
Earwigs make up the insect order Dermaptera. With about 2,000 species in 12 families, they are one of the smaller insect orders. Earwigs have characteristic cerci, a pair of forcep-like pincers on their abdomen, and membranous wings folded underneath short, rarely used forewings, hence the scientific order name, "skin wings". Some groups are tiny parasites on mammals and lack the typical pincers. Earwigs are found on all continents except Antarctica.

Pouched rats are a group of African rodents in the subfamily Cricetomyinae. They are members of the family Nesomyidae, which contains other African muroids such as climbing mice, Malagasy mice, and the white-tailed rat. All nesomyids are in the superfamily Muroidea, a large and complex clade containing 1⁄4 of all mammal species. Sometimes the pouched rats are placed in the family Muridae along with all other members of the superfamily Muroidea.

Pygidicranidae is a family of earwigs, formerly placed in the suborder Forficulina, now in the suborder Neodermaptera. The family currently contains twelve subfamilies and twenty six genera. Eight of the subfamilies are monotypic, each containing a single genus. Of the subfamilies, both Astreptolabidinae and Burmapygiinae are extinct and known solely from fossils found in Burmese amber. Similarly Archaeosoma, Gallinympha, and Geosoma, which have not been placed into any of the subfamilies, are also known only from fossils. Living members of the family are found in Australia, South Africa, North America, and Asia. The monotypic genus Anataelia, described by Ignacio Bolivar in 1899, is found only on the Canary Islands. As with all members of Neodermaptera, pygidicranids do not have any ocelli. The typical pygidicranid bodyplan includes a small, flattened-looking body, which has a dense covering of bristly hairs (setae). The pair of cerci at the end of the abdomen are symmetrical in structure. The head is broad, with the fourth, fifth and sixth antenna segments (antennomeres) that are not transverse. In general Pygidicranids also have equally sized ventral cervical sclerites, and in having the rearmost sclerite separated from, or only touching the center of the prosternum. Cannibalism of young has been observed in at least one species in the family, Challia hongkongensis, in which an adult female was found eating a still-living nymph of the same species. The same species in a different area has been observed possibly eating fruits or seeds, making the species an omnivore.

Forficulidae is a family of earwigs in the order Dermaptera. There are more than 70 genera and 490 described species in Forficulidae.

Arixeniidae is a family of earwigs in the suborder Neodermaptera. Arixeniidae was formerly considered a suborder, Arixeniina, but was reduced in rank to family and included in the new suborder Neodermaptera.
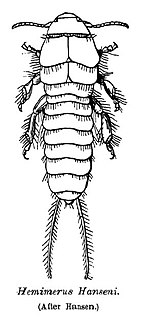
Hemimerus is a genus of earwigs, in the family Hemimeridae. It is one of two genera in the family of Hemimeridae, and contains ten species:
Araeomerus is a genus of earwigs, in the family Hemimeridae, the suborder Hemimerina, and the order Dermaptera. It one of two genera in the family Hemimeridae, and contains two species.

Anisolabididae is a family of earwigs, in the suborder Forficulina and the order Dermaptera. It is one of nine families in the suborder Forficulina, and contains thirty-eight genera spread across thirteen subfamilies.

Diplatyidae is a family of earwigs in the suborder Neodermaptera. It contains only one subfamily, Diplatyinae, which contains six genera, five modern and one extinct known from fossils. The genus Tytthodiplatys was described in 2011 from a fossil found in Burmese amber which dates to the Albian age of the Cretaceous. It was not placed into the subfamily Diplatyinae, and is the oldest confirmed member of the family.

Labiduridae, whose members are known commonly as striped earwigs, is a relatively large family of earwigs in the suborder Forficulina.
Araeomerus morrisi is a species of earwig, in the genus Araeomerus, family Hemimeridae, suborder Hemimerina.

Astreptolabis is an extinct genus of earwig in the Dermaptera family Pygidicranidae known from a group of Cretaceous fossils found in Myanmar. The genus contains two described species, Astreptolabis ethirosomatia and Astreptolabis laevis and is the sole member of the subfamily Astreptolabidinae.

Tytthodiplatys is an extinct genus of earwig in the family Diplatyidae known from a Cretaceous fossil found in Myanmar. The genus contains a single described species, Tytthodiplatys mecynocercus.
Zigrasolabis is an extinct genus of earwig in the family Labiduridae known from Cretaceous fossils found in Myanmar. The genus contains a single described species, Zigrasolabis speciosa.
Toxolabis is an extinct genus of earwig in the dermapteran family Anisolabididae known from a Cretaceous fossil found in Burma. The genus contains a single described species, Toxolabis zigrasi.
This taxonomy of the Dermaptera follows Engel & Haas (2007) to the rank of Tribe.

Spongiphoridae is a family of little earwigs in the suborder Neodermaptera. There are more than 40 genera and 510 described species in Spongiphoridae.

Neodermaptera is a suborder of earwigs in the order Dermaptera. There are about 14 families and more than 2,000 described species in Neodermaptera.
Dermapteridae is an extinct family of earwigs known from the Late Triassic to Mid Cretaceous, it is part of the extinct suborder Archidermaptera, alongside Protodiplatyidae and Turanovia. It was first named as a subfamily by Vishniakova in 1980, and elevated to family status by Engel in 2003 without discussion.
Eodermaptera is an extinct suborder of earwigs known from the Middle Jurassic to Mid Cretaceous. Defining characteristics include "tarsi three-segmented, tegmina retain venation, 8th and 9th abdominal tergite in females are narrowed, but separate from 10th tergite and not covered by 7th tergite and exposed ovipositor" They are considered to be more closely related to Neodermaptera than the more basal Archidermaptera.












