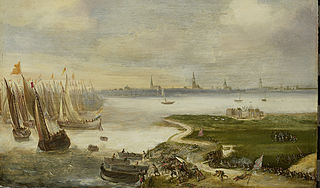Het Steen is a medieval fortress in the old city centre of Antwerp, Belgium, one of Europe's biggest ports. The surviving structure was built between 1200 and 1225 as a gateway to a larger castle of the Dukes of Brabant which was demolished in the 19th century. As the first stone fortification of Antwerp, Het Steen is Antwerp's oldest building and used to be part of its oldest urban centre. The words "Het Steen", translated from Dutch mean "the rock" in English, although that is not the equivalent etymological meaning.

Menno, Baron van Coehoorn was a Dutch States Army officer and engineer, regarded as one of the most significant figures in Dutch military history. In an era when siege warfare dominated military campaigns, he and his French counterpart Vauban were the acknowledged experts in designing, taking and defending fortifications.
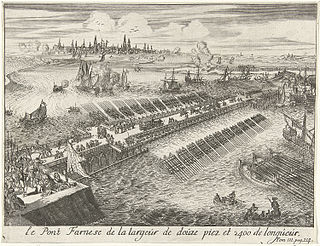
The fall of Antwerp on 17 August 1585 took place during the Eighty Years' War, after a siege lasting over a year from July 1584 until August 1585. The city of Antwerp was the focal point of the Protestant-dominated Dutch Revolt, but was forced to surrender to the Spanish forces under the command of Alessandro Farnese. Under the terms agreed, all the Protestants of Antwerp were given four years to settle their affairs and leave the city. Many migrated north, especially to Amsterdam. Apart from losing a high proportion of its middle class and mercantile population, Antwerp's trade suffered for two centuries afterwards as Dutch forts blockaded the River Scheldt until 1795.

The 1695 siege of Namur or second siege of Namur took place during the Nine Years' War between 2 July and 4 September 1695. Its capture by the French in the 1692 siege and recapture by the Grand Alliance in 1695 are often viewed as the defining events of the war; the second siege is considered to be William III's most significant military success during the war.

The siege of Antwerp took place after fighting in the Belgian Revolution ended. On 15 November 1832, the French Armée du Nord under Marshal Gérard began to lay siege to the Dutch troops there under David Chassé. The siege ended on 23 December 1832. The French had agreed with the Belgian rebels that the latter would not participate in the battle.

Bornem Castle, also known as the Marnix de Sainte-Aldegonde Castle, is a country house, formerly a castle, located in Bornem, province of Antwerp, Belgium. Bornem Castle is situated at an elevation of 1 meters.

Antwerp is a city and a municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of Antwerp Province, and the third largest city in Belgium by area at 208.22 km2 (80.39 sq mi) after Tournai and Couvin. With a population of 565,039, it is the most populous municipality in Belgium, and with a metropolitan population of over 1.2 million people, the country's second-largest metropolitan area after Brussels.
Verdussen was a dynasty of printers in Antwerp, starting with Hieronymus Verdussen I in the late sixteenth century, and ending around 1800. Many other printers in Antwerp were also related to the Verdussens through marriage. They specialized in religious works and works in Spanish, but also published newspapers, almanachs, poetry, scientific works, .... By the end of the 17th century, they produced about 21% of the Spanish books printed in the Netherlands, and with 5 presses was second only to Moretus in Antwerp. In 1876, the Verdussenstraat was named after the family in Antwerp.
The following is a timeline of the history of the municipality of Antwerp, Belgium.

The Sterckshof castle is in Deurne, Antwerp, Belgium. From 1994 to 2014 it housed the Sterckshof silver museum of the Province of Antwerp. Built on the site of a much older castle, or great house, the present building is a reconstruction erected in the 1920s.

Couwelaar Castle, also known as De Drie Torekens, is a castle in the Deurne district of Antwerp. The castle is L-shaped and consists of a main building with wings, as well as several outbuildings including a coach house. The main building is characterized by two round towers at the front and a built-in, square tower at the rear. Over the centuries, the castle has been extensively altered and restored several times and has stylistic elements of the Neo-Renaissance and Rococo, among others. Couwelaar Castle is a historical monument.

The Monster Mortar was one of the largest mortars ever developed. Also called Leopold or the Liège mortar, the 24 inches (610 mm) caliber mortar was conceived by the French artillery officer Henri-Joseph Paixhans. The mortar was manufactured under the direction of the Belgian Minister of War Baron Louis Evain and cast at the Royal Canon Foundry in Liège, Belgium in 1832. It saw action at the Battle of Antwerp in December 1832.

Pieter Scheemaeckers, Pieter Scheemackers, Pieter Scheemaeckers I or Pieter Scheemaeckers the Elder was a Flemish sculptor who played an important role in the development of Baroque church sculpture in the late 17th-century Habsburg Netherlands. He was also known for his marble funerary monuments and small scale ivory works. He was the father of Peter Scheemakers who became a leading sculptor of portraits and church monuments in 18th century London.

Antwerp was developed as a fortified city, but very little remains of the 10th century enceinte. Only some remains of the first city wall can be seen near the Vleeshuis museum at the corner of Bloedberg and Burchtgracht, and a replica of a burg (castle) named Steen has been partly rebuilt near the Scheldt-quais during the 19th century. Parts of the canals that protected the city between the 12th and 16th century have been covered and used as a sewage system. Both the 16th century city walls and the 19th century fortifications have been covered up by major infrastructure works during the 19th and 20th century.

Don Francisco Marcos de Velasco y Alvear, Marquess of Pico de Velasco, was a Spanish military governor and commander of Antwerp Citadel.
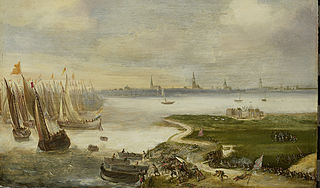
Don Íñigo de Borja y Velasco (1575–1622) was a Spanish nobleman and military commander who served as governor of Antwerp Citadel.

Barbara Ogier was a Flemish playwright of De Olijftak, a chamber of rhetoric in Antwerp. Her motto was "Deugd voeght yder".

The Groningen class was a class of steam corvettes of the Royal Netherlands Navy. The class comprised Groningen, Citadel van Antwerpen and Vice-Admiraal Koopman

Norbertus van den Eynde (I), Norbrecht van den Eynde and Norbert van den Eynde (also spelled: Norbertus van den Eynden, Norbert van den Eynden, and Norbertus van den Eynden) (Antwerp, baptized 11 December 1628 – Antwerp, 7 October 1704) was a Flemish sculptor. He is mainly known for his religious sculptures and church furniture. He was the son of the prominent sculptor Huibrecht van den Eynde and a member of the van den Eynde family of sculptors. Van den Eynde was a close associate of Artus Quellinus II. He undertook several commission in the Antwerp Cathedral, including several altarpieces.