
3Com Corporation was an American digital electronics manufacturer best known for its computer network products. The company was co-founded in 1979 by Robert Metcalfe, Howard Charney and others. Bill Krause joined as President in 1981. Metcalfe explained the name 3Com was a contraction of "Computer Communication Compatibility", with its focus on Ethernet technology that he had co-invented, which enabled the networking of computers.

Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 3 gigahertz (GHz), also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one tenth of a meter. Radio waves with frequencies above the UHF band fall into the super-high frequency (SHF) or microwave frequency range. Lower frequency signals fall into the VHF or lower bands. UHF radio waves propagate mainly by line of sight; they are blocked by hills and large buildings although the transmission through building walls is strong enough for indoor reception. They are used for television broadcasting, cell phones, satellite communication including GPS, personal radio services including Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, walkie-talkies, cordless phones, satellite phones, and numerous other applications.

IEEE 802.20 or Mobile Broadband Wireless Access (MBWA) was a specification by the standard association of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) for mobile broadband networks. The main standard was published in 2008. MBWA is no longer being actively developed.

AT&T Mobility, LLC, also known as AT&T Wireless and marketed as simply AT&T, is an American telecommunications company. It is a wholly owned subsidiary of AT&T Inc. and provides wireless services in the United States. AT&T Mobility is the third largest wireless carrier in the United States, with 115.4 million subscribers as of June 31, 2024.
4G is the fourth generation of broadband cellular network technology, succeeding 3G and preceding 5G. A 4G system must provide capabilities defined by ITU in IMT Advanced. Potential and current applications include amended mobile web access, IP telephony, gaming services, high-definition mobile TV, video conferencing, and 3D television.

Base station is – according to the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) Radio Regulations (RR) – a "land station in the land mobile service."

A cell site, cell phone tower, cell base tower, or cellular base station is a cellular-enabled mobile device site where antennas and electronic communications equipment are placed to create a cell, or adjacent cells, in a cellular network. The raised structure typically supports antenna and one or more sets of transmitter/receivers transceivers, digital signal processors, control electronics, a GPS receiver for timing, primary and backup electrical power sources, and sheltering.
In many disciplines, a greenfield project is one that lacks constraints imposed by prior work. The analogy is to that of construction on greenfield land where there is no need to work within the constraints of existing buildings or infrastructure.
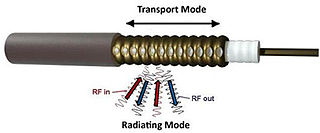
A leaky feeder is a communications system used in underground mines and inside tunnels. Manufacturers and cabling professionals use the term "radiating cable" as this implies that the cable is designed to radiate: something that a typical coaxial cable is generally not intended to do.

Alvarion Technologies Ltd. is a global provider of autonomous Wi-Fi networks designed with self-organizing capabilities for carrier-grade Wi-Fi, enterprise connectivity, smart city planning, smart hospitality, connected campuses, and connected events.

In radio, multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) is a method for multiplying the capacity of a radio link using multiple transmission and receiving antennas to exploit multipath propagation. MIMO has become an essential element of wireless communication standards including IEEE 802.11n, IEEE 802.11ac, HSPA+ (3G), WiMAX, and Long Term Evolution (LTE). More recently, MIMO has been applied to power-line communication for three-wire installations as part of the ITU G.hn standard and of the HomePlug AV2 specification.

Andrew Corporation, a former hardware manufacturer for communications networks, was founded by Victor J. Andrew in the basement of his Chicago, Illinois home in 1937, and further established in Orland Park, Illinois in 1953. Andrew was a renowned global telecommunications company that played a significant role in the development of wireless communication technologies.

CommScope Holding Company, Inc. is an American network infrastructure provider based in Claremont, North Carolina. CommScope employs over 22,000 employees. The company joined the Nasdaq stock exchange on October 25, 2013.
International Mobile Telecommunications-Advanced are the requirements issued by the ITU Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R) of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) in 2008 for what is marketed as 4G mobile phone and Internet access service.

2degrees is a New Zealand full service telecommunications provider. It’s the third-largest wireless carrier in New Zealand, with 1.3 million subscribers as of July 2015. Since launching its mobile network, 2degrees broke up the New Zealand mobile duopoly halving the price of Prepay overnight. 2degrees offers services across mobile, broadband, business and power.

RUCKUS Networks is a brand of wired and wireless networking equipment and software owned by CommScope. Ruckus offers switches, Wi-Fi access points, CBRS access points, controllers, management systems, cloud management, AAA/BYOD software, AI and ML analytics software, location software and IoT controller software products to mobile carriers, broadband service providers, and corporate enterprises. As a company, Ruckus invented and has patented wireless voice, video, and data technology, such as adaptive antenna arrays that extend signal range, increase data rates, and avoid interference, providing distribution of delay-sensitive content over standard 802.11 Wi-Fi.
C-RAN (Cloud-RAN), also referred to as Centralized-RAN, is an architecture for cellular networks. C-RAN is a centralized, cloud computing-based architecture for radio access networks that supports 2G, 3G, 4G and future wireless communication standards. Its name comes from the four 'C's in the main characteristics of C-RAN system, "Clean, Centralized processing, Collaborative radio, and a real-time Cloud Radio Access Network".
The first smart antennas were developed for military communications and intelligence gathering. The growth of cellular telephone in the 1980s attracted interest in commercial applications. The upgrade to digital radio technology in the mobile phone, indoor wireless network, and satellite broadcasting industries created new opportunities for smart antennas in the 1990s, culminating in the development of the MIMO technology used in 4G wireless networks.

Artemis Networks is a wireless technology company responsible for the software-defined radio technologies pCell and pWave. Artemis claims pCell technology is capable of speeds hundreds of times faster than other technologies under conditions of heavy usage and interference. Its founder and CEO is Steve Perlman.

MikroTik is a Latvian network equipment manufacturing company. MikroTik develops and sells wired and wireless network routers, network switches, access points, as well as operating systems and auxiliary software. The company was founded in 1996, and as of 2022, it was reported that the company employed 351 employees.














