
Jacob Abraham Camille Pissarro was a Danish-French Impressionist and Neo-Impressionist painter born on the island of St Thomas. His importance resides in his contributions to both Impressionism and Post-Impressionism. Pissarro studied from great forerunners, including Gustave Courbet and Jean-Baptiste-Camille Corot. He later studied and worked alongside Georges Seurat and Paul Signac when he took on the Neo-Impressionist style at the age of 54.

The Musée d'Orsay is a museum in Paris, France, on the Left Bank of the Seine. It is housed in the former Gare d'Orsay, a Beaux-Arts railway station built between 1898 and 1900. The museum holds mainly French art dating from 1848 to 1914, including paintings, sculptures, furniture, and photography. It houses the largest collection of Impressionist and post-Impressionist masterpieces in the world, by painters including Berthe Morisot, Claude Monet, Édouard Manet, Degas, Renoir, Cézanne, Seurat, Sisley, Gauguin, and van Gogh. Many of these works were held at the Galerie nationale du Jeu de Paume prior to the museum's opening in 1986. It is one of the largest art museums in Europe.

Henri Fantin-Latour was a French painter and lithographer best known for his flower paintings and group portraits of Parisian artists and writers.

Jean Désiré Gustave Courbet was a French painter who led the Realism movement in 19th-century French painting. Committed to painting only what he could see, he rejected academic convention and the Romanticism of the previous generation of visual artists. His independence set an example that was important to later artists, such as the Impressionists and the Cubists. Courbet occupies an important place in 19th-century French painting as an innovator and as an artist willing to make bold social statements through his work.

The Barbizon school of painters were part of an art movement towards Realism in art, which arose in the context of the dominant Romantic Movement of the time. The Barbizon school was active roughly from 1830 through 1870. It takes its name from the village of Barbizon, France, on the edge of the Forest of Fontainebleau, where many of the artists gathered. Most of their works were landscape painting, but several of them also painted landscapes with farmworkers, and genre scenes of village life. Some of the most prominent features of this school are its tonal qualities, color, loose brushwork, and softness of form.

Jean-Honoré Fragonard was a French painter and printmaker whose late Rococo manner was distinguished by remarkable facility, exuberance, and hedonism. One of the most prolific artists active in the last decades of the Ancien Régime, Fragonard produced more than 550 paintings, of which only five are dated. Among his most popular works are genre paintings conveying an atmosphere of intimacy and veiled eroticism.

Georges de La Tour was a French Baroque painter, who spent most of his working life in the Duchy of Lorraine, which was temporarily absorbed into France between 1641 and 1648. He painted mostly religious chiaroscuro scenes lit by candlelight.

Armand Guillaumin was a French impressionist painter and lithographer.

The Musée Cognacq-Jay is a museum located in the Hôtel Donon in the 3rd arrondissement at 8 rue Elzévir, Paris, France. It is open daily except Monday; admission is free. The nearest Metro stations are Saint-Paul and Chemin Vert.

Hippolyte Emmanuel Boulenger was a Belgian landscape painter influenced by the French Barbizon school, considered to be "the Belgian Corot".

Adolphe Étienne Auguste Moreau-Nélaton was a French painter, art collector and art historian. His large collection is today held in its entirety by French national museums.

The Musée d'art moderne André Malraux is a museum in Le Havre, France containing one of the nation's most extensive collections of impressionist paintings. It was designed by Atelier LWD, an architecture studio led by Guy Lagneau, Michel Weill and Jean Dimitrijevic. It is named after André Malraux, Minister of Culture when the museum was opened in 1961.
Joachim Pissarro is an art historian, theoretician, curator, educator, and director of the Hunter College Galleries and Bershad Professor of Art History at Hunter College of the City University of New York. Since 2002, Pissarro has served as the Editorial Director of Wildenstein Publications. His latest book, authored with art critic David Carrier, is called Wild Art. Pissarro was curator at the Museum of Modern Art's Department of Painting and Sculpture from 2003 to 2007.

The Musée des Beaux-Arts de Quimper is an art museum located in Quimper, Brittany, France. It was founded after Jean-Marie de Silguy (1785-1864) left a legacy of 1200 paintings and 2000 drawings to the town of Quimper on condition that the town build a museum to accommodate them. Today, it is one of the principal art museums in western France, presenting rich collections of French, Italian, Flemish, and Dutch paintings from the 14th century to present day.
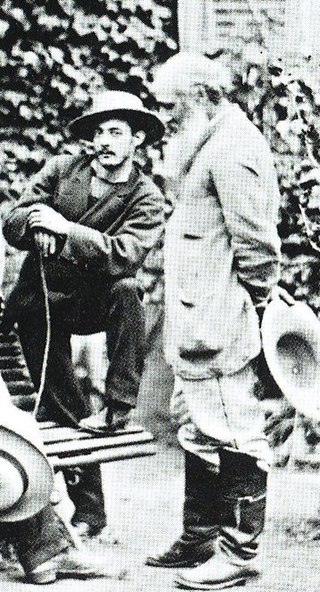
Victor Alfred Paul Vignon was a French Impressionist landscape painter and graphic artist. He was involved with the impressionism movement and its protagonists, as he exhibited at the fifth, sixth, seventh, and eight Paris Impressionist Exhibitions from 1880 to 1886.
Léon-Honoré Labande (1867-1939) was a French museum curator, historian and archivist. He was the curator of the Calvet Museum in Avignon from 1890 to 1906. He was the archivist of the Prince's Palace of Monaco from 1906 to 1939. He was the author of many books about prominent families from Provence, the city of Avignon, and the principality of Monaco.
Edmond-René Labande (1908-1992) was a French archivist and historian.

The Château d'Orrouy is an historic castle in Orrouy, Oise, Hauts-de-France, France.

Gustave-Henri Colin (1828–1910) was a French painter.

Etienne Aimé de Ganay, 5th Marquis de Ganay was a French aristocrat and art collector.


















