
Plasmodium falciparum is a unicellular protozoan parasite of humans, and the deadliest species of Plasmodium that causes malaria in humans. The parasite is transmitted through the bite of a female Anopheles mosquito and causes the disease's most dangerous form, falciparum malaria. It is responsible for around 50% of all malaria cases. P. falciparum is therefore regarded as the deadliest parasite in humans. It is also associated with the development of blood cancer and is classified as a Group 2A (probable) carcinogen.

Plasmodium vivax is a protozoal parasite and a human pathogen. This parasite is the most frequent and widely distributed cause of recurring malaria. Although it is less virulent than Plasmodium falciparum, the deadliest of the five human malaria parasites, P. vivax malaria infections can lead to severe disease and death, often due to splenomegaly. P. vivax is carried by the female Anopheles mosquito; the males do not bite.

Plasmodium knowlesi is a parasite that causes malaria in humans and other primates. It is found throughout Southeast Asia, and is the most common cause of human malaria in Malaysia. Like other Plasmodium species, P. knowlesi has a life cycle that requires infection of both a mosquito and a warm-blooded host. While the natural warm-blooded hosts of P. knowlesi are likely various Old World monkeys, humans can be infected by P. knowlesi if they are fed upon by infected mosquitoes. P. knowlesi is a eukaryote in the phylum Apicomplexa, genus Plasmodium, and subgenus Plasmodium. It is most closely related to the human parasite Plasmodium vivax as well as other Plasmodium species that infect non-human primates.
Malaria vaccines are vaccines that prevent malaria, a mosquito-borne infectious disease which annually affects an estimated 247 million people worldwide and causes 619,000 deaths. The first approved vaccine for malaria is RTS,S, known by the brand name Mosquirix. As of April 2023, the vaccine has been given to 1.5 million children living in areas with moderate-to-high malaria transmission. It requires at least three doses in infants by age 2, and a fourth dose extends the protection for another 1–2 years. The vaccine reduces hospital admissions from severe malaria by around 30%.
The Burroughs Wellcome Fund (BWF) is an American non-profit medical research organization that provides funding for biomedical research, STEM education, and areas of career development for scientists. Since 1970, it has been headquartered in North Carolina's Research Triangle Park.
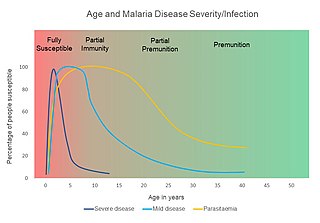
Premunition, also known as infection-immunity, is a host response that protects against high numbers of parasite and illness without eliminating the infection. This type of immunity is relatively rapid, progressively acquired, short-lived, and partially effective. For malaria, premunition is maintained by repeated antigen exposure from infective bites. Thus, if an individual departs from an endemic area, he or she may lose premunition and become susceptible to malaria.
Lucy S. Tompkins is a practicing internist, the Lucy Becker Professor of Medicine for infectious diseases at Stanford University, and a professor of microbiology and immunology. Since 1989, she has been the Epidemiologist and Medical Director of the Infection Control and Epidemiology Department for Stanford Hospital. She also has been the Associate Dean for Academic Affairs at the Stanford School of Medicine since 2001. She has been the recipient of multiple fellowships throughout her career, including the American Association for the Advancement of Science. Her current research centers around healthcare-related infections and bacterial pathogenesis.
Sanaria is a biotechnology company developing vaccines protective against malaria and other infectious diseases as well as related products for use in malaria research. Sanaria's vaccines are based on the use of the sporozoite (SPZ) stage of the malaria parasite, Plasmodium, as an immunogen, and as a platform technology for liver-vectored gene delivery. SPZ are normally introduced into humans by mosquito bite where they migrate to the liver and further develop to liver stages, and eventually back into the blood stream where the parasite infects red blood cells (RBC) and causes malaria. Plasmodium falciparum is the species responsible for more than 95% deaths caused by malaria. The WHO estimates there were 247 million clinical cases and 619,000 deaths in 2021 alone.

