
Winsted is a census-designated place and an incorporated city in Litchfield County, Connecticut, United States. It is part of the town of Winchester. The population of Winsted was 7,712 at the 2010 census, out of 11,242 in the entire town of Winchester.

Waterbury is a city in the U.S. state of Connecticut on the Naugatuck River, 33 miles (53 km) southwest of Hartford and 77 miles (124 km) northeast of New York City. Waterbury is the second-largest city in New Haven County, Connecticut. According to the 2020 US Census, in 2020 Waterbury had a population of 114,403. As of the 2010 census, Waterbury had a population of 110,366, making it the 10th largest city in the New York Metropolitan Area, 9th largest city in New England and the 5th largest city in Connecticut.

The New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad, commonly known as The Consolidated, or simply as the New Haven, was a railroad that operated in the New England region of the United States from 1872 to December 31, 1968. Founded by the merger of the New York and New Haven and Hartford and New Haven railroads, the company had near-total dominance of railroad traffic in Southern New England for the first half of the 20th century.
Timex Group USA, Inc. is an American global watch manufacturing company founded in 1854 as the Waterbury Clock Company in Waterbury, Connecticut. In 1944, the company became insolvent but was reformed into Timex Corporation. In 2008, the company was acquired by Timex Group B.V. and was renamed Timex Group USA.
A grandfather clock is a tall, freestanding, weight-driven pendulum clock with the pendulum held inside the tower or waist of the case. Clocks of this style are commonly 1.8–2.4 metres (6–8 feet) tall with an enclosed pendulum and weights suspended by either cables or chains which have to be calibrated occasionally to keep the proper time. The case often features elaborately carved ornamentation on the hood, which surrounds and frames the dial, or clock face. The English clockmaker William Clement is credited with the development of this form in 1670. Until the early 20th century, pendulum clocks were the world's most accurate timekeeping technology, and longcase clocks, due to their superior accuracy, served as time standards for households and businesses. Today they are kept mainly for their decorative and antique value, having been widely replaced by both analog and digital timekeeping.

Chauncey Jerome (1793–1868) was an American clockmaker in the early 19th century. He made a fortune selling his clocks, and his business grew quickly. However, his company failed in 1856, and he died in poverty.
The New Haven Register is a daily newspaper published in New Haven, Connecticut. It is owned by Hearst Communications. The Register's main office is located at 100 Gando Drive in New Haven. The Register was established about 1812 and is one of the oldest continuously published newspapers in the U.S. In the early 20th century it was bought by John Day Jackson. The Jackson family owned the Register, published weekday evenings and Saturday and Sunday mornings, and The Journal-Courier, a morning weekday paper, until they were combined in 1987 into a seven-day morning Register.
The Republican-American is a conservative-leaning, family-owned newspaper based in Waterbury, Connecticut. It is the result of the combination of two separate newspapers – the Waterbury American and the Waterbury Republican.

Founded in 1996, the Naugatuck Railroad is a common carrier railroad owned by the Railroad Museum of New England and operated by Naugatuck Railroad on tracks leased by Naugatuck Railroad from the Connecticut Department of Transportation. The original Naugatuck Railroad was a railroad chartered to operate through south central Connecticut in 1845, with the first section opening for service in 1849. In 1887 the line was leased by the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad, and became wholly owned by 1906. At its greatest extent the Naugatuck ran from Bridgeport north to Winsted. Today's Naugatuck Railroad runs from Waterbury to the end of track in Torrington, Connecticut. From Waterbury south to the New Haven Line, Metro-North Railroad operates commuter service on the Waterbury Branch.

Eli Terry Sr. was an inventor and clockmaker in Connecticut. He received a United States patent for a shelf clock mechanism. He introduced mass production to the art of clockmaking, which made clocks affordable for the average American citizen. Terry occupies an important place in the beginnings of the development of interchangeable parts manufacturing. Terry is considered the first person in American history to actually accomplish interchangeable parts with no government funding. Terry became one of the most accomplished mechanics in New England during the early part of the nineteenth century. The village of Terryville, Connecticut is named for his son, Eli Terry Jr.

The Waterbury Union Station building is located on Meadow Street in the city of Waterbury, Connecticut, United States. It is a brick building dating to the first decade of the 20th century. Its tall clock tower, built by the Seth Thomas Company, is the city's most prominent landmark.

The Connecticut Company was the primary electric street railway company in the U.S. state of Connecticut, operating both city and rural trolleys and freight service. It was controlled by the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad, which also controlled most steam railroads in the state. After 1936, when one of its major leases was dissolved, it continued operating streetcars and, increasingly, buses in certain Connecticut cities until 1976, when its assets were purchased by the state government.
The history of Connecticut Industry is a major part of the history of Connecticut. Between the birth of the U.S. patent system in 1790 and 1930, Connecticut had more patents issued per capita than any other state; in the 19th century, when the U.S. as a whole was issued one patent per three thousand population, Connecticut inventors were issued one patent for every 700–1000 residents. Connecticut's first recorded invention was a lapidary machine, by Abel Buell of Killingworth, in 1765.

The Timexpo Museum in Waterbury, Connecticut was dedicated to the history of Timex Group and its predecessors, featuring exhibits dating to the founding of Waterbury Clock Company in 1854. The museum was located in the Brass Mill Commons shopping center with its location marked by a 40-foot (12 m) high replica of an Easter Island Moai statue which connected with the museum's archaeology exhibit. The museum covered 14,000 square feet (1,300 m2) with 8,000 square feet (740 m2) dedicated to the two main exhibits: the company's history of timepieces and archaeology.
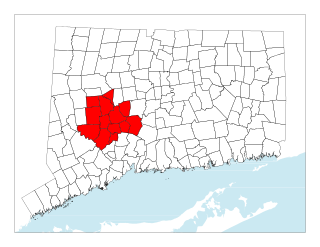
The Central Naugatuck Valley is a region of Connecticut in New Haven and Litchfield counties located approximately 70 miles (110 km) northeast of New York City and 110 miles (180 km) southwest of Boston, United States. The region comprises 13 towns: Beacon Falls, Bethlehem, Cheshire, Middlebury, Naugatuck, Oxford, Prospect, Southbury, Thomaston, Waterbury, Watertown, Wolcott, and Woodbury.
The American Brass Company was an American brass manufacturing company based in Connecticut and active from 1893 to 1960. The company's predecessors were the Wolcottville Brass Company and the Ansonia Brass and Battery Company. It was the first large brass manufacturing firm in the United States, and for much of its existence was the largest brass manufacturer in the country. It was purchased by the Anaconda Copper Company in 1922, and merged into Anaconda's other brass manufacturing concerns in 1960.
Peter Anthony Rosazza is an American prelate of the Roman Catholic Church. He served as an auxiliary bishop of the Archdiocese of Hartford from 1978 to 2010.
The E. Ingraham Company was one of the premier American clock and watch manufacturers during the 19th and 20th centuries. Headquartered in Bristol, Connecticut, the firm was founded in 1831 by Elias Ingraham and controlled by members of the Ingraham family until 1956.











