Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world and seventh most densely populated with a population of 173,562,364 in an area of 148,460 square kilometres (57,320 sq mi). Bangladesh shares land borders with India to the north, west, and east, and Myanmar to the southeast. To the south, it has a coastline along the Bay of Bengal. To the north, it is separated from Bhutan and Nepal by the Siliguri Corridor, and from China by the mountainous Indian state of Sikkim. Dhaka, the capital and largest city, is the nation's political, financial, and cultural centre. Chittagong is the second-largest city and the busiest port. The official language is Bengali, with Bangladeshi English also used in government.

Bengal is a historical geographical, ethnolinguistic and cultural term referring to a region in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. The region of Bengal proper is divided between the modern-day sovereign nation of Bangladesh and the Indian states of West Bengal, and some parts of Assam.

Dhaka, formerly known as Dacca, is the capital and largest city of Bangladesh. It is the ninth-largest and seventh-most densely populated city in the world with a density of 23,234 people per square kilometer within a total area of approximately 300 square kilometers. Dhaka is a megacity, and has a population of 10.2 million residents as of 2024, and a population of over 23.9 million residents in Dhaka Metropolitan Area. It is widely considered to be the most densely populated built-up urban area in the world. Dhaka is the most important cultural, economic, and scientific hub of Eastern South Asia, as well as a major Muslim-majority city. Dhaka ranks third in South Asia and 39th in the world in terms of GDP. Lying on the Ganges Delta, it is bounded by the Buriganga, Turag, Dhaleshwari and Shitalakshya rivers. Dhaka is also the largest Bengali-speaking city in the world.

The economy of Bangladesh is a major developing mixed economy. As the second-largest economy in South Asia, Bangladesh's economy is the 35th largest in the world in nominal terms, and 25th largest by purchasing power parity. Bangladesh is seen by various financial institutions as one of the Next Eleven. It has been transitioning from being a frontier market into an emerging market. Bangladesh is a member of the South Asian Free Trade Area and the World Trade Organization. In fiscal year 2021–2022, Bangladesh registered a GDP growth rate of 7.2% after the global pandemic. Bangladesh is one of the fastest growing economies in the world.

International Society for Krishna Consciousness (ISKCON), commonly referred to as the Hare Krishna movement, is a Gaudiya Vaishnava Hindu religious organization. It was founded by A. C. Bhaktivedanta Swami Prabhupada on 13 July 1966 in New York City. ISKCON's main headquarters is in Mayapur, West Bengal, India and it claims approximately 1 million members globally.

Divisions are the first-level administrative divisions in Bangladesh. As of 2024, there are eight divisions of Bangladesh, each named after the major city within its jurisdiction that also serves as the administrative seat of that division. Each division is divided into several districts which are further subdivided into upazilas(sub-districts), then union councils.

Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, popularly known by the honorific Bangabandhu, was a Bangladeshi politician, revolutionary, statesman, activist and diarist, who was the founding leader of Bangladesh. As the leader of Bangladesh, he had held continuous positions either as Bangladesh's president or as its prime minister from April 1971 until his assassination in August 1975. His nationalist ideology, socio-political theories, and political doctrines are collectively known as Mujibism.

Chittagong, officially Chattogram, is the second-largest city in Bangladesh. Home to the Port of Chittagong, it is the busiest port in Bangladesh and the Bay of Bengal. The city is also known as business capital of Bangladesh. It is the administrative seat of an eponymous division and district. The city is located on the banks of the Karnaphuli River between the Chittagong Hill Tracts and the Bay of Bengal. The Greater Chittagong Area had a population of more than 8.2 million in 2022. In 2020, the city area had a population of more than 5.2 million. The city is home to many large local businesses and plays an important role in the Bangladeshi economy.

The Bangladesh Awami League, simply known as Awami League, is one of the major political parties in Bangladesh. The oldest existing political party in the country, the party played the leading role in achieving the independence of Bangladesh. It is also one of the two most dominant parties in the country, along with its archrival Bangladesh Nationalist Party.

