
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the United Nations Conference on the Human Environment in Stockholm in June 1972. Its mandate is to provide leadership, deliver science and develop solutions on a wide range of issues, including climate change, the management of marine and terrestrial ecosystems, and green economic development. The organization also develops international environmental agreements; publishes and promotes environmental science and helps national governments achieve environmental targets.

Man and the Biosphere Programme (MAB) is an intergovernmental scientific program, launched in 1971 by UNESCO, that aims to establish a scientific basis for the improvement of relationships between people and their environments.

The economy of Asia comprises about 4.7 billion people living in 50 different nations. Asia is the fastest growing economic region, as well as the largest continental economy by both GDP Nominal and PPP in the world. Moreover, Asia is the site of some of the world's longest modern economic booms.
MegaLink is a Philippine-based developer of mobile and banking software as well as a service provider for banks, specifically for Automatic Teller Machine (ATM) networks and point of sale systems for banks. From its establishment in 1989 until 2015, it has pioneered in the interconnectivity of several banks in the country by being the first Interbank Network with different banks as its members.
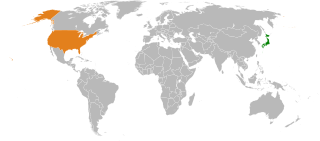
International relations between Japan and the United States began in the late 18th and early 19th century with the diplomatic but force-backed missions of U.S. ship captains James Glynn and Matthew C. Perry to the Tokugawa shogunate. Following the Meiji Restoration, the countries maintained relatively cordial relations. Potential disputes were resolved. Japan acknowledged American control of Hawaii and the Philippines, and the United States reciprocated regarding Korea. Disagreements about Japanese immigration to the U.S. were resolved in 1907. The two were allies against Germany in World War I.

The Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP), or Trans-Pacific Partnership Agreement (TPPA), was a proposed trade agreement between 12 Pacific Rim economies: Australia, Brunei, Canada, Chile, Japan, Malaysia, Mexico, New Zealand, Peru, Singapore, Vietnam, and the United States. In the United States, the proposal was signed on 4 February 2016 but not ratified, being opposed by many Democrats and Republicans, including both major-party presidential nominees, Donald Trump and Hillary Clinton. After taking office, the newly elected President Donald Trump formally withdrew the United States from TPP in January 2017, therefore the TPP could not be ratified as required and did not enter into force. The remaining countries negotiated a new trade agreement called Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership, which incorporates most of the provisions of the TPP and which entered into force on 30 December 2018.

Diplomatic relations between South Korea and the United States commenced in 1950, when the United States helped establish the modern state of South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea, and fought on its UN-sponsored side in the Korean War (1950–1953). During the subsequent decades, South Korea experienced tremendous economic, political and military growth.
The Pacific Economic Cooperation Council (PECC) is a network of member committees composed of individuals and institutions dedicated to promoting cooperation across the Asia Pacific region, headquartered in Singapore. PECC has 23 full member committees Australia; Brunei Darussalam; Canada; Chile; China; Colombia; Ecuador; Hong Kong; Indonesia; Japan; Korea; Malaysia; Mexico; Mongolia; New Zealand; Peru; the Philippines; Singapore; Taiwan; Thailand; the United States; Vietnam and the Pacific Island Forum, one associate member: France, and 2 institutional members: Pacific Trade and Development Conference (PAFTAD) and the Pacific Basin Economic Council (PBEC).
The U.S. Climate Action Partnership (USCAP), formed in 2006 and launched publicly on January 22, 2007, is a co-operative group of businesses and leading environmental organizations. The group's primary purpose is to call on the U.S. government to require significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions.

The Global Peace Foundation (GPF) is an international nonprofit organization with a stated mission to promote “an innovative, values-based approach to peacebuilding, guided by the vision of One Family under God.” GPF partners with government ministries, community and faith-based organizations, and United Nations offices to develop and execute programs in 20 countries.

Partnerships in Environmental Management for the Seas of East Asia (PEMSEA) is a regional partnership programme implemented by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and executed by the United Nations Office for Project Services (UNOPS). The project, started in 1994, was originally known as Prevention and Management of Marine Pollution in the East Asian Seas (SDS-SEA).

Green growth is a concept in economic theory and policymaking used to describe paths of economic growth that are environmentally sustainable. It is based on the understanding that as long as economic growth remains a predominant goal, a decoupling of economic growth from resource use and adverse environmental impacts is required. As such, green growth is closely related to the concepts of green economy and low-carbon or sustainable development. A main driver for green growth is the transition towards sustainable energy systems. Advocates of green growth policies argue that well-implemented green policies can create opportunities for employment in sectors such as renewable energy, green agriculture, or sustainable forestry.

Crawford School of Public Policy is a research-intensive policy school within the ANU College of Asia and the Pacific at The Australian National University which focuses on Australia and the Asia-Pacific region. The school was named after Sir John Crawford, and its current director is Professor Helen Sullivan.
U.S. President Barack Obama's East Asia Strategy (2009–2017), also known as the Pivot to Asia, represented a significant shift in the foreign policy of the United States since the 2010s. It shifted the country's focus away from the Middle Eastern and European sphere and allowed it to invest heavily and build relationships in East Asian and Southeast Asian countries, especially countries which are in close proximity to the People's Republic of China (PRC) either economically, geographically or politically to counter its rise as a rival superpower.
Edwin O. Reischauer Center for East Asian Studies at Johns Hopkins University is a research center within the Paul H. Nitze School of Advanced International Studies (SAIS) that supports the research and study of transpacific and intra-Asian relations and seeks to advance mutual understanding between Northeast Asia and the United States.

Tan Sri Zakri bin Abdul Hamid has had a distinguished career in science as a researcher, educator, administrator and diplomat.
The East Asian Bureau of Economic Research (EABER) is a forum for economic research and analysis of the major issues facing the economies of East Asia.

Mohammad Rakibul Hasan, also known as M R Hasan and MRH, is a Bangladeshi documentary photographer, photojournalist, filmmaker and visual artist. He has made black and white photographs about climate change, political violence and the Rohingya refugee crisis. He has also been practicing fine art photography and digital art since many years.
The North Pacific Marine Science Organization, also called PICES, is an intergovernmental organization that promotes and coordinates marine scientific research in the North Pacific Ocean and provides a mechanism for information and data exchange among scientists in its member countries.

Robert K. Dixon is an energy, environment, and economic expert at the Office of International Affairs, US Department of Energy headquarters in Washington, DC, USA.













