Peptides are short chains of between two and fifty amino acids, linked by peptide bonds. Chains of fewer than ten or fifteen amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides.
Beta cells are a type of cell found in pancreatic islets that synthesize and secrete insulin and amylin. Beta cells make up 50–70% of the cells in human islets. In patients with Type I Diabetes, beta-cell mass and function are diminished, leading to insufficient insulin secretion and hyperglycemia.

Glucagon is a peptide hormone, produced by alpha cells of the pancreas. It works to raise the concentration of glucose and fatty acids in the bloodstream, and is considered to be the main catabolic hormone of the body. It is also used as a medication to treat a number of health conditions. Its effect is opposite to that of insulin, which lowers extracellular glucose. It is produced from proglucagon, encoded by the GCG gene.

Biochemistry is the study of the chemical processes in living organisms. It deals with the structure and function of cellular components such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids and other biomolecules.

Amyloids are aggregates of proteins characterised by a fibrillar morphology of 7–13 nm in diameter, a β-sheet secondary structure and ability to be stained by particular dyes, such as Congo red. In the human body, amyloids have been linked to the development of various diseases. Pathogenic amyloids form when previously healthy proteins lose their normal structure and physiological functions (misfolding) and form fibrous deposits in plaques around cells which can disrupt the healthy function of tissues and organs.

Calcitonin is a 32 amino acid peptide hormone secreted by parafollicular cells (also known as C cells) of the thyroid gland in humans, and in many other animals in the ultimopharyngeal body. It acts to reduce blood calcium (Ca2+), opposing the effects of parathyroid hormone (PTH).

Amylin, or islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP), is a 37-residue peptide hormone. It is cosecreted with insulin from the pancreatic β-cells in the ratio of approximately 100:1 (insulin:amylin). Amylin plays a role in glycemic regulation by slowing gastric emptying and promoting satiety, thereby preventing post-prandial spikes in blood glucose levels.
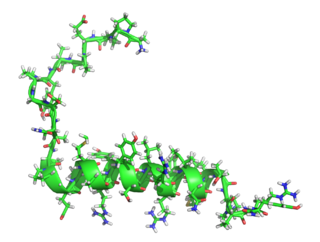
Pancreatic polypeptide (PP) is a polypeptide secreted by PP cells in the endocrine pancreas predominantly in the head of the pancreas. It consists of 36 amino acids and has molecular weight about 4200 Da. The function of PP is to self-regulate pancreatic secretion activities. It also has effects on hepatic glycogen levels and gastrointestinal secretions.
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) is a member of the calcitonin family of peptides, which in humans exists in two forms: α-CGRP and β-CGRP, also known as CGRP I and CGRP II. CGRP I or α-CGRP is a 37-amino acid neuropeptide and is formed from the alternative splicing of the calcitonin/CGRP gene located on chromosome 11. CGRP II or β-CGRP is less studied. In humans, β-CGRP differs from the α-CGRP by three amino acids and is encoded in a separate gene within the same vicinity. The CGRP family includes calcitonin (CT), adrenomedullin (AM), and amylin (AMY). This article outlines the basic function of CGRP as well as sources of production and synthesis. It further introduces receptors and regulation of CGRP, with a focus on human and mammalian systems.

Adrenomedullin is a vasodilator peptide hormone of uncertain significance in human health and disease. It was initially isolated in 1993 from a pheochromocytoma, a tumor of the adrenal medulla: hence the name.
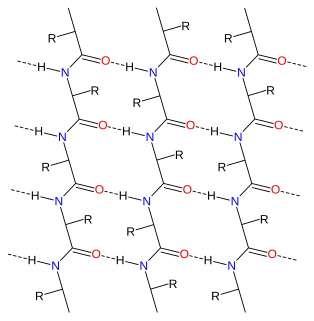
Alpha sheet is an atypical secondary structure in proteins, first proposed by Linus Pauling and Robert Corey in 1951. The hydrogen bonding pattern in an alpha sheet is similar to that of a beta sheet, but the orientation of the carbonyl and amino groups in the peptide bond units is distinctive; in a single strand, all the carbonyl groups are oriented in the same direction on one side of the pleat, and all the amino groups are oriented in the same direction on the opposite side of the sheet. Thus the alpha sheet accumulates an inherent separation of electrostatic charge, with one edge of the sheet exposing negatively charged carbonyl groups and the opposite edge exposing positively charged amino groups. Unlike the alpha helix and beta sheet, the alpha sheet configuration does not require all component amino acid residues to lie within a single region of dihedral angles; instead, the alpha sheet contains residues of alternating dihedrals in the traditional right-handed (αR) and left-handed (αL) helical regions of Ramachandran space. Although the alpha sheet is only rarely observed in natural protein structures, it has been speculated to play a role in amyloid disease and it was found to be a stable form for amyloidogenic proteins in molecular dynamics simulations. Alpha sheets have also been observed in X-ray crystallography structures of designed peptides.

The gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (GIP-R), also known as the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GIPR gene. GIP-R is a member of the 7-transmembrane protein family, a class of G protein

Carboxypeptidase E (CPE), also known as carboxypeptidase H (CPH) and enkephalin convertase, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CPE gene. This enzyme catalyzes the release of C-terminal arginine or lysine residues from polypeptides.
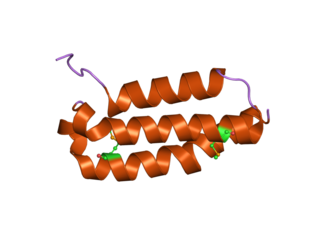
Receptor activity modifying protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAMP1 gene.
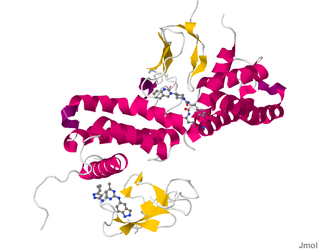
Calcitonin receptor-like (CALCRL), also known as the calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CRLR), is a human protein; it is a receptor for calcitonin gene-related peptide.
Secretin family receptor proteins, also known as Family B or family 2 of G-protein coupled receptors are regulated by peptide hormones from the glucagon hormone family. The family is different from adhesion G protein-coupled receptors.

Glucagon/GIP/secretin/VIP hormones are a family of evolutionarily related peptide hormones that regulate activity of G-protein coupled receptors from secretin receptor family.

Morin is a yellow chemical compound that can be isolated from Maclura pomifera (Osage orange), Maclura tinctoria (old fustic), and from leaves of Psidium guajava (common guava). In a preclinical in vitro study, morin was found to be a weak inhibitor of fatty acid synthase with an IC50 of 2.33 μM. Morin was also found to inhibit amyloid formation by islet amyloid polypeptide (or amylin) and disaggregate amyloid fibers.

In molecular biology, chaperone DnaJ, also known as Hsp40, is a molecular chaperone protein. It is expressed in a wide variety of organisms from bacteria to humans.
Neuroendocrine differentiation is a term primarily used in relation to prostate cancers that display a significant neuroendocrine cell population on histopathological examination. These types of prostate cancer comprise true neuroendocrine cancers, such as small cell carcinoma, carcinoid and carcinoid-like tumors, as well as prostatic adenocarcinoma exhibiting focal neuroendocrine phenotype.















