
Defensins are small cysteine-rich cationic proteins across cellular life, including vertebrate and invertebrate animals, plants, and fungi. They are host defense peptides, with members displaying either direct antimicrobial activity, immune signalling activities, or both. They are variously active against bacteria, fungi and many enveloped and nonenveloped viruses. They are typically 18-45 amino acids in length, with three or four highly conserved disulphide bonds.
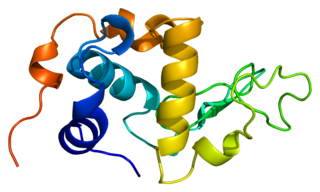
Lactalbumin, alpha-, also known as LALBA, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LALBA gene.

SMAD family member 6, also known as SMAD6, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD6 gene.

Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 7 or SMAD7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD7 gene.

The activin A receptor also known as ACVR1C or ALK-7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACVR1C gene. ACVR1C is a type I receptor for the TGFB family of signaling molecules.

Apoptosis regulator BAX, also known as bcl-2-like protein 4, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BAX gene. BAX is a member of the Bcl-2 gene family. BCL2 family members form hetero- or homodimers and act as anti- or pro-apoptotic regulators that are involved in a wide variety of cellular activities. This protein forms a heterodimer with BCL2, and functions as an apoptotic activator. This protein is reported to interact with, and increase the opening of, the mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC), which leads to the loss in membrane potential and the release of cytochrome c. The expression of this gene is regulated by the tumor suppressor P53 and has been shown to be involved in P53-mediated apoptosis.

Caspase-3 is a caspase protein that interacts with caspase-8 and caspase-9. It is encoded by the CASP3 gene. CASP3 orthologs have been identified in numerous mammals for which complete genome data are available. Unique orthologs are also present in birds, lizards, lissamphibians, and teleosts.

Lymphotoxin beta receptor (LTBR), also known as tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 3 (TNFRSF3), is a cell surface receptor for lymphotoxin involved in apoptosis and cytokine release. It is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily.

Caspase-6 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CASP6 gene. CASP6 orthologs have been identified in numerous mammals for which complete genome data are available. Unique orthologs are also present in birds, lizards, lissamphibians, and teleosts. Caspase-6 has known functions in apoptosis, early immune response and neurodegeneration in Huntington's and Alzheimer's disease.

Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BIRC2 gene.

Caspase-10 is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the CASP10 gene.

Interferon beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFNB1 gene. The natural and recombinant protein forms have antiviral, antibacterial, and anticancer properties.

Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 14 also known as NF-kappa-B-inducing kinase (NIK) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAP3K14 gene.

Decoy receptor 2 (DCR2), also known as TRAIL receptor 4 (TRAILR4) and tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 10D (TNFRSF10D), is a human cell surface receptor of the TNF-receptor superfamily.

Protein AATF is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AATF gene.

Krueppel-like factor 10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KLF10 gene.

Death-inducer obliterator 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DIDO1 gene.
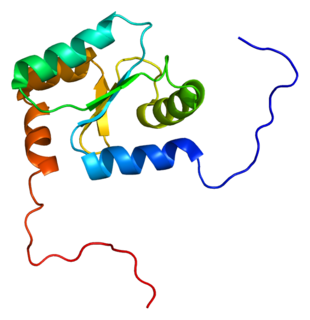
Glutaredoxin 2 (GLRX2) is an enzyme that in humans encoded by the GLRX2 gene. GLRX2, also known as GRX2, is a glutaredoxin family protein and a thiol-disulfide oxidoreductase that maintains cellular thiol homeostasis. This gene consists of four exons and three introns, spanned 10 kilobase pairs, and localized to chromosome 1q31.2–31.3.

BCL2-like 13 , also known as BCL2L13 or Bcl-rambo, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the BCL2L13 gene on chromosome 22. This gene encodes a mitochondrially-localized protein which is classified under the Bcl-2 protein family. Overexpression of the encoded protein results in apoptosis. As a result, it has been implicated in cancers such as childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been observed for this gene, such as Bcl-rambo beta.

Forkhead box protein O1 (FOXO1) also known as forkhead in rhabdomyosarcoma (FKHR) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FOXO1 gene. FOXO1 is a transcription factor that plays important roles in regulation of gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis by insulin signaling, and is also central to the decision for a preadipocyte to commit to adipogenesis. It is primarily regulated through phosphorylation on multiple residues; its transcriptional activity is dependent on its phosphorylation state.

















