The cloudinids, an early metazoan family containing the genera Acuticocloudina, Cloudina and Conotubus, lived in the late Ediacaran period about 550 million years ago. and became extinct at the base of the Cambrian. They formed millimetre-scale conical fossils consisting of calcareous cones nested within one another; the appearance of the organism itself remains unknown. The name Cloudina honors the 20th-century geologist and paleontologist Preston Cloud.

Cyclomedusa is a circular fossil of the Ediacaran biota; it has a circular bump in the middle and as many as five circular growth ridges around it. Many specimens are small, but specimens in excess of 20 cm are known. The concentric disks are not necessarily circular, especially when adjacent individuals interfere with each other's growth. Many radial segment lines — somewhat pineapple-like — extend across the outer disks. A few specimens show what might be a stem extending from the center in some direction or other.

Charnia is a genus of frond-like lifeforms belonging to the Ediacaran biota with segmented, leaf-like ridges branching alternately to the right and left from a zig-zag medial suture. The genus Charnia was named after Charnwood Forest in Leicestershire, England, where the first fossilised specimen was found. Charnia is significant because it was the first Precambrian fossil to be recognized as such.

Ediacaria is a fossil genus dating to the Ediacaran Period of the Neoproterozoic Era. Unlike most Ediacaran biota, which disappeared almost entirely from the fossil record at the end of the Period, Ediacaria fossils have been found dating from the Baikalian age of the Upper Riphean to 501 million years ago, well into the Cambrian Period. Ediacaria consists of concentric rough circles, radial lines between the circles and a central dome, with a diameter from 1 to 70 cm.

Aspidella is an Ediacaran disk-shaped fossil of uncertain affinity. It is known from the single species A. terranovica.
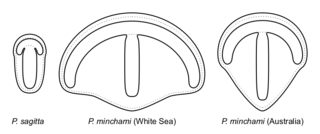
Parvancorina is a genus of shield-shaped bilaterally symmetrical fossil animal that lived in the late Ediacaran seafloor. It has some superficial similarities with the Cambrian trilobite-like arthropods.
Namacalathus is a problematic metazoan fossil occurring in the latest Ediacaran. The first, and only described species, N. hermanastes, was first described in 2000 from the Nama Group of central and southern Namibia.
The Khatyspyt Formation is a Neoproterozoic formation exposed in the Olenëk Uplift of north central Siberia, which contains the only known instance of the Ediacara biota preserved in a limestone bed. The Khatyspyt Formation forms one of the major parts of the Khorbusuonka Group; underlying the Khatyspyt are dolomites of the Mastakh Formation and their overlying red beds; the Turkut Formation overlies the Khatyspyt. The Khatyspyt and part of the overlying Turkut comprise a major shallowing upward marine carbonate sequence. Khatyspytia is named after this formation.

Arumberia is an enigmatic fossil from the Ediacaran period originally described from the Arumbera Sandstone, Northern Territory, Australia but also found in the Urals, East Siberia, England and Wales, Northern France, the Avalon Peninsula and India. Several morphologically distinct species are recognized.
The Blueflower Formation is a geologic formation in Northwest Territories. It preserves fossils dating back to the Ediacaran period.
Sekwitubulus annulatus is an Ediacaran tubular fossil from the Blueflower Formation in Canada. Sekwitubulus is a monotypic genus, containing only the single species. S. annulatus is possibly a type of annelid worm. The name derives from the area the type specimen was found, Sekwi.
Mezenia is a genus of macroalgae described by Boris Sokolov in 1976. Mezenia lived in Eurasia during the Ediacaran between 560 and 551 Ma.
Orbisiana is an Ediacaran benthic organism formed out of series of agglutinated spherical or hemispherical chambers. It is believed to be a close relative of Palaeopascichnus.
Namalia was first described in 1968 by G. J. B. Germs from an outcrop near Helmeringhausen, Namibia and Namalia dates back to the Ediacaran Period . Namalia has a conical structure and it is thought that it lived semi-buried in sediment along the seafloor.
Pomoria rhomboidalis is a Late Ediacaran microfossils of cyanobacterial trichome which is a characteristic taxon of the fossil microbiota in the East European Platform, it is also found in the Siberia and China. It is the only species in the genus Pomoria.

Medusinites is a genus of disc shaped fossilised organisms associated with the Ediacaran biota. They have been found in rocks dated to be 580 to 541 million years old.

The Ediacaran fossil Hallidaya, a close relative of Skinnera lived in Belomorian of the Late Ediacaran period prior to the Cambrian explosion and thrived in the marine strata on the ocean floor of what is now considered Australia. These fossils were disk-shaped organisms that were slightly dome shaped with tri-radial symmetry. These Ediacaran organisms thrived by living in low-energy inner shelf, in the wave- and current-agitated shoreface, and in the high-energy distributary systems.

The petalonamids (Petalonamae) are an extinct group of archaic animals typical of the Ediacaran biota, also called frondomorphs, dating from approximately 635 million years ago to 516 million years ago. They are benthic and motionless animals, that have the shape of leaves, fronds (frondomorphic), feathers or spindles and were initially considered algae, octocorals or sea pens. It is now believed that there are no living decedents of the group, which shares a probable relation to the Ediacaran animals known as Vendozoans.

Eocyathispongia is a genus of sponge-like organisms which lived in the Ediacaran period about 60 million years before the Cambrian. The current fossil record has found this genus in only one location, the Doushantuo Formation in Guizhou, China. It lived in the shallow parts of seas, filter feeding.

Nenoxites is an extinct genus of Ediacaran ichnofossils described by Mikhail Fedonkin in 1973. The genus is monotypic; the only species to have been described is Nenoxites curvus.










