Notes
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Smith, William (1870). "Apollodorus". In Smith, William (ed.). Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology . Vol. 1. p. 233.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Smith, William (1870). "Apollodorus". In Smith, William (ed.). Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology . Vol. 1. p. 233.
Apollodorus from Boeotia was a man of 2nd-century BCE ancient Greece who, together with Epaenetus, went as ambassador from Boeotia to Messenia in 183 BCE, just at the time when the Messenians, terrified by Lycortas, the general of the Achaeans, were inclined to negotiate for peace. The influence of the Boeotian ambassadors decided the question, and the Messenians concluded peace with the Achaeans. [1]
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Smith, William (1870). "Apollodorus". In Smith, William (ed.). Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology . Vol. 1. p. 233.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Smith, William (1870). "Apollodorus". In Smith, William (ed.). Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology . Vol. 1. p. 233.

The Heracleidae or Heraclids were the numerous descendants of Heracles (Hercules), especially applied in a narrower sense to the descendants of Hyllus, the eldest of his four sons by Deianira. Other Heracleidae included Macaria, Lamos, Manto, Bianor, Tlepolemus, and Telephus. These Heraclids were a group of Dorian kings who conquered the Peloponnesian kingdoms of Mycenae, Sparta and Argos; according to the literary tradition in Greek mythology, they claimed a right to rule through their ancestor. Since Karl Otfried Müller's Die Dorier, I. ch. 3, their rise to dominance has been associated with a "Dorian invasion". Though details of genealogy differ from one ancient author to another, the cultural significance of the mythic theme, that the descendants of Heracles, exiled after his death, returned some generations later to reclaim land that their ancestors had held in Mycenaean Greece, was to assert the primal legitimacy of a traditional ruling clan that traced its origin, thus its legitimacy, to Heracles

There are several characters named Amphion in Greek mythology:
In Greek mythology, Hyllus or Hyllas (Ὕλᾱς) was son of Heracles and Deianira, husband of Iole, nursed by Abia.
Aphareus may refer to the following figures.

Aetolia is a mountainous region of Greece on the north coast of the Gulf of Corinth, forming the eastern part of the modern regional unit of Aetolia-Acarnania.

The Catalogue of Ships is an epic catalogue in Book 2 of Homer's Iliad (2.494–759), which lists the contingents of the Achaean army that sailed to Troy. The catalogue gives the names of the leaders of each contingent, lists the settlements in the kingdom represented by the contingent, sometimes with a descriptive epithet that fills out a half-verse or articulates the flow of names and parentage and place, and gives the number of ships required to transport the men to Troy, offering further differentiations of weightiness. A similar, though shorter, Catalogue of the Trojans and their allies follows (2.816–877). A similar catalogue appears in the Pseudo-Apollodoran Bibliotheca.
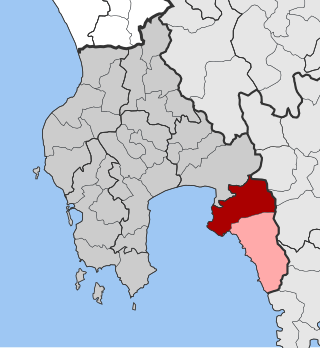
Avia is a village and a former municipality in Messenia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality West Mani, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 179.828 km2. In 2011 its population was 281 for the village, 611 for the community and 2,246 for the municipal unit. The seat of the municipality was in Kampos. Avia is a popular tourist destination. It also has a large olive production. Avia is situated on the east coast of the Messenian Gulf, southeast of Kalamata, southwest of Sparta and northwest of Kardamyli.
Epaenetus is a name that comes from Ancient Greek, meaning 'praised', and may refer to:

