
Aurel Vlaicu was a Romanian engineer, inventor, airplane constructor and early pilot.

The Hansa-Brandenburg C.I, also known as Type LDD, was a 2-seater armed single-engine reconnaissance biplane designed by Ernst Heinkel, who worked at that time for the parent company in Germany. The C.I had similarities with the earlier B.I, including inward-sloping interplane bracing struts. Like other early-war Austro-Hungarian reconnaissance aircraft, such as C-types of Lloyd or Lohner, the Type LDD had a communal cockpit for its crew.
Societatea Pentru Exploatări Technice or SET was a Romanian aircraft manufacturer. It was the second biggest Romanian pre-war aircraft manufacturer, after Industria Aeronautică Română (IAR).
The IAR-23 and IAR-24 were low-wing monoplane light multipurpose aircraft with a conventional undercarriage, built by IAR of Romania.
The Romanian Air Corps or Aviation Corps (RAC) was the air arm of the Romanian army until the formation of the Romanian Air Force. It was established on 1 April 1913 as the Military Aeronautics Service and subordinated to the Engineer Inspectorate, being organized in two branches – the aviation and the balloon branch. On 23 August 1915, the RAC was formed as an independent military arm and operated until 1 January 1924 when it became an equal to the Army and Navy, being redesignated as the Royal Romanian Air Force.
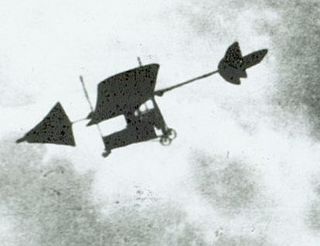
The A Vlaicu II was the second powered airplane designed and built by Aurel Vlaicu.

The A Vlaicu I was the first powered airplane built by Aurel Vlaicu.

The Astra-Protopopescu or Astra-Proto was a Romanian reconnaissance aircraft flown and tested in 1925.

Întreprinderea de Construcții Aeronautice Românești, was a Romanian aircraft manufacturer. The company produced aircraft of its own design and under license.

The Romanian air tours over Africa were a series of trips, called "raids" in Romanian literature, made by the Romanian airmen over Africa between 1933 and 1935, with the purpose of promoting air tourism, Romanian airplanes, as well as Romanian aviation in general. Given global aviation development, exploring its possibilities and setting up aircraft records were an everyday occurrence.

Proto 1 was a training biplane designed by Major Ștefan Protopopescu in collaboration with Dumitru Baziliu and Gheorghe Ticău at Arsenalul Aeronautic in Bucharest in 1922. It was the first Romanian airplane to be built in a specialized enterprise.

Proto 2 was a training biplane manufactured at the Fabrica de avioane Astra in Arad in 1924.

The Astra Aircraft Factory in Arad was the second Romanian factory to build aircraft. Its activity took place between 1923 and 1925, producing four models of aircraft: Astra-Șeșefschi, Proto 1, Proto 2 and Astra-Proto.
Cerchez & Co. was the first aircraft company, the first aerodrome and the first flight school in Romania. The company was founded and registered on 20 November 1909, being inaugurated on 11 June 1910 by the lawyer and industrialist Mihail Cerchez. The company manufactured the first serial production aircraft in Romania in 1911.

Rezerva generală a aviației (RGA) or the General Aviation Reserve in English was a Romanian aircraft factory founded during the First World War. It operated between 1916 and 1919 in Iași. After the war it was transferred to Bucharest and renamed to Arsenalul Aeronautic. The maintenance, repair, and assembly of the aircraft and aircraft engines received by Romania during the war took place here.

Ștefan Protopopescu was a Romanian officer and aviation pioneer, he held the no. 1 pilot license in Romania, being the first licensed pilot in Romania and the first pilot of the Romanian Army.

The Vuia 1, also nicknamed Liliacul, was a pioneer aircraft designed and built by Romanian inventor Traian Vuia. It was finished in December 1905 in France and first flew on 18 March 1906 at Montesson.

The Army Arsenal of Bucharest was the main arsenal of the Romanian Army, established in 1861 with the task of manufacturing, maintaining, and storing weapons, as well as limbers and caissons for the artillery. The old flags, uniforms, and weapons of the Romanian Army were also stored at the Arsenal until 1919.

















