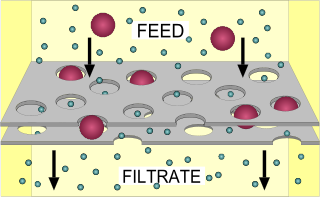
Filtration is a physical separation process that separates solid matter and fluid from a mixture using a filter medium that has a complex structure through which only the fluid can pass. Solid particles that cannot pass through the filter medium are described as oversize and the fluid that passes through is called the filtrate. Oversize particles may form a filter cake on top of the filter and may also block the filter lattice, preventing the fluid phase from crossing the filter, known as blinding. The size of the largest particles that can successfully pass through a filter is called the effective pore size of that filter. The separation of solid and fluid is imperfect; solids will be contaminated with some fluid and filtrate will contain fine particles. Filtration occurs both in nature and in engineered systems; there are biological, geological, and industrial forms. In everyday usage the verb "strain" is more often used; for example, using a colander to drain cooking water from cooked pasta.

In chemistry, a solution is a special type of homogeneous mixture composed of two or more substances. In such a mixture, a solute is a substance dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. If the attractive forces between the solvent and solute particles are greater than the attractive forces holding the solute particles together, the solvent particles pull the solute particles apart and surround them. These surrounded solute particles then move away from the solid solute and out into the solution. The mixing process of a solution happens at a scale where the effects of chemical polarity are involved, resulting in interactions that are specific to solvation. The solution usually has the state of the solvent when the solvent is the larger fraction of the mixture, as is commonly the case. One important parameter of a solution is the concentration, which is a measure of the amount of solute in a given amount of solution or solvent. The term "aqueous solution" is used when one of the solvents is water.

Gasification is a process that converts biomass- or fossil fuel-based carbonaceous materials into gases, including as the largest fractions: nitrogen (N2), carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), and carbon dioxide (CO2). This is achieved by reacting the feedstock material at high temperatures (typically >700 °C), without combustion, via controlling the amount of oxygen and/or steam present in the reaction. The resulting gas mixture is called syngas (from synthesis gas) or producer gas and is itself a fuel due to the flammability of the H2 and CO of which the gas is largely composed. Power can be derived from the subsequent combustion of the resultant gas, and is considered to be a source of renewable energy if the gasified compounds were obtained from biomass feedstock.

Ferrofluid is a liquid that is attracted to the poles of a magnet. It is a colloidal liquid made of nanoscale ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic particles suspended in a carrier fluid. Each magnetic particle is thoroughly coated with a surfactant to inhibit clumping. Large ferromagnetic particles can be ripped out of the homogeneous colloidal mixture, forming a separate clump of magnetic dust when exposed to strong magnetic fields. The magnetic attraction of tiny nanoparticles is weak enough that the surfactant's Van der Waals force is sufficient to prevent magnetic clumping or agglomeration. Ferrofluids usually do not retain magnetization in the absence of an externally applied field and thus are often classified as "superparamagnets" rather than ferromagnets.
A supercritical fluid (SCF) is any substance at a temperature and pressure above its critical point, where distinct liquid and gas phases do not exist, but below the pressure required to compress it into a solid. It can effuse through porous solids like a gas, overcoming the mass transfer limitations that slow liquid transport through such materials. SCFs are superior to gases in their ability to dissolve materials like liquids or solids. Also, near the critical point, small changes in pressure or temperature result in large changes in density, allowing many properties of a supercritical fluid to be "fine-tuned".

An optical table is a vibration control platform that is used to support systems used for laser- and optics-related experiments in science, engineering and manufacturing. The surfaces of these tables are designed to be very rigid with minimum deflection so that the alignment of optical elements remains stable over time. Many optical systems require that vibration of optical elements be kept small. As a result, optical tables are typically very heavy and incorporate vibration isolation and damping features in their structure. Many use pneumatic isolators that act as mechanical low-pass filters, reducing the ability of vibrations in the floor to cause vibrations in the tabletop.

Fluidization is a process similar to liquefaction whereby a granular material is converted from a static solid-like state to a dynamic fluid-like state. This process occurs when a fluid is passed up through the granular material.

