Related Research Articles
Asante, also known as Ashanti, Ashante, or Asante Twi, is one of the principal members of the Akan dialect continuum. It is one of the three mutually intelligible dialects of Akan which are collectively known as Twi, the others being Bono and Akuapem. There are over 20 million speakers of the Asante language, mainly concentrated in Ghana and southeastern Cote D'Ivoire, and especially in and around the Ashanti Region of Ghana.
Akan is a group of several closely related languages within the wider Central Tano languages. These languages are the principal native languages of the Akan people of Ghana, spoken over much of the southern half of Ghana. About 80% of Ghana's population can speak an Akan language as a first or second language, and about 44% of Ghanaians are native speakers. There are populations of polyglots in Ghana who speak an Akan language as a third language. They are also spoken in parts of Côte d'Ivoire.
The Akan people are a Kwa group living primarily in present-day Ghana and in parts of Ivory Coast and Togo in West Africa. The Akan speak dialects within the Central Tano branch of the Potou–Tano subfamily of the Niger–Congo family. Subgroups of the Akan people include: the Agona, Akuapem, Akwamu, Akyem, Anyi, Ashanti, Baoulé, Bono, Chakosi, Fante, Kwahu, Sefwi, Wassa, Ahanta, and Nzema, among others. The Akan subgroups all have cultural attributes in common; most notably the tracing of matrilineal descent in the inheritance of property, and for succession to high political office.
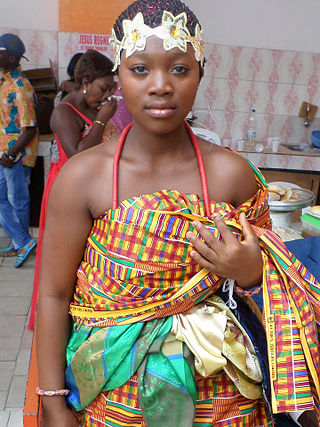
The Bono, also called the Brong and the Abron, are an Akan people of West Africa. Bonos are normally tagged Akan piesie or Akandifo of which Akan is a derivative name. Bono is the genesis and cradle of Akans. Bono is one of the largest ethnic group of Akan and are matrilineal people. Bono people speak the Bono Twi of Akan language. Twi language, thus the dialect of Bono is a derivative of a Bono King Nana Twi. In the late fifteenth century, the Bono people founded the Gyaaman kingdom as extension of Bono state in what is now Ghana and Côte d'Ivoire.
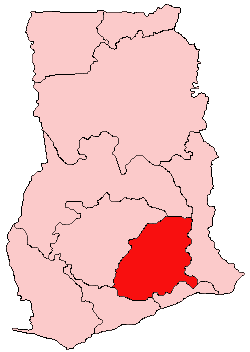
Kwahu is an area and group of people that live in Ghana and are part of the Twi-speaking Akan group. The region has been dubbed Asaase Aban, or the Natural Fortress, given its position as the highest habitable elevation in the country. Kwahu lies in the Eastern Region of Ghana, on the west shore of Lake Volta. The Kwahus share the Eastern Region with the Akyem and Akuapem, as well as the Adangbe-Krobos. Among Kwahu lands, a significant migrant population works as traders, farm-hands, fisherfolk, and caretakers in the fertile waterfront 'melting pot' of Afram plains. These migrants are mostly from the Northern and Volta Regions, as well as, some indigenous Guans from the bordering Oti and Brong-Ahafo regions live in the Afram Plains area. Kwahus are traditionally known to be wealthy traders, owning a significant number of businesses and industries in Ghana.

Adinkra are symbols from Ghana that represent concepts or aphorisms. Adinkra are used extensively in fabrics, logos and pottery. They are incorporated into walls and other architectural features. Adinkra symbols appear on some traditional Akan goldweights. The symbols are also carved on stools for domestic and ritual use. Tourism has led to new departures in the use of symbols in items such as T-shirts and jewellery.

Ghana is a multilingual country in which about eighty languages are spoken. Of these, English, which was inherited from the colonial era, is the official language and lingua franca. Of the languages indigenous to Ghana, Akan is the most widely spoken in the south. Dagbani is most widely spoken in the north.

Akropong is a town in South Ghana and is the capital of the Akuapim North District, a district in the Eastern Region of South Ghana. This town is known for producing snails and palm oil. Akropong has a 2013 settlement population of 13,785 people.
Abusua is the name in Akan culture for a group of people that share common maternal ancestry governed by seven major ancient female abosom (deities). The Abusua line is considered to be passed through the mother's blood . There are several Abusua that transcend the different ethnic subgroups outside of the ancient seven. People of the same Abusua share a common ancestor somewhere within their bloodline, which may go back as far as thousands of years. It is a taboo to marry someone from the same Abusua. The different Abusua are the Agona (parrot), the Aduana (dog), the Asenie (bat), Oyoko (falcon/hawk), the Asakyiri (vulture), the Asona (crow), the Bretuo (leopard), and the Ekuona (bull).

The Asante, also known as Ashanti in English, are part of the Akan ethnic group and are native to the Ashanti Region of modern-day Ghana. Asantes are the last group to emerge out of the various Akan civilisations. Twi is spoken by over nine million Asante people as their native language.

Twi is a variety of the Akan language spoken in southern and central Ghana by several million people, mainly of the Akan people, the largest of the seventeen major ethnic groups in Ghana. Twi has about 4.4 million speakers.

Okyenhene is the title of the Tribal King of Akyem Abuakwa, an old traditional kingdom in the Eastern Region of Ghana. The Okyenhene is also referred to as the Kwaebibiremhene as his traditional territory is an area of a dense forest. Again, the Okyenhene is considered the head of the Asona clan. Asona is the largest of the clans of the Akans which includes the Oyoko, Aduana, Agona, Asakyire, Bretuo, Ekuona among others.
The Oyoko is one of the eight major Abusua; its characteristic is patience. It is a clan from Ghana and the origins of the clan can be traced back to at least c. 1570. The Oyoko Clan is bigger than Asante. The Oyoko family traces its origins to the contemporary Akan Town of Techiman. The original Oyoko royal family of Techimanhene’s palace. The Asantehene and Techimanhene, in that case, are of the same clan.
Bretuo is one of the eight major Akan clans, a group of ethnic people in West Africa primarily located in Ghana as well as parts of Ivory Coast and Togo.
Agona Clan is one of the eight major Akan clans.
Asona is one of the eight main Akan clans.
Aduana is one of the Eight major Akan clans of Ghana. It is also the second largest clan in terms of population.
Ekuona is one of the eight major Akan clans.
Asenie is one of the eight Akan major clans.
Amanokrom is a town in the Akuapim North District of the Eastern Region of Ghana. It shares border with Mamfe and Abotakyi
References
- ↑ "twi.bb - Online Twi Dictionary - The Akan People - Abusua". www.twi.bb. Retrieved 2015-06-16.
- ↑ Ntiamoa-Baidu, Yaa (1995). "Conservation education in threatened species management in Africa". Bird Conservation International. 5 (4): 455–462. doi: 10.1017/S0959270900001179 .
- ↑ "KDA - totemism". www.kwahuman.com. Retrieved 2015-06-16.