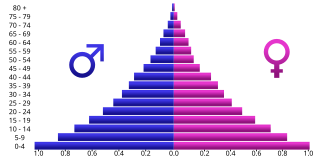An anemometer is a device that measures wind speed and direction. It is a common weather station instrument. The term is derived from the Greek word anemos (wind), and is used to describe any wind-speed instrument used in meteorology. The earliest known description of an anemometer was by Italian architect and author Leon Battista Alberti (1404–1472) in 1450.

Leon Battista Alberti was an Italian Renaissance humanist author, artist, architect, poet, priest, linguist, philosopher, and cryptographer; he epitomised the nature of those identified now as polymaths. He is considered the founder of Western cryptography, a claim he shares with Johannes Trithemius.

A pyramid scheme is a business model that recruits members via a promise of payments or services for enrolling others into the scheme, rather than supplying investments or sale of products. As recruiting multiplies, recruiting becomes quickly impossible, and most members are unable to profit; as such, pyramid schemes are unsustainable and often illegal.
A polyalphabetic cipher is any cipher based on substitution, using multiple substitution alphabets. The Vigenère cipher is probably the best-known example of a polyalphabetic cipher, though it is a simplified special case. The Enigma machine is more complex but is still fundamentally a polyalphabetic substitution cipher.

Mathematics and architecture are related, since, as with other arts, architects use mathematics for several reasons. Apart from the mathematics needed when engineering buildings, architects use geometry: to define the spatial form of a building; from the Pythagoreans of the sixth century BC onwards, to create forms considered harmonious, and thus to lay out buildings and their surroundings according to mathematical, aesthetic and sometimes religious principles; to decorate buildings with mathematical objects such as tessellations; and to meet environmental goals, such as to minimise wind speeds around the bases of tall buildings.
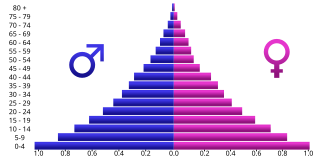
A population pyramid or "age-sex pyramid" is a graphical illustration of the distribution of a population by age groups and sex; it typically takes the shape of a pyramid when the population is growing. Males are usually shown on the left and females on the right, and they may be measured in absolute numbers or as a percentage of the total population. The pyramid can be used to visualize the age of a particular population. It is also used in ecology to determine the overall age distribution of a population; an indication of the reproductive capabilities and likelihood of the continuation of a species. Number of people per unit area of land is called population density.
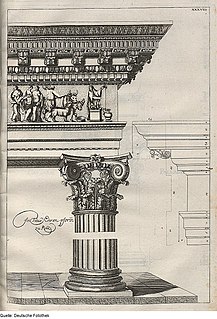
The Composite order is a mixed order, combining the volutes of the Ionic order capital with the acanthus leaves of the Corinthian order. In many versions the composite order volutes are larger, however, and there is generally some ornament placed centrally between the volutes. The column of the composite order is typically ten diameters high, though as with all the orders these details may be adjusted by the architect for particular buildings. The Composite order is essentially treated as Corinthian except for the capital, with no consistent differences to that above or below the capital.
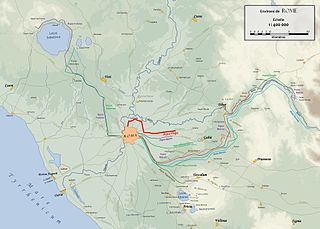
The Aqua Virgo was one of the eleven Roman aqueducts that supplied the city of ancient Rome. It was completed in 19 BC by Marcus Agrippa, during the reign of the emperor Augustus and was built mainly to supply the contemporaneous Baths of Agrippa in the Campus Martius.

De re aedificatoria is a classic architectural treatise written by Leon Battista Alberti between 1443 and 1452. Although largely dependent on Vitruvius's De architectura, it was the first theoretical book on the subject written in the Italian Renaissance, and in 1485 it became the first printed book on architecture. It was followed in 1486 with the first printed edition of Vitruvius.

The Basilica of Sant'Andrea is a Roman Catholic co-cathedral and minor basilica in Mantua, Lombardy (Italy). It is one of the major works of 15th-century Renaissance architecture in Northern Italy. Commissioned by Ludovico III Gonzaga, the church was begun in 1472 according to designs by Leon Battista Alberti on a site occupied by a Benedictine monastery, of which the bell tower (1414) remains. The building, however, was only finished 328 years later. Though later changes and expansions altered Alberti's design, the church is still considered to be one of Alberti's most complete works. It looms over the Piazza Mantegna.
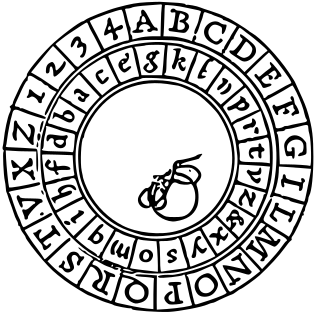
The Alberti Cipher, created in 1467 by Italian architect Leon Battista Alberti, was one of the first polyalphabetic ciphers. In the opening pages of his treatise De componendis cifris he explained how his conversation with the papal secretary Leonardo Dati about a recently developed movable type printing press led to the development of his cipher wheel.

San Sebastiano is an Early Renaissance church in Mantua, northern Italy. Begun in 1460 according to the designs of Leon Battista Alberti, it was left partially completed in the mid-1470s, by which time construction had slowed and was no longer being directed by Alberti. As a consequence, little remains of Alberti’s work apart from the plan, which is considered one of the earliest and most significant examples of Renassiances centrally-planned churches. The plan is in the shape of a Greek cross, with three identical arms centering apses, under a central cross-vaulted space without any interior partitions. The church sits on a ground-level crypt which was intended to serve as a mausoleum for the Gonzaga family.

Giovan Battista Bellaso was an Italian cryptologist.

San Pancrazio is a church in Florence, Italy, in Piazza San Pancrazio, behind Palazzo Rucellai. With the exception of the Rucellai Chapel, it is deconsecrated and is home to the museum dedicated to the sculptor Marino Marini. The Rucellai Chapel contains the Rucellai Sepulchre or Tempietto del Santo Sepolcro. Since February 2013 it has been possible to visit the chapel from within the Marini museum.

An ideal city is the concept of a plan for a city that has been conceived in accordance with a particular rational or moral objective.

De pictura is a treatise or commentarii written by the Italian humanist and artist Leon Battista Alberti. The first version, composed in Latin in 1435, was not published until 1450. It is one of his three treatises on art; the other two are De statua and De re aedificatoria, that would form the Renaissance concept for the fine arts: painting, sculpture, and architecture.
In astronomy, geography, and related sciences and contexts, a direction or plane passing by a given point is said to be vertical if it contains the local gravity direction at that point. Conversely, a direction or plane is said to be horizontal if it is perpendicular to the vertical direction. In general, something that is vertical can be drawn from up to down, such as the y-axis in the Cartesian coordinate system.

The hamburger button, so named for its unintentional resemblance to a hamburger, is a button typically placed in a top corner of a graphical user interface. Its function is to toggle a menu or navigation bar between being collapsed behind the button or displayed on the screen. The icon which is associated with this widget, consisting of three horizontal bars, is also known as the collapsed menu icon.

Marino Marini (1901–1980) was one of the most important Italian artists of the twentieth century, especially as a sculptor. He was born in Pistoia, but he studied art in Florence, before moving to Monza as a teacher and finally arriving at the prestigious Academy of Fine Arts of Brera in Milan. The museum houses the second-largest collection of his works, after collection dedicated to him in his hometown.