president of Argentina. She was an Argentine senator for the Buenos Aires Province at the time of her victory in the 2007 presidential election. Cristina Fernández de Kirchner became the second female president of Argentina, and the first one directly elected as such. In elections of November 2015, she was succeeded by Mauricio Macri as president.
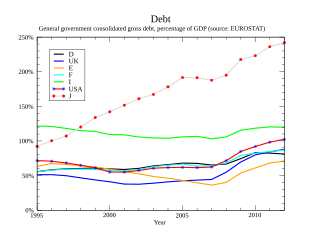
Debt crisis is a situation in which a government loses the ability of paying back its governmental debt. When the expenditures of a government are more than its tax revenues for a prolonged period, the government may enter into a debt crisis. Various forms of governments finance their expenditures primarily by raising money through taxation. When tax revenues are insufficient, the government can make up the difference by issuing debt.

Hernán Gaspar Lorenzino is an Argentine lawyer and public policy maker. He was appointed Minister of Economy of Argentina by President Cristina Kirchner in 2011.

Axel Kicillof is an Argentine economist and politician who has been Governor of Buenos Aires Province since 2019.
Gustavo Ferraro is an Argentine investment banker who has worked for many years for major U.S. banks and investment firms, specializing in Latin America-focused investment banking and capital markets. He played the leading role in negotiating the terms of the 2010 restructuring of Argentina's sovereign debt.
The Bicentennial fund was created in 2010 in Argentina by then president Cristina Fernández de Kirchner, to pay external debt with resources from the Central Bank. The president of the Bank, Martín Redrado, refused to do so, claiming that the autonomy of the Central Bank was not respected.
References
- ↑ "Una solicitada de los holdouts para denunciar "los mitos" argentinos" [An editorial from the holdouts to denounce the Argentine "myths"] (in Spanish). La Nación. July 10, 2014. Retrieved December 10, 2014.