The First Messenian War was a war between Messenia and Sparta. It began in 743 BC and ended in 724 BC, according to the dates given by Pausanias.
Thuria or Thouria was a town of ancient Messenia, situated in the eastern part of the southern Messenian plain, upon the river Aris, and at the distance of 80 stadia from Pharae, which was about a mile from the coast. It was generally identified with the Homeric Antheia, though others supposed it to be Aepeia. It must have been a place of considerable importance, since the distant Messenian Gulf was even named after it. It was also one of the chief towns of the Lacedaemonian Perioeci after the subjugation of Messenia; and it was here that the Third Messenian War took its rise in 464 BCE. On the restoration of the Messenians by Epaminondas, Thuria, like the other towns in the country, was dependent upon the newly-founded capital Messene; but after the capture of that city by the Achaeans in 182 BCE, Thuria, Pharae, and Abia joined the Achaean League as independent members. Thuria was annexed to Laconia by Augustus; but it was restored to Messenia by Tiberius.
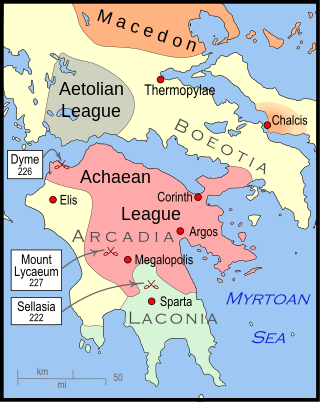
The Social War, also War of the Allies and the Aetolian War, was fought from 220 BC to 217 BC between the Hellenic League under Philip V of Macedon and the Aetolian League, Sparta and Elis. It was ended with the Peace of Naupactus.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to ancient Greece:
In Greek mythology, Peneleos or, less commonly, Peneleus, son of Hippalcimus (Hippalmus) and Asterope, was an Achaean soldier in the Trojan War.
Neon was the name of a number of figures from classical antiquity:
Archedemus or Archedamus was an Aetolian who commanded the Aetolian troops which assisted the Romans in the Second Macedonian War with Philip V of Macedon.
Archon of Aegeira was an Achaean statesman of the 2nd century BCE.
Pharae was an ancient town of Messenia, situated upon a hill rising from the left bank of the river Nedon, and at a distance of a mile (1.5 km) from the Messenian Gulf. Strabo describes it as situated 5 stadia from the sea, and Pausanias 6. William Smith states that it is probable that the earth deposited at the mouth of the river Nedon has, in the course of centuries, encroached upon the sea. Pausanias distinguishes this city from the Achaean city of Pharae (Φαραὶ), 150 stadia from Patrae and 70 stadia from the coast. Pherae occupied the site of Kalamata, the modern capital of Messenia; and in antiquity also it seems to have been the chief town in the southern Messenian plain.
Leuctra or Leuktra, also Leuctrum or Leuktron, was a town of ancient Laconia, situated on the eastern side of the Messenian Gulf, 20 stadia north of Pephnus, and 60 stadia south of Cardamyle. Strabo speaks of Leuctrum as a colony of the Leuctra in Boeotia, near the minor Pamisus, but this river flows into the sea at Pephnus, about three miles south of Leuctrum. Leuctrum was said to have been founded by Pelops, and was claimed by the Messenians as originally one of their towns. It was awarded to the latter people by Philip II of Macedon in 338 BCE, but in the time of the Roman Empire it was one of the Eleuthero-Laconian towns. Pausanias saw in Leuctra a temple and statue of Athena on the acropolis, a temple and statue of Cassandra, a marble statue of Asclepius, another of Ino, and wooden figures of Apollo Carneius.
Corone or Korone was a town of ancient Messenia, situated upon the western side of the Messenian Gulf, which was sometimes called after it, the Coronaean. According to Pausanias, it was built on the site of the Homeric Aepeia, at the time of the restoration of the Messenians to their native country, by Epaminondas; and received the name of Coroneia because Epimelides, who founded the new town, was a native of Coroneia, in Boeotia. This name was changed by the Messenians into that of Corone. According to others, Corone corresponded to the Homeric Pedasus.
Ariston of Megalopolis was a political figure of some sort in Achaea in the 2nd century BCE. At the outbreak of the Third Macedonian War in 171 BCE, pitting the Romans against Perseus of Macedon, Ariston advised the Achaeans to ally themselves with the Romans, and not to remain neutral between the two belligerent parties.