Related Research Articles
Special Operations Executive (SOE) was a British organisation formed in 1940 to conduct espionage, sabotage and reconnaissance in German-occupied Europe and to aid local resistance movements during World War II.
Gustave Biéler DSO MBE CdeG was a Canadian Special Operations Executive agent during World War II.

Lieutenant-Colonel George Reginald Starr, code name Hilaire, was a British mining engineer and an agent of the United Kingdom's clandestine Special Operations Executive (SOE) organisation in World War II. He was the organiser (leader) of the Wheelwright network in southwestern France from November 1942 until the liberation of France from Nazi German occupation in September 1944. The purpose of SOE was to conduct espionage, sabotage and reconnaissance in occupied Europe against the Axis powers. SOE agents in France allied themselves with French Resistance groups and supplied them with weapons and equipment parachuted in from England.

Major-General Sir Colin McVean Gubbins, was the prime mover of the Special Operations Executive (SOE) in the Second World War.

Lieutenant-General Arthur Ernest Percival, was a British Army officer. He saw service in the First World War and built a successful military career during the interwar period, but is best known for his defeat in the Second World War, when Percival commanded British Commonwealth forces during the Malayan campaign, which culminated in a catastrophic defeat at the Battle of Singapore.

The fall of Singapore, also known as the Battle of Singapore, took place in the South–East Asian theatre of the Pacific War. The Japanese Empire captured the British stronghold of Singapore, with fighting lasting from 8 to 15 February 1942. Singapore was the foremost British military base and economic port in South–East Asia and had been of great importance to British interwar defence strategy. The capture of Singapore resulted in the largest British surrender in history.
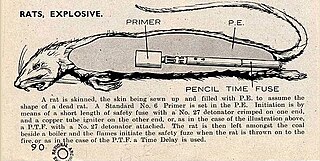
The explosive rat, also known as a rat bomb, was a weapon developed by the British Special Operations Executive (SOE) in World War II for use against Germany. Rat carcasses were filled with plastic explosives, and were to be distributed near German boiler rooms where it was expected they would be disposed of by burning, with the subsequent explosion having a chance of causing a boiler explosion.

Syonan, officially Syonan Island, was the name for Singapore when it was occupied and ruled by the Empire of Japan, following the fall and surrender of British military forces on 15 February 1942 during World War II.

Z Special Unit was a joint Allied special forces unit formed during the Second World War to operate behind Japanese lines in South East Asia. Predominantly Australian, Z Special Unit was a specialist clandestine operation, direct action, long-range penetration, sabotage, and special reconnaissance unit that included British, Dutch, New Zealand, Timorese and Indonesian members, predominantly operating on Borneo and the islands of the former Dutch East Indies.

Force 136 was a far eastern branch of the British World War II intelligence organisation, the Special Operations Executive (SOE). Originally set up in 1941 as the India Mission with the cover name of GSI(k), it absorbed what was left of SOE's Oriental Mission in April 1942. The man in overall charge for the duration of its existence was Colin Mackenzie.
A limpet mine is a type of naval mine attached to a target by magnets. It is so named because of its superficial similarity to the shape of the limpet, a type of sea snail that clings tightly to rocks or other hard surfaces.

Aston is a village and civil parish in the East Hertfordshire district of Hertfordshire, England. According to the 2001 census it had a population of 844, increasing to 871 at the 2011 Census. Located on a ridge between Stevenage and the Beane Valley, Aston is a 10 minutes drive from the A1(M).
Dalforce, officially the Singapore Overseas Chinese Anti-Japanese Volunteer Army was an irregular forces/guerrilla unit within the British Straits Settlements Volunteer Force during World War II. Its members were recruited among the ethnic Chinese people of Singapore. It was created on 25 December 1941 by Lieutenant Colonel John Dalley of the Federated Malay States Police Force. The unit was known to the British colonial administration as Dalforce, after its chief instructor and commanding officer, John Dalley, whereas the Chinese in Singapore only knew it as the Singapore Overseas Chinese Anti-Japanese Volunteer Army. This formation took part in the Battle of Singapore and some members conducted a guerrilla campaign against Japanese forces during the Japanese occupation. The British noted how ferociously the Chinese volunteers in Dalforce fought, earning them the nickname Dalley's Desperadoes.

Claude Marie Marc Boucherville de Baissac, DSO and bar, CdeG, known as Claude de Baissac or by his codename David was a Mauritian of French descent who was an agent of the United Kingdom's clandestine Special Operations Executive (SOE) organization in France during World War II. The purpose of SOE was to conduct espionage, sabotage, and reconnaissance in countries occupied by the Axis powers, especially Nazi Germany. SOE agents allied themselves with resistance groups and supplied them with weapons and equipment parachuted in from England.

The Motorised Submersible Canoe (MSC), nicknamed Sleeping Beauty, was an underwater vehicle built by the British Special Operations Executive (SOE) during the Second World War. It was designed to enable a single frogman to sabotage enemy ships, though it would also be used for short-range reconnaissance. They were replaced by the diver propulsion vehicle after the end of the war.
Major Cecil Vandepeer Clarke MC (1897–1961) was an engineer, inventor and soldier who served in both the First and Second World Wars.

The Secret Intelligence Service (SIS), commonly known as MI6, is the foreign intelligence service of the United Kingdom, tasked mainly with the covert overseas collection and analysis of human intelligence on foreign nationals in support of its Five Eyes partners. SIS is one of the British intelligence agencies and the Chief of the Secret Intelligence Service ("C") is directly accountable to the Foreign Secretary.
Lieutenant Commander Claude Michael Bulstrode Cumberlege, was a British Royal Navy officer and Special Operations Executive agent of the Second World War. He was tortured, and eventually executed, by the Germans after being captured while on Operation Locksmith in Greece.

Aston House was a prominent 17th-century residence with large parkland situated opposite the parish church in Aston, Hertfordshire in southern England. The house was demolished in 1961 by the Stevenage New Town Development Corporation after occupying it as its initial HQ. The site was developed and named Yeomans Drive in memory of Arthur Yeomans, the last owner in 1939 when it was requisitioned by the War Office. The adjoining parkland became Stevenage Golf and Conference Centre in April 1980.
References
- 1 2 3 Turner, Des (30 September 2011). Station 12: SOE's Secret Weapons Centre. The History Press. pp. 150–152. ISBN 978-0-7524-6818-1.
- 1 2 3 Willis, John (2 August 2022). Nagasaki: The Forgotten Prisoners. Bloomsbury Publishing. p. 61. ISBN 978-1-912914-43-2.
- ↑ Ltd, East Anglia Network. "Fall of Malaya and Singapore". www.britain-at-war.org.uk. Retrieved 10 December 2024.