Related Research Articles

Time Team is a British television programme that originally aired on Channel 4 from 16 January 1994 to 7 September 2014. It returned online in 2022 for two episodes released on YouTube. Created by television producer Tim Taylor and presented by actor Tony Robinson, each episode featured a team of specialists carrying out an archaeological dig over a period of three days, with Robinson explaining the process in lay terms. The specialists changed throughout the programme's run, although it consistently included professional archaeologists such as Mick Aston, Carenza Lewis, Francis Pryor and Phil Harding. The sites excavated ranged in date from the Palaeolithic to the Second World War.

Antonio Verrio was an Italian painter. He was responsible for introducing Baroque mural painting into England and served the Crown over a thirty-year period.

Stirling Castle, located in Stirling, is one of the largest and most important castles in Scotland, both historically and architecturally. The castle sits atop an intrusive crag, which forms part of the Stirling Sill geological formation. It is surrounded on three sides by steep cliffs, giving it a strong defensive position. Its strategic location, guarding what was, until the 1890s, the farthest downstream crossing of the River Forth, has made it an important fortification in the region from the earliest times.

Tintagel Castle is a medieval fortification located on the peninsula of Tintagel Island adjacent to the village of Tintagel (Trevena), North Cornwall in the United Kingdom. The site was possibly occupied in the Romano-British period, as an array of artefacts dating from this period have been found on the peninsula, but as yet no Roman-era structure has been proven to have existed there. It was settled during the early medieval period, when it was probably one of the seasonal residences of the regional king of Dumnonia. A castle was built on the site by Richard, 1st Earl of Cornwall in the 13th century, during the High Middle Ages. It later fell into disrepair and ruin.

The Palace of Placentia, also known as Greenwich Palace, was an English royal residence that was initially built by Humphrey, Duke of Gloucester, in 1443. The palace was a pleasaunce; a place designed for pleasure, entertainment and an escape from the city. It was located at Greenwich on the south bank of the River Thames, downstream from London. On a hill behind the palace he built Duke Humphrey's Tower, later known as Greenwich Castle; it was subsequently demolished to make way for the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, which survives. The original river-side residence was extensively rebuilt around 1500 by Henry VII. A detached residence, the Queen's House, was built on the estate in the early 1600s and also survives. In 1660, the main palace was demolished by Charles II to make way for a proposed new palace, which was never constructed. Nearly forty years later, the Greenwich Hospital was built on the site.

Roxburgh is a civil parish and formerly a royal burgh, in the historic county of Roxburghshire in the Scottish Borders, Scotland. It was an important trading burgh in High Medieval to early modern Scotland. In the Middle Ages it had at least as much importance as Edinburgh, Stirling, Perth, or Berwick-upon-Tweed, for a time acting as de facto capital.
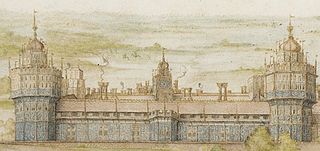
Nonsuch Palace was a Tudor royal palace, commissioned by Henry VIII in Surrey, England and completed in 1538. Its site lies in what is now Nonsuch Park on the boundaries of the borough of Epsom and Ewell in Surrey and the London Borough of Sutton.

The Nymphenburg Palace is a Baroque palace situated in Munich's western district Neuhausen-Nymphenburg, in Bavaria, southern Germany. Combined with the adjacent Nymphenburg Palace Park it constitutes one of the premier royal palaces of Europe. Its frontal width of 632 m (2,073 ft) even surpasses Versailles Palace. The Nymphenburg served as the main summer residence for the former rulers of Bavaria of the House of Wittelsbach.

Christiansborg Palace is a palace and government building on the islet of Slotsholmen in central Copenhagen, Denmark. It is the seat of the Danish Parliament, the Danish Prime Minister's Office, and the Supreme Court of Denmark. Also, several parts of the palace are used by the Danish monarch, including the Royal Reception Rooms, the Palace Chapel and the Royal Stables.
On 20 November 1992, a fire broke out in Windsor Castle, the largest inhabited castle in the world and one of the official residences of the British Monarch. The castle suffered extensive damage and was fully repaired within the next five years at a cost of £36.5 million, in a project led by the conservation architects Donald Insall Associates. It led to Queen Elizabeth II paying tax on her income, and to Buckingham Palace, the former monarch's other official residence, being opened to the public to help pay for the restoration work. This event was part of what Queen Elizabeth II called her annus horribilis.

Fredensborg Palace is a palace located on the eastern shore of Lake Esrum in Fredensborg on the island of Zealand (Sjælland) in Denmark. It is the Danish Royal Family’s spring and autumn residence, and is often the site of important state visits and events in the Royal Family. It is the most used of the Royal Family’s residences.

Windsor Castle is a royal residence at Windsor in the English county of Berkshire. It is strongly associated with the English and succeeding British royal family, and embodies almost a millennium of architectural history.

Broughton Castle is a medieval fortified manor house in the village of Broughton, which is about two miles south-west of Banbury in Oxfordshire, England, on the B4035 road. It is the home of the Fiennes family, Barons Saye and Sele. The castle sits on an artificial island in pastureland and is surrounded by a wide moat. Across the small bridge lies the parish church of St Mary the Virgin, surrounded by its historic cemetery. A Grade I listed building, it opens to the public over the summer.

Mark Chatwin Horton, FSA, is a British maritime and historical archaeologist, television presenter, and writer

Urasoe Castle is a Ryukyuan gusuku which served as the capital of the medieval Okinawan principality of Chūzan prior to the unification of the island into the Ryukyu Kingdom, and the moving of the capital to Shuri. In the 14th century, Urasoe was the largest castle on the island, but today only ruins remain.

The image of Elizabeth II, Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms and Head of the Commonwealth from 1952 to 2022, was generally favourable throughout her years as a reigning monarch. Conservative in dress, she was well known for her solid-colour overcoats and matching hats, which allowed her to be seen easily in a crowd. She attended many cultural events as part of her public role. Her main leisure interests included horse racing, photography, and dogs, especially her Pembroke Welsh corgis. Her views on political issues and other matters were largely subject to conjecture. She never gave a press interview and was otherwise not known to discuss her personal opinions publicly.
This is a list of Time Team special episodes that aired between 1997 and 2014. These special episodes often depart somewhat from the regular Time Team format, by revisiting previous sites to do a follow-up story; travelling outside the UK to excavate other sites of interest; chronicling digs overseen by other organisations; or using information gleaned from other Time Team episodes to draw a more complete picture of ordinary life during a particular historical era. Other specials may focus on a dig with a particular holiday theme; a more complex excavation over a longer period than the standard three days; or a visit to a particularly famous historical site.
Time Team Live is a British television series that airs on Channel 4. The first programme was shown in 1997 and the most recent was in 2006. Presented by the actor Tony Robinson and guest presenters, this is a live version of the archaeology series Time Team, showing more of what happens in real time, than when the cut-down episode airs on Channel 4.
Castle Hill is a suburb of the town of Ipswich, partly in the ward of Castle Hill, in the Ipswich district, in the county of Suffolk, England. Castle Hill United Reformed Church was completed in 1956. There was a Roman villa at Castle Hill.
This is a list of Time Team episodes from series 20. The series was released on DVD in 2014.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Brindle and Kerr, p.4.
- ↑ "Upper Ward complete decorated medieval floor tile". Big Royal Dig - Time Team. Channel 4.
- ↑ "Latest from Windsor Castle". Big Royal Dig - Time Team. Channel 4.