
The Prince Charles Mountains are a major group of mountains in Mac. Robertson Land in Antarctica, including the Athos Range, the Porthos Range, and the Aramis Range. The highest peak is Mount Menzies. Other prominent peaks are Mount Izabelle and Mount Stinear. These mountains together with other scattered peaks form an arc about 260 miles long, extending from the vicinity of Mount Starlight in the north to Goodspeed Nunataks in the south.
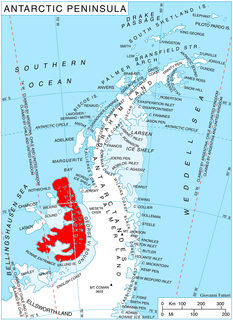
Shaw Nunatak is a nunatak rising to 500 m in Nichols Snowfield, northern Alexander Island, Antarctica. It is situated 5.3 km north-northeast of Rachenitsa Nunatak, 4.23 km east-southeast of Tipits Knoll and 7 km southeast of Mount Kliment Ohridski in Sofia University Mountains, 7.5 km southwest of Lizard Nunatak and 8.1 km northwest of Tegra Nunatak. The feature was photographed from the air by Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition in 1947–48, and mapped from these photographs by D. Searle of Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey, 1960. The nunatak was named by United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1977 after Colin Shaw (1944–78), British Antarctic Survey surveyor who worked in Alexander Island, from 1975 to 1976.

Simon Peak is a mountain rising to about 1,000 m on the west side of the Havre Mountains, situated in the northwest portion of Alexander Island, Antarctica. The peak lies northeast of Umber Island, an island situated in Lazarev Bay off the west coast of Alexander Island. It is situated 9.9 km east-southeast of Buneva Point, 6.4 km northeast of Kamhi Point, 14.65 km west of Mount Pontida and 6.15 km north-northeast of Gazey Nunatak, and surmounts Pipkov Glacier to the north and Oselna Glacier to the southwest. Possibly sighted by FAE, 1908–10, in January 1909; surveyed by British Antarctic Survey in 1975-76. Named after Alec Edward Simon, British Antarctic Survey aircraft mechanic, who worked on nearby Adelaide Island during the summers of years 1972 to 1976.
Adams Nunatak is a nunatak on the south side of Neptune Glacier, 6 miles (10 km) west of Cannonball Cliffs, and lies about 7.4 miles (12 km) inland from George VI Sound in eastern Alexander Island, Antarctica. Mapped by Directorate of Overseas Surveys from satellite imagery supplied by NASA in cooperation with U.S. Geological Survey. Named by United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in association with Neptune Glacier after John Couch Adams, the Cambridge mathematician who deduced the existence of the planet Neptune.

Bartók Glacier is a glacier, 7 nautical miles (13 km) long and 3 nautical miles (6 km) wide, flowing southwest from the southern end of the Elgar Uplands in the northern part of Alexander Island. It was first photographed from the air and roughly mapped by the British Graham Land Expedition in 1937, and more accurately mapped from air photos taken by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition, 1947–48, by D. Searle of the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey in 1960. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee after the Hungarian composer Béla Bartók.
The Juno Peaks are two steep-sided nunataks with a small rock to the west, forming part of an east-west ridge 6 nautical miles (11 km) southwest of Mimas Peak, lying near the head of Saturn Glacier in southern Alexander Island, Antarctica. They were mapped from trimetrogon air photography taken by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition, 1947–48, and from survey by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey, 1948–50. The nunataks were named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee after Juno, one of the asteroids lying between the orbits of the planets Mars and Jupiter.
Delius Glacier is a glacier, 6 nautical miles (11 km) long and 2 nautical miles (4 km) wide, flowing west from the Elgar Uplands into Nichols Snowfield, in the northern part of Alexander Island, Antarctica. It was first seen from the air and roughly mapped by the British Graham Land Expedition in 1937. It was more accurately mapped from air photos taken by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition, 1947–48, by D. Searle of the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey in 1960, and from U.S. Landsat imagery of February 1975. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee after Frederick Delius, the British composer.

Jordan Nunatak is a nunatak standing between the heads of Rochray Glacier and Cox Glacier in the southwest part of Thurston Island, Antarctica. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from ground surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1960–66, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Joe Jordan of the U.S. Army Aviation Detachment, a helicopter mechanic on the Ellsworth Land Survey in the 1968–69 season.

