Related Research Articles

Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist who is widely held as one of the most influential scientists. Best known for developing the theory of relativity, Einstein also made important contributions to quantum mechanics. His mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, which arises from special relativity, has been called "the world's most famous equation". He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect", a pivotal step in the development of quantum theory.

Johann Christian Bach was a German composer of the Classical era, the youngest son of Johann Sebastian Bach. He received his early musical training from his father, and later from his half-brother, Carl Philipp Emanuel Bach in Berlin. After his time in Berlin he made his way to Italy to study with famous Padre Martini in Bologna. While in Italy, J.C. Bach was appointed as an organist at the Milan Cathedral. In 1762 he became a composer to the King’s Theatre in London where he wrote a number of successful Italian operas and became known as "The English Bach". He is responsible for the development of the sinfonia concertante form. He became one of the most influential figures of the classical period, influencing compositional styles of prolific musicians like Haydn and Mozart.
Ralph Leonard Kirkpatrick was an American harpsichordist and musicologist, widely known for his chronological catalog of Domenico Scarlatti's keyboard sonatas as well as for his performances and recordings.

Alfred Einstein was a German-American musicologist and music editor. He was born in Munich and fled Nazi Germany after Hitler's Machtergreifung, arriving in the United States by 1939. He is best known for being the editor of the first major revision of the Köchel catalogue, which was published in 1936. The Köchel catalogue is the extensive catalogue of the works of Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart.

The String Quartet No. 20 in D major, K. 499, was written in 1786 in Vienna by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart. It was published by – if not indeed written for – his friend Franz Anton Hoffmeister. Because of this, the quartet has acquired the nickname Hoffmeister. Hoffmeister had started issuing a series of chamber-music publications in 1785, including Mozart's K. 499 as well as Joseph Haydn's String Quartet No. 35, Op. 42.

The German Bach-Gesellschaft was a society formed in 1850 for the express purpose of publishing the complete works of Johann Sebastian Bach without editorial additions. The collected works are known as the Bach-Gesellschaft-Ausgabe. On completion of the project, the Society dissolved itself.
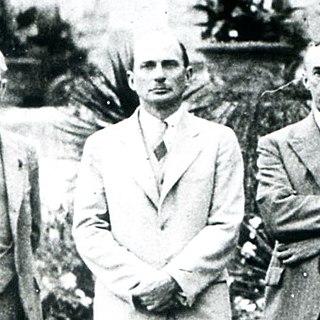
Roger Sherman Loomis (1887–1966) was an American scholar and one of the foremost authorities on medieval and Arthurian literature. Loomis is perhaps best known for showing the roots of Arthurian legend, in particular the Holy Grail, in native Celtic mythology.

Maria Constanze Cäcilia Josepha Johanna Aloysia Mozart was a trained Austrian singer. She was married twice, first to Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart; then to Georg Nikolaus von Nissen. She and Mozart had six children: Karl Thomas Mozart, Franz Xaver Wolfgang Mozart, and four others who died in infancy. She became Mozart's biographer jointly with her second husband.

The Piano Concerto No. 26 in D major, K. 537, was written by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart and completed on 24 February 1788. It is generally known as the Coronation Concerto.
Elaine Rochelle Sisman is an American musicologist. The Anne Parsons Bender Professor of Music at Columbia University, Sisman specializes in music, rhetoric, and aesthetics of the 18th and 19th centuries, and has written on such topics as memory and invention in late Beethoven, ideas of pathétique and fantasia around 1800, Haydn's theater symphonies, the sublime in Mozart's music, and Brahms's slow movements. She is the author of Haydn and the Classical Variation and Mozart: The 'Jupiter' Symphony and editor of Haydn and His World. Her monograph-length article on "variations" appears in the revised New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians, and she is at work on studies of music and melancholy, of Don Giovanni, and of the opus-concept in the eighteenth century.
Maynard Elliott Solomon was an American music executive and musicologist, a co-founder of Vanguard Records as well as a music producer. Later, he became known for his biographical studies of Viennese Classical composers, specifically Beethoven, Mozart (biography), and Schubert. Solomon was the first to propose the highly disputed theory of Schubert's homosexuality in a scholarly publication.
The Divertimento in E♭ major, K. 563, is a string trio, written by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart in 1788, the year in which he completed his last three symphonies and his "Coronation" Piano Concerto. It is his last divertimento and different from his other divertimenti not only in its instrumentation but also in its compositorial ambition and scope.

Marius Casadesus was a French violinist and composer. He was the brother of Henri Casadesus, uncle of the famed pianist Robert Casadesus, and grand-uncle to Jean Casadesus.

The Alte Mozart-Ausgabe is the name by which the first complete edition of the music of Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, is known. It was published by Breitkopf & Härtel from January 1877 to December 1883, with supplements published until 1910. The name Alte Mozart-Ausgabe is actually a modern invention to distinguish the edition from the second Mozart complete works edition, the Neue Mozart-Ausgabe; the publication title of Breitkopf & Härtel's edition was Wolfgang Amadeus Mozarts Werke. Kritisch durchgesehene Gesammtausgabe.
Michael Haydn's Symphony No. 26 in E-flat major, Perger 17, Sherman 26, MH 340, written in Salzburg in 1783, was the first of the only three symphonies published in his lifetime. It was one of several E-flat major symphonies attributed to Joseph Haydn.
Edward Toner Cone was an American composer, music theorist, pianist, and philanthropist.
John Butt is an English orchestral and choral conductor, organist, harpsichordist and scholar. He holds the Gardiner Chair of Music at the University of Glasgow and is music director of the Dunedin Consort with whom he has made award-winning recordings in historically informed performance. He is a prolific scholar, conductor and performer of works by Johann Sebastian Bach.
Carl Weinrich was an American organist, choral conductor, and teacher. He was particularly known for his recitals and recordings of Bach's organ music and as a leader in the revival of Baroque organ music in the United States during the 1930s.

The Piano Sonata in B-flat major, K. 498a, is a piano sonata in four movements. It was first printed in 1798 by P. J. Thonus in Leipzig on behalf of Breitkopf & Härtel and attributed to Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart; an edition printed in c. 1805 already credited it as opus 26 of the Thomascantor August Eberhard Müller (1767–1817). Some publications still attribute it to Mozart, often as Piano Sonata No. 20.
Peter Williams was an English musicologist, author, harpsichordist, organist, and professor. Williams was considered one of the leading scholars on the organ and the life and works of Johann Sebastian Bach.
References
- 1 2 3 "Arthur Mendel, Music Professor At Princeton and Expert on Bach". The New York Times. October 18, 1979. Retrieved 20 October 2022.
- 1 2 3 "Arthur Mendel (Conductor, Music Scholar)". Bach Cantatas Website. Retrieved 20 October 2022.
This article needs additional or more specific categories .(October 2022) |