The Salian dynasty was a dynasty in the High Middle Ages. The dynasty provided four German Kings (1024–1125), all of whom went on to be crowned Holy Roman Emperor (1027–1125); as such, the term Salic dynasty is also used to refer to the Holy Roman Empire of the time as a separate term.
In the administrative divisions of France, the department is one of the three levels of government below the national level, between the administrative regions and the commune. Ninety-six departments are in metropolitan France, and five are overseas departments, which are also classified as regions. Departments are further subdivided into 334 arrondissements, themselves divided into cantons; the last two have no autonomy, and are used for the organisation of police, fire departments, and sometimes, elections.

The Palatinate, historically also Rhenish Palatinate, is a region in southwestern Germany. It occupies roughly the southernmost quarter of the German federal state of Rhineland-Palatinate (Rheinland-Pfalz), covering an area of 5,451 square kilometres (2,105 sq mi) with about 1.4 million inhabitants. Its residents are known as Palatines.

Haut-Rhin is a department in the Grand Est region of France, named after the river Rhine. Its name means Upper Rhine. Haut-Rhin is the smaller and less populated of the two departments of the former administrative Alsace region, especially after the 1871 cession of the southern territory known since 1922 as Territoire de Belfort, although it is still densely populated compared to the rest of metropolitan France.

Speyer is a town in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, with approximately 50,000 inhabitants. Located beside the river Rhine, Speyer is 25 km south of Ludwigshafen and Mannheim. Founded by the Romans, it is one of Germany's oldest cities. Speyer is dominated by the Speyer Cathedral, a number of churches and the Altpörtel. In the cathedral, beneath the high altar, are the tombs of eight Holy Roman Emperors and German kings.
An arrondissement is a level of administrative division in France generally corresponding to the territory overseen by a subprefect. As of 2018, the 101 French departments were divided into 332 arrondissements.

The administrative divisions of France are concerned with the institutional and territorial organization of French territory. These territories are located in many parts of the world. There are many administrative divisions, which may have political, electoral (districts), or administrative objectives. All the inhabited territories are represented in the National Assembly, Senate and Economic and Social Council and their citizens have French citizenship.

Mont-Tonnerre[mɔ̃.tɔ.nɛʁ] was a department of the First French Republic and later the First French Empire in present-day Germany. It was named after the highest point in the Palatinate, the Donnersberg. It was the southernmost of four departments formed in 1798 when the west bank of the Rhine was annexed by France. Prior to the French occupation, its territory was divided between the Archbishopric of Mainz, the Bishopric of Speyer, the Bishopric of Worms, Nassau-Weilburg, Hesse-Darmstadt, the Electorate of the Palatinate and the imperial cities of Worms and Speyer. Its territory is now part of the German states of Rhineland-Palatinate and Saarland. Its capital was Mainz.
Lippe[lip] was a department of the First French Empire in present-day Germany. It was named after the river Lippe. It was formed in 1811, when Principality of Salm and a part of the Grand Duchy of Berg was annexed by France. Its territory is now part of the German lands of Lower Saxony and North Rhine-Westphalia. Its capital was Münster.
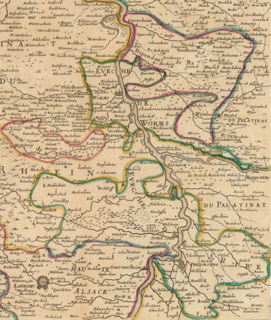
The Bishopric of Speyer, or Prince-Bishopric of Speyer, was an ecclesiastical principality in what are today the German states of Rhineland-Palatinate and Baden-Württemberg. It was secularized in 1803. The prince-bishop resided in Speyer, a Free Imperial City, until the 14th century when he moved his residence to Uddenheim (Philippsburg), then in 1723 to Bruchsal, in large part due to the tense relationship between successive prince-bishops and the civic authorities of the Free City, officially Protestant since the Reformation. The prince-provostry of Wissemburg in Alsace was ruled by the prince-bishop of Speyer in a personal union.
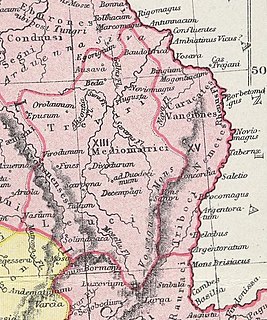
The Nemetes were a tribe settled along the Upper Rhine by Ariovistus in the 1st century BC. Their capital, Noviomagus Nemeton, was close to the site of medieval Speyer.

The County of Nice is a historical region of France located around the south-eastern city of Nice, and roughly equivalent to the modern arrondissement of Nice.

The Arrondissement of Waremme is one of the four administrative arrondissements in the Province of Liège, Belgium. Its size is 389.86 km2 (150.53 sq mi) and its population on 1 January 2015 was 78,851 people.

The Arrondissement of Turnhout is one of the three administrative arrondissements in the Province of Antwerp, Belgium. It is both an administrative and a judicial arrondissement. The territory of the Judicial Arrondissement of Turnhout coincides with that of the Administrative Arrondissement of Turnhout and part of the Campine region.

Dakar Department is one of the Departments of Senegal, located in the Dakar Region.
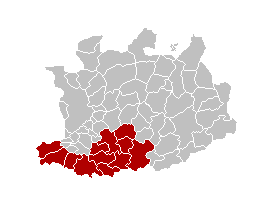
The Arrondissement of Mechelen is one of the three administrative arrondissements in the Province of Antwerp, Belgium. It is both an administrative and a judicial arrondissement, as the territory for both coincides.

The Arrondissement of Namur is one of the three administrative arrondissements in the Province of Namur, Belgium. It is both an administrative and a judicial arrondissement. The territory of the Judicial Arrondissement of Namur coincides with that of the Administrative Arrondissement of Namur.

The German University of Administrative Sciences Speyer, is a national graduate school for administrative sciences and public management located in Speyer, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. Founded in 1947 by the French occupational authorities as a grande école, today it is operated under the joint responsibility of both the Federal Republic (Bund) and all 16 German states (Länder). It runs four Master's programs, grants doctoral degrees and habilitations, offers a postgraduate certificate program, and administers programs of executive education. The school is a major training ground for German and international senior government officials. Noted alumni and faculty include former President of Germany Roman Herzog, former President of the Bundesbank Helmut Schlesinger, former Attorney General of Germany Alexander von Stahl, and CEO of BASF Jürgen Strube.


















