
Cape Coast Castle is one of about forty "slave castles", or large commercial forts, built on the Gold Coast of West Africa by European traders. It was originally a Portuguese "feitoria" or trading post, established in 1555, which they named Cabo Corso.

The Dutch Gold Coast or Dutch Guinea, officially Dutch possessions on the Coast of Guinea was a portion of contemporary Ghana that was gradually colonized by the Dutch, beginning in 1612. The Dutch began trading in the area around 1598, joining the Portuguese which had a trading post there since the late 1400s. Eventually, the Dutch Gold Coast became the most important Dutch colony in West Africa after Fort Elmina was captured from the Portuguese in 1637, but fell into disarray after the abolition of the slave trade in the early 19th century. On 6 April 1872, the Dutch Gold Coast was, in accordance with the Anglo-Dutch Treaties of 1870–71, ceded to the United Kingdom.

The Treaty of Butre between the Netherlands and Ahanta was signed at Butre, Dutch Gold Coast on 27 August 1656. The treaty regulated the jurisdiction of the Netherlands and the Dutch West India Company over the town of Butre and the surrounding country of Upper Ahanta, creating a Dutch protectorate over the area, and permitting the establishment of Fort Batenstein. The treaty lasted until the Dutch departure from the Gold Coast in April 1872.

The Treaty of Axim was concluded between the Netherlands and the chiefs of Axim in the western region of the Gold Coast and signed at Fort St. Anthony near Axim on 17 February 1642. The treaty regulated the jurisdiction of the Netherlands and the Dutch West India Company in the town and polity of Axim after the Dutch West India Company had successfully attacked the Portuguese who were the occupants of Fort St. Anthony in the town. Over time, the agreement was in part superseded and replaced by new contracts and agreements. The treaty did remain the basis for Dutch jurisdiction and political relations between Axim and the Dutch until the latter left the Gold Coast in 1872.

Fort Patience is a Dutch-built fort located in the township of Apam, in the Central Region of Ghana. Originally built in 1697, it served as a defensive fortification and a trading post. Because of its testimony to European pre-colonial and colonial influence in West Africa, the fort was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List along with several other forts and castles in Ghana.

The Ahanta/Ayinda are Akan People who live to the north and east of the Nzema. The Ahanta land has been historically known as one of the richest areas on the coast of what is now Ghana.
The Anglo-Dutch Treaties of 1870–1871 were three related treaties between Great Britain and the Netherlands, dealing with colonial disputes and other colonial affairs between the two countries.

Fort Saint Anthony was a fort built by the Portuguese in 1515 near the town of Axim, in what is now Ghana. In 1642, the Dutch captured the fort and subsequently made it part of the Dutch Gold Coast. The Dutch expanded the fort considerably before they turned it over, with the rest of their colony, to the British in 1872. The fort is now the property of the Ghanaian state and is open to the public.
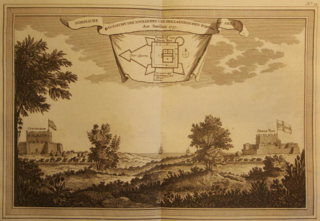
Ussher Fort is a fort in Accra, Ghana. It was built by the Dutch in 1649 as Fort Crèvecœur, and is two days' march from Elmina and to the east of Accra on a rocky point between two lagoons. It was one of three forts that Europeans built in the region during the middle of the 17th century. Fort Crèvecœur was part of the Dutch Gold Coast. The Anglo-Dutch Gold Coast Treaty (1867), which defined areas of influence on the Gold Coast, transferred it to the British in 1868. Because of its significance in the history of European colonial trade and exploitation in Africa, the fort was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1979.

Fort Batenstein was a fort and trading post established by the Dutch on the Gold Coast in 1656. It was situated near Butre. The fort was ceded with the entire Dutch Gold Coast to Britain in 1872.

Fort Vredenburgh was a Dutch fort on the Gold Coast, established on the left bank of the Komenda River. The fort exists as preserved ruins. Because of its testimony to European economic and colonial influence in West Africa, the fort was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1979, along with other nearby forts and castles.