Electrorheological (ER) fluids are suspensions of extremely fine non-conducting but electrically active particles in an electrically insulating fluid. The apparent viscosity of these fluids changes reversibly by an order of up to 100,000 in response to an electric field. For example, a typical ER fluid can go from the consistency of a liquid to that of a gel, and back, with response times on the order of milliseconds. The effect is sometimes called the Winslow effect after its discoverer, the American inventor Willis Winslow, who obtained a US patent on the effect in 1947 and wrote an article published in 1949.

Sand filters are used as a step in the water treatment process of water purification.
Hardening is a metallurgical metalworking process used to increase the hardness of a metal. The hardness of a metal is directly proportional to the uniaxial yield stress at the location of the imposed strain. A harder metal will have a higher resistance to plastic deformation than a less hard metal.

Fouling is the accumulation of unwanted material on solid surfaces. The fouling materials can consist of either living organisms or a non-living substance (inorganic). Fouling is usually distinguished from other surface-growth phenomena in that it occurs on a surface of a component, system, or plant performing a defined and useful function and that the fouling process impedes or interferes with this function.
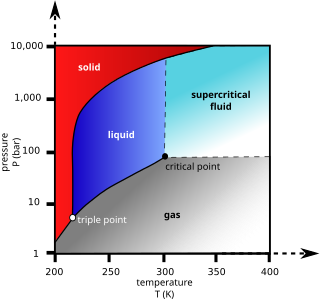
Supercritical carbon dioxide is a fluid state of carbon dioxide where it is held at or above its critical temperature and critical pressure.

Pneumatic tires are manufactured according to relatively standardized processes and machinery, in around 455 tire factories in the world. With over 1 billion tires manufactured worldwide annually, the tire industry is a major consumer of natural rubber. Tire factories start with bulk raw materials such as synthetic rubber, carbon black, and chemicals and produce numerous specialized components that are assembled and cured.
This glossary of chemistry terms is a list of terms and definitions relevant to chemistry, including chemical laws, diagrams and formulae, laboratory tools, glassware, and equipment. Chemistry is a physical science concerned with the composition, structure, and properties of matter, as well as the changes it undergoes during chemical reactions; it features an extensive vocabulary and a significant amount of jargon.
Dry lubricants or solid lubricants are materials that, despite being in the solid phase, are able to reduce friction between two surfaces sliding against each other without the need for a liquid oil medium.

Ultrasonic machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that removes material from the surface of a part through high frequency, low amplitude vibrations of a tool against the material surface in the presence of fine abrasive particles. The tool travels vertically or orthogonal to the surface of the part at amplitudes of 0.05 to 0.125 mm. The fine abrasive grains are mixed with water to form a slurry that is distributed across the part and the tip of the tool. Typical grain sizes of the abrasive material range from 100 to 1000, where smaller grains produce smoother surface finishes.

Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter. The others are solid, liquid, and plasma. A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms, elemental molecules made from one type of atom, or compound molecules made from a variety of atoms. A gas mixture, such as air, contains a variety of pure gases. What distinguishes gases from liquids and solids is the vast separation of the individual gas particles. This separation usually makes a colorless gas invisible to the human observer.
The circulating fluidized bed (CFB) is a type of fluidized bed combustion that utilizes a recirculating loop for even greater efficiency of combustion. while achieving lower emission of pollutants. Reports suggest that up to 95% of pollutants can be absorbed before being emitted into the atmosphere. The technology is limited in scale however, due to its extensive use of limestone, and the fact that it produces waste byproducts.
Vibratory Fluidized Bed (VFB) is a type of fluidized bed where the mechanical vibration enhances the performance of fluidization process. Since the first discovery of vibratory fluidized bed, its vibration properties proves to be more efficient in dealing with fine particles which appears to be very difficult to achieve with normal fluidized bed. Even though numerous publications and its popularity in industrial applications, the knowledge about vibratory dynamics and properties are very limited. Future research and development are needed to further improve this technology to bring it to another level.
This glossary of engineering terms is a list of definitions about the major concepts of engineering. Please see the bottom of the page for glossaries of specific fields of engineering.