Akiko Iwasaki is a Sterling Professor of Immunobiology and Molecular, Cellular and Developmental Biology at Yale University. She is also a principal investigator at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. Her research interests include innate immunity, autophagy, inflammasomes, sexually transmitted infections, herpes simplex virus, human papillomavirus, respiratory virus infections, influenza infection, T cell immunity, commensal bacteria, COVID-19 and Long COVID.

Arturo Casadevall is a Bloomberg Distinguished Professor of Molecular Microbiology & Immunology and Infectious Diseases at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, and the Alfred and Jill Sommer Professor and Chair of the W. Harry Feinstone Department of Molecular Microbiology and Immunology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. He is an internationally recognized expert in infectious disease research, with a focus on fungal and bacterial pathogenesis and basic immunology of antibody structure-function. He was elected a member of the National Academy of Sciences in 2022.
Ruth Sonntag Nussenzweig was an Austrian-Brazilian immunologist specializing in the development of malaria vaccines. In a career spanning over 60 years, she was primarily affiliated with New York University (NYU). She served as C.V. Starr Professor of Medical and Molecular Parasitology at Langone Medical Center, Research Professor at the NYU Department of Pathology, and finally Professor Emerita of Microbiology and Pathology at the NYU Department of Microbiology.

Lalita Ramakrishnan is an Indian-born American microbiologist who is known for her contributions to the understanding of the biological mechanism of tuberculosis. As of 2019 she serves as a professor of Immunology and Infectious Diseases at the University of Cambridge, where she is also a Wellcome Trust Principal Research Fellow and a practicing physician. Her research is conducted at the MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, where she serves as the Head of the Molecular Immunity Unit of the Department of Medicine embedded at the MRC LMB. Working with Stanley Falkow at Stanford, she developed the strategy of using Mycobacterium marinum infection as a model for tuberculosis. Her work has appeared in a number of journals, including Science, Nature, and Cell. In 2018 and 2019 Ramakrishnan coauthored two influential papers in the British Medical Journal (BMJ) arguing that the widely accepted estimates of the prevalence of latent tuberculosis—estimates used as a basis for allocation of research funds—are far too high. She is married to Mark Troll, a physical chemist.

Plasmodium cynomolgi is an apicomplexan parasite that infects mosquitoes and Asian Old World monkeys. In recent years, a number of natural infections of humans have also been documented. This species has been used as a model for human Plasmodium vivax because Plasmodium cynomolgi shares the same life cycle and some important biological features with P. vivax.
Karla Satchell, born Karla Fullner, is an American microbiologist who is currently a professor at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine and an elected fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science.

Maria Manuel Mota is a Portuguese malariologist and executive director of the Instituto de Medicina Molecular João Lobo Antunes, Lisbon.

Sean Whelan is a British-American virologist. He is known for identifying the cellular protein used as a receptor by Ebola virus, for defining the entry pathway that rabies virus uses to enter neurons, and for identifying the ribosome as a possible target for antiviral drugs. In July 2019, he was announced as the new Chair of the Department of Molecular Microbiology at Washington University School of Medicine in St Louis, Missouri. In February 2020, Whelan was recognized as the LGBTQ+ Scientist of the Year 2020 by the National Organization of Gay and Lesbian Scientists and Technical Professionals.
Sara R. Cherry is an American microbiologist who is John W. Eckman Professor of Medical Science and Professor of Microbiology in Biochemistry and Biophysics at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Her research involves genetic and mechanistic studies of virus–host interactions. During the COVID-19 pandemic, Cherry looked to identify novel therapeutic strategies.
Eric P. Skaar is an American microbiologist, the Ernest W. Goodpasture Professor of Pathology, Microbiology and Immunology at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, and a University Distinguished Professor at Vanderbilt University.
Maurizio Del Poeta is a Distinguished Professor in the Department of Microbiology and Immunology at the Stony Brook University Renaissance School of Medicine. His research focuses on novel anti-fungal drug discovery and lipid-mediated fungal pathogenesis.
Vanessa Sperandio is a professor at the UT Southwestern Medical Center in both the departments of microbiology and biochemistry. She will join the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health as the chair of the Department of Medical Microbiology and Immunology in spring 2022.