Turnpike Bluff is a conspicuous rock formation in Antarctica. First mapped in 1957 by the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition, and so named because it marks entry to a crevassed area of Recovery Glacier through which the Expedition's vehicles had difficulty in passing on their journey from Shackleton Base to the South Pole in 1957, it lies five nautical miles (9 km) southwest of Mount Homard, at the southwest extremity of the Shackleton Range.
Eureka Glacier is a broad, gently sloping glacier, 18 nautical miles (33 km) long and 17 nautical miles (31 km) wide at its mouth, which flows westward from the west side of Palmer Land into George VI Sound. It is bounded on its north side by the nunataks south of Mount Edgell, on its south side by the Traverse Mountains and Terminus Nunatak, and at its head Prospect Glacier provides a route to the Wordie Ice Shelf. It was first surveyed in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under John Rymill and resurveyed in 1948 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey. The name, from the ancient Greek word eureka, expresses the triumph of discovery and arose because the BGLE sledge party found their way to George VI Sound via this glacier in 1936.

Lizard Nunatak is a nunatak rising to about 800 metres (2,600 ft) situated within the Nichols Snowfield, in the northern portion of Alexander Island, Antarctica. It is situated 12 km east by north of Mount Kliment Ohridski and 9 km south-southeast of the summit of Landers Peaks in Sofia University Mountains, and 6.4 km southwest of Serpent Nunatak and 9.38 km north by west of Tegra Nunatak in Rouen Mountains. The feature was so named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1977 from its shape and in association with Serpent Nunatak lying to the northeast.
Hesperus Nunatak is a sharp-pointed nunatak lying 2 nautical miles (4 km) southwest of Titania Peak and about 18 nautical miles (33 km) west of Venus Glacier in the southeastern portion of Alexander Island, Antarctica. It was mapped by the Directorate of Overseas Surveys from satellite imagery supplied by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration in cooperation with the U.S. Geological Survey, and was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee from association with Venus Glacier, Hesperus being a variant name for the "evening star," Venus.

Lyubimets Nunatak is the partly ice-covered rocky ridge extending 3.9 km in north-northeast to south-southwest direction and 1.8 km wide, rising to 1100 m in Bartók Glacier on the west side of Elgar Uplands in northern Alexander Island, Antarctica. The feature is named after the town of Lyubimets in Southern Bulgaria.

Kandidiana Ridge is the partly ice-free ridge extending 6 km and 1.1 km wide, rising to 1000 m on the west side of Elgar Uplands in northern Alexander Island, Antarctica. It is crescent-shaped facing north-northwest, and surmounts Nichols Snowfield to the northwest, Delius Glacier to the northeast and Bartók Glacier to the south. The vicinity was visited on 30 January 1988 by the geological survey team of Christo Pimpirev and Borislav Kamenov, and Philip Nell and Peter Marquis.

Zavoy Nunatak is the mostly ice-free rocky ridge extending 2.8 km in north-northwest to south-southeast direction and 1.4 km wide, rising to 950 m on the west side of Elgar Uplands in northern Alexander Island, Antarctica. It surmounts Nichols Snowfield to the northwest, Gilbert Glacier to the southwest, and the head of Bartók Glacier to the southeast. The vicinity was visited on 30 January 1988 by the geological survey team of Christo Pimpirev and Borislav Kamenov, and Philip Nell and Peter Marquis.

Nebush Nunatak is the mostly ice-free rocky ridge extending 1.54 km in north-south direction and 1.1 km wide, rising to 900 m on the west side of Elgar Uplands in northern Alexander Island, Antarctica. It surmounts Nichols Snowfield to the west and its tributary Delius Glacier to the east. The vicinity was visited on 30 January 1988 by the geological survey team of Christo Pimpirev and Borislav Kamenov, and Philip Nell and Peter Marquis.

Tegra Nunatak is the mostly ice-free rocky ridge extending 2.6 km in east-west direction and 700 m wide, rising to 1200 m at the west extremity of Elgar Uplands in northern Alexander Island, Antarctica. It surmounts Delius Glacier to the southeast and Nichols Snowfield to the north and west. The nunatak was visited on 30 January 1988 by the geological survey team of Christo Pimpirev and Borislav Kamenov, and Philip Nell and Peter Marquis.

Atanasov Ridge is the partly ice-covered rocky ridge extending 3.8 km in south-southeast to north-northwest direction and 2.1 km wide, rising to 800 m on the southwest side of Elgar Uplands, northern Alexander Island in Antarctica. It surmounts Gilbert Glacier to the southwest.

Kozhuh Peak is the ice-covered peak rising to 1250 m on the west side of Elgar Uplands, northern Alexander Island in Antarctica. It surmounts Delius Glacier to the north and Bartók Glacier to the south-southwest.








