
Odisha, formerly Orissa, is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th-largest state by area, and the 11th-largest by population, with over 41 million inhabitants. The state also has the third-largest population of Scheduled Tribes in India. It neighbours the states of Jharkhand and West Bengal to the north, Chhattisgarh to the west, and Andhra Pradesh to the south. Odisha has a coastline of 485 kilometres (301 mi) along the Bay of Bengal in Indian Ocean. The region is also known as Utkala and is mentioned by this name in India's national anthem, "Jana Gana Mana". The language of Odisha is Odia, which is one of the Classical Languages of India.

Languages spoken in the Republic of India belong to several language families, the major ones being the Indo-Aryan languages spoken by 78.05% of Indians and the Dravidian languages spoken by 19.64% of Indians; both families together are sometimes known as Indic languages. Languages spoken by the remaining 2.31% of the population belong to the Austroasiatic, Sino–Tibetan, Tai–Kadai, and a few other minor language families and isolates. According to the People's Linguistic Survey of India, India has the second highest number of languages (780), after Papua New Guinea (840). Ethnologue lists a lower number of 456.

Odia is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in the Indian state of Odisha. It is the official language in Odisha, where native speakers make up 82% of the population, and it is also spoken in parts of West Bengal, Jharkhand, Andhra Pradesh and Chhattisgarh. Odia is one of the many official languages of India; it is the official language of Odisha and the second official language of Jharkhand. The language is also spoken by 700,000 people in Chhattisgarh.

Rasgulla is a syrupy dessert popular in the eastern part of South Asia. It is made from ball-shaped dumplings of chhena dough, cooked in light sugar syrup made of sugar. This is done until the syrup permeates the dumplings.
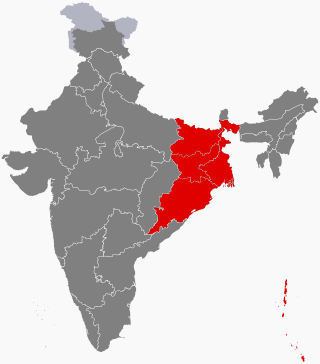
East India is a region of India consisting of the Indian states of Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal and also the union territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The region roughly corresponds to the historical region of Magadha from which it inherits its various Eastern Indo-Aryan languages.
Das is a common last name in South Asia, among adherents of Hinduism and Sikhism, as well as those who converted to Islam or Christianity. It is a derived from the Sanskrit word Dasa meaning servant, devotee, or votary. "Das" may be inferred to be one who has surrendered to God. The surname is often used by those in the Vaishnav community.
The Odia (ଓଡ଼ିଆ), formerly spelled Oriya, are an Indo-Aryan ethnic group native to the Indian state of Odisha who speak the Odia language. They constitute a majority in the eastern coastal state, with significant minority populations existing in the neighboring states of Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand and West Bengal.

Ras malai, also known as rosomalai, or roshmalai, is a dessert from the Indian subcontinent. The dessert is called roshmalai/rosmalai in Bengali, ras malai in Hindi, and rasa malei in Odia. It is popular in India, Bangladesh and Pakistan.
The Tanti bania are a Hindu vaishya cloth merchant community in India. The greatest concentration is believed to be in the states of Gujarat, Maharashtra, Jharkhand, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, Assam and Odisha. The community is not very concentrated because their designation was defined based on their occupation rather than particular beliefs or group identity.

The history of Odisha begins in the Lower Paleolithic era, as Acheulian tools dating to the period have been discovered in various places in the region. The early history of Odisha can be traced back to writings found in ancient texts like the Mahabharata, Maha Govinda Sutta and some Puranas. The region was also known to other kingdoms in region of East Indies due to maritime trade relations.

Manoj Das was an Indian author who wrote in Odia and English. In 2000, Manoj Das was awarded the Saraswati Samman. He was awarded Padma Shri in 2001, the fourth-highest Civilian Award in India, and Padma Bhusan in 2020, the third-highest Civilian Award in India for his contribution to the field of Literature & Education.

Konark Sun Temple is a 13th-century CE Sun temple at Konark about 35 kilometres (22 mi) northeast from Puri city on the coastline in Puri district, Odisha, India. The temple is attributed to king Narasimhadeva I of the Eastern Ganga dynasty about 1250 CE.

Radhanath Ray was an Odia writer of initial modernity era in Odia poetry during the later part of nineteenth century. He was born in a Zamindar family in Baleshwar, now in Odisha, and is honoured in Odia literature with the title Kabibara . In his early life, he composed in both Odia and Bengali languages, but later he shifted his writings in Odia only. He was born on 28 September 1848, at Kedarpur village in Baleswar district, Odisha. He has contributed verses and poetry for Odia literature in the nineteenth century.

Ghugni or ghuguni or guguni is a curry made of peas or chickpeas. Different variations of the dish use different types of peas or chickpeas, such as black gram, green peas, or white peas. It is a snack native to the Indian subcontinent, especially popular in Eastern India, Northeast India and in Bangladesh.

Sitakant Mahapatra is an Indian poet and literary critic in Odia as well as English. He served in the Indian Administrative Service (IAS) from 1961 until he retired in 1995, and has held ex officio posts such as the Chairman of National Book Trust, New Delhi since then.

The Eastern Indo-Aryan languages, also known as Māgadhan languages, are spoken throughout the eastern region of the subcontinent, which includes Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Jharkhand, Bengal region, Tripura, Assam, and Odisha; alongside other regions surrounding the northeastern Himalayan corridor. Bengali is official language of Bangladesh and the state of West Bengal, Tripura and the Barak valley of Assam while Assamese and Odia are the official languages of Assam and Odisha, respectively. The Eastern Indo-Aryan languages descend from Abahattha, which descends from Magadhan Apabhraṃśa and ultimately from Magadhi Prakrit.

Pana Sankranti,, also known as Maha Bishuba Sankranti, is the traditional new year day festival of Odia people in Odisha, India. The festival occurs in the solar Odia calendar on the first day of the traditional solar month of Meṣa, hence equivalent lunar month Baisakha. This falls on the Purnimanta system of the Indian Hindu calendar. It therefore falls on 13/14 April every year on the Gregorian calendar.

Swami Nigamananda Paramahansa was an Indian yogi, guru and mystic well known in Eastern India. He is associated with the Shakta tradition and viewed as a perfect spiritual master of vedanta, tantra, yoga and prema or bhakti. His followers idealized him as their worshipped and beloved thakura.
Kansabanik or Kansari is a Hindu caste found from West Bengal, Odisha and Assam state of India. They are traditionally braziers and coppersmiths by profession. Kansabanik represents one of the fourteen castes belonging to 'Nabasakh' group in Bengal. Kanshabaniks are recognized as Other Backward Class by the Government of West Bengal.

The Gaudi script, also known as the Proto-Bengali script or the Proto-Oriya script is an abugida in the Brahmic family of scripts. Gaudi script gradually developed into the Bengali-Assamese, Odia, and Tirhuta script.