The Dutch Gold Coast expedition of 1869–1870 followed the resistance to Dutch rule of the local Fante people surrounding the forts assigned to the Netherlands in the 1868 forts trade along the Gold Coast with Britain. Although the Dutch managed to eventually control the situation, the events marked the end of Dutch involvement in the Gold Coast. Without a profit for almost a century, the escalation finally made the political balance shift in favour of the liberal faction, which wanted to sell the colony to Britain, and away from the nationalist faction, which wanted to retain the colony for reasons of national prestige.

Fort Komenda was a British fort on the Gold Coast, currently preserved as a ruin. Because of its testimony to the Atlantic slave trade and European economic and colonial influence in West Africa, the fort was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1979, along with several other castles and forts in Ghana.

Cornelis Johannes Marius Nagtglas was a Dutch politician and civil servant, who made a career in the administration on the Dutch Gold Coast. After originally beginning his career at the advanced age of 36, he was promoted through the ranks to eventually become Governor of the Dutch Gold Coast in 1858. He retired to the Netherlands in 1862, but returned to the Gold Coast as governor in 1869, to restore order in the embattled colony. In 1871, he left the Gold Coast again, one year before the transfer of the colony to the United Kingdom.
The Dutch–Ahanta War was a conflict between the Netherlands and the Ahanta between 1837 and 1839. Beginning with a mere economic dispute between the Ahanta and the Dutch, who were based at the Dutch Gold Coast, the conflict ended with the hanging of Ahanta king Badu Bonsu II and the reorganization of the Ahanta state, establishing a Dutch protectorate over the Ahanta.

The Komenda Wars were a series of wars from 1694 until 1700 largely between the Dutch West India Company and the English Royal African Company in the Eguafo Kingdom in the present day state of Ghana, over trade rights. The Dutch were trying to keep the English out of the region to maintain a trade monopoly, while the English were attempting to re-establish a fort in the city of Komenda. The fighting included forces of the Dutch West India Company, the Royal African Company, the Eguafo Kingdom, a prince of the kingdom attempting to rise to the throne, the forces of a powerful merchant named John Cabess, other Akan tribes and kingdoms like Twifo and Denkyira. There were four separate periods of warfare, including a civil war in the Eguafo Kingdom, and the wars ended with the English placing Takyi Kuma into power in Eguafo. Because of the rapidly shifting alliances between European and African powers, historian John Thornton has found that "there is no finer example of [the] complicated combination of European rivalry merging with African rivalry than the Komenda Wars."

Henri Alexander Elias was a Dutch colonial administrator, who served as governor of the Dutch Gold Coast.
Willem Pieter Antonie Le Jeune, born as Willem Pieter Antonie Tenwinkel, was a Dutch colonial administrator and diplomat, who made a career in the administration on the Dutch Gold Coast and who was interim governor between 28 October 1871 and 15 November 1871. After the Netherlands sold its possessions on the Gold Coast to the United Kingdom in 1872, Le Jeune became the first Dutch consul in Elmina.

The documented history of Elmina begins in 1482 with an agreement between the Portuguese navigator Diogo de Azambuja and the ruler of Elmina, called Caramansa by the Portuguese. In it, the Portuguese were allowed to build the first European fortress in sub-Saharan Africa. For the next 150 years until the conquest by the Dutch in 1637, Elmina was the capital of the Portuguese bases on the Gold Coast, then for about 250 years the capital of the Dutch Empire in West Africa. Since the capture of the lease for the two fortresses of Elmina by the Ashanti in 1701, the city was also important to the Ashanti Empire. Until the 19th century, Elmina was one of the most populous cities in the Gold Coast, surpassing Accra and Kumasi. The trade in gold, slaves and palm oil brought the city into direct contact with Europe, North America, Brazil and, through the recruitment of soldiers, also with Southeast Asia. It was not until the takeover and destruction of the city by the British in 1873 that Elmina lost its prominent position in the Gold Coast.
Hubertus Varlet was a Dutch architect and colonial administrator, who served on the Dutch Gold Coast. In his capacity as master of works and stores, he rebuilt Fort Crèvecoeur in Accra in 1839. Following the promotion of Anthony van der Eb to governor of the Dutch Gold Coast, Varlet succeeded him as the second vice governor for the Ahanta protectorate, which the Dutch had proclaimed following the conclusion of the Dutch–Ahanta War.