The prime minister of Bangladesh, officially prime minister of the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is the chief executive of the government of Bangladesh. The prime minister and the cabinet are collectively accountable for their policies and actions to the Parliament, to their political party and ultimately to the electorate. The prime minister is ceremonially appointed by the president of Bangladesh.

Muhammad Yunus is a Bangladeshi economist, entrepreneur, politician, and civil society leader, who has been serving as Chief Adviser of the interim government of Bangladesh since 8 August 2024. Yunus was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 2006 for founding the Grameen Bank and pioneering the concepts of microcredit and microfinance. Yunus has received several other national and international honors, including the United States Presidential Medal of Freedom in 2009 and the Congressional Gold Medal in 2010.

Sheikh Hasina is a Bangladeshi politician who served as the tenth prime minister of Bangladesh from June 1996 to July 2001 and again from January 2009 to August 2024. She is the daughter of Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, the first president of Bangladesh. She served in the position of prime minister for over 20 years, making her the longest-serving prime minister in history of Bangladesh. Thus, she became the world's longest-serving female head of government. Her authoritarian regime ended in self-imposed exile following an uprising in 2024.

The Bangladesh Liberation War, also known as the Bangladesh War of Independence and known as the Liberation War in Bangladesh, was an armed conflict sparked by the rise of the Bengali nationalist and self-determination movement in East Pakistan, which resulted in the independence of Bangladesh. The war began when the Pakistani military junta based in West Pakistan—under the orders of Yahya Khan—launched Operation Searchlight against East Pakistanis on the night of 25 March 1971, initiating the Bangladesh genocide.

The Bangladesh men's national cricket team, popularly known as The Tigers, is administered by the Bangladesh Cricket Board (BCB). It is a Full Member of the International Cricket Council (ICC) with Test, One-Day International (ODI) and Twenty20 International (T20I) status.

The Bangladesh national football team is the national recognised football team of Bangladesh and is controlled by the Bangladesh Football Federation (BFF). It is a member of the Asian Football Confederation (AFC) since 1973 and of FIFA since 1976, even though the Bangladesh Football Federation was first founded in 1972. Bangladesh was elected as a member of the AFC Executive Committee in 1982–1986 and 1998–2002. The current Executive Committee was elected democratically, under an AFC approved constitution and direct supervision of FIFA & AFC, in October 2020.

Bengalis, also rendered as endonym Bangalee, are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the Bengal region of South Asia. The population is divided between the sovereign country Bangladesh and the Indian regions of West Bengal, Tripura, Barak Valley, Goalpara, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, and parts of Meghalaya, Manipur and Jharkhand. Most speak Bengali, a language from the Indo-Aryan language family. Sub-section 2 of Article 6 of the Constitution of Bangladesh states, "The people of Bangladesh shall be known as Bengalis as a nation and as Bangladeshis as citizens."
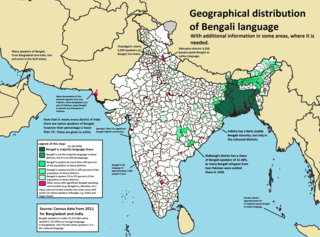
Bengali, also known by its endonym Bangla, is a classical Indo-Aryan language from the Indo-European language family native to the Bengal region of South Asia. With over 237 million native speakers and another 41 million as second language speakers as of 2024, Bengali is the fifth most spoken native language and the seventh most spoken language by the total number of speakers in the world. It is the fifth most spoken Indo-European language.

Climate change is a critical issue in Bangladesh. as the country is one of the most vulnerable to the effects of climate change. In the 2020 edition of Germanwatch's Climate Risk Index, it ranked seventh in the list of countries most affected by climate calamities during the period 1999–2018. Bangladesh's vulnerability to the effects of climate change is due to a combination of geographical factors, such as its flat, low-lying, and delta-exposed topography. and socio-economic factors, including its high population density, levels of poverty, and dependence on agriculture. The impacts and potential threats include sea level rise, temperature rise, food crisis, droughts, floods, and cyclones.

The divisions of Bangladesh are further divided into districts or zilas. The headquarters of a district is called the district seat. There are 64 districts in Bangladesh. The districts are further subdivided into 495 subdistricts or upazilas.