
Forficula auricularia, the common earwig or European earwig, is an omnivorous insect in the family Forficulidae. The European earwig survives in a variety of environments and is a common household insect in North America. The name earwig comes from the appearance of the hindwings, which are unique and distinctive among insects, and resemble a human ear when unfolded; the species name of the common earwig, auricularia, is a specific reference to this feature. However, they are considered a pest because of the damage they do to crops, their frightening appearance, their ability to fly, foul odor, and tendency to invade crevices in homes and consume pantry foodstuffs.

The Saint Helena earwig or Saint Helena giant earwig was a large species of earwig endemic to the oceanic island of Saint Helena in the south Atlantic Ocean. It is now considered extinct.
Labium is the Latin word for lip. In English, it may refer to:

Forficulidae is a family of earwigs in the suborder Forficulina.

Iverson Minter, known as Louisiana Red, was an African-American blues guitarist, harmonica player, and singer, who recorded more than 50 albums. He was best known for his song "Sweet Blood Call".

Labidura riparia is a species of earwig in the family Labiduridae characterized by their modified cerci as forceps, and light tan color. They are more commonly known as the striped earwig, due to two dark longitudinal stripes down the length of the pronotum. They are sometimes wrongly referred to as Labidura japonica, although said species is actually a subspecies, Labidura riparia japonica, found only in Japan. L. riparia are a cosmopolitan species primarily in tropical to subtropical regions. Body size varies greatly, ranging from 16 mm to 30 mm, with 10 abdominal segments. Males and females differ in forcep size, with males having much larger and stronger curve, while females have smaller, straighter forceps with a slight curve at the end. Earwigs use these forceps to assist in predation, defense, sexual selection, courting and mating, and wing folding.

Forficulina is the largest of the four suborders of earwigs, in the order Dermaptera. The other three are Archidermaptera, which is extinct, Arixeniina, and Hemimerina. They make up the largest and most familiar group. The cerci are unsegmented, and modified into large, forcep-like structures. Females have unhooked cerci, while males have hooked cerci.
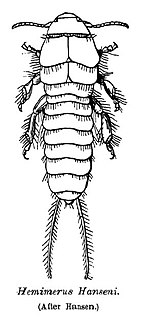
Hemimeridae is a family of earwigs, the only family in the suborder Hemimerina, one of the four suborders in the order Dermaptera. The other three suborders are Archidermaptera, which is extinct, Arixeniina, and Forficulina, the largest of the four. Hemimeridae is represented by two genera, Hemimerus and Araeomerus. They are wingless, blind and viviparous ectoparasites of African rodents, and have filiform segmented cerci. The best known species is Hemimerus bouvieri. Hemimeridae contains eleven described species placed within two genera: Hemimerus and Araeomerus. Hemimerids are relatively small (5–15 mm) and inhabit the fur of giant murid rats in Africa. Hemimerids have short, broad legs with grooves that allow them to cling to the host and specialized mouthparts for scraping dead skin and fungus from their host. Araeomerus is found in the nest of long-tailed pouch rats (Beamys) and Hemimerus is found on giant (Cricetomys) rats. Araeomerus are found more often in the burrows and nests of Beamys rat than on the rat itself, while Hemimerus less frequently leaves its host.

Hemimerus is a genus of earwigs, in the family Hemimeridae. It one of two genera in the family Hemimeridae, and contains ten species:
Araeomerus hubbardi is a species of earwigs, in the genus Araeomerus, family Hemimeridae, the suborder Hemimerina, and the order Dermaptera.

Anisolabididae is a family of earwigs, in the suborder Forficulina and the order Dermaptera. It is one of nine families in the suborder Forficulina, and contains thirty-eight genera spread across thirteen subfamilies.
Apachyidae is a small family of earwigs, in the suborder Forficulina and the order Dermaptera. It is one of nine families in the suborder Forficulina, and contains two genera. It has been cited by Henrik Steinmann in his book, The Animal Kingdom, by Brindle in The Dermaptera of Africa, and by at least two others.
Chelisochidae is a family of earwigs whose members are commonly known as black earwigs. The family contains a total of approximately 96 species, spread across sixteen genera in three subfamilies.

Labiduridae, whose members are known commonly as striped earwigs, is a relatively large family of earwigs in the suborder Forficulina.

The ringlegged earwig is a species of earwig in the family Anisolabididae.
Araeomerus morrisi is a species of earwig, in the genus Araeomerus, family Hemimeridae, suborder Hemimerina.

Tytthodiplatys is an extinct genus of earwig in the family Diplatyidae known from a Cretaceous fossil found in Myanmar. The genus contains a single described species, Tytthodiplatys mecynocercus.
This taxonomy of the Dermaptera follows Engel & Haas (2007) to the rank of Tribe.










