
Pre-eclampsia is a multi-system disorder specific to pregnancy, characterized by the onset of high blood pressure and often a significant amount of protein in the urine. When it arises, the condition begins after 20 weeks of pregnancy. In severe cases of the disease there may be red blood cell breakdown, a low blood platelet count, impaired liver function, kidney dysfunction, swelling, shortness of breath due to fluid in the lungs, or visual disturbances. Pre-eclampsia increases the risk of undesirable as well as lethal outcomes for both the mother and the fetus including preterm labor. If left untreated, it may result in seizures at which point it is known as eclampsia.

Pulmonary hypertension is a condition of increased blood pressure in the arteries of the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath, fainting, tiredness, chest pain, swelling of the legs, and a fast heartbeat. The condition may make it difficult to exercise. Onset is typically gradual. According to the definition at the 6th World Symposium of Pulmonary Hypertension in 2018, a patient is deemed to have pulmonary hypertension if the pulmonary mean arterial pressure is greater than 20mmHg at rest, revised down from a purely arbitrary 25mmHg, and pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) greater than 3 Wood units.

Nitric oxide synthases (NOSs) are a family of enzymes catalyzing the production of nitric oxide (NO) from L-arginine. NO is an important cellular signaling molecule. It helps modulate vascular tone, insulin secretion, airway tone, and peristalsis, and is involved in angiogenesis and neural development. It may function as a retrograde neurotransmitter. Nitric oxide is mediated in mammals by the calcium-calmodulin controlled isoenzymes eNOS and nNOS. The inducible isoform, iNOS, involved in immune response, binds calmodulin at physiologically relevant concentrations, and produces NO as an immune defense mechanism, as NO is a free radical with an unpaired electron. It is the proximate cause of septic shock and may function in autoimmune disease.
NADPH oxidase is a membrane-bound enzyme complex that faces the extracellular space. It can be found in the plasma membrane as well as in the membranes of phagosomes used by neutrophil white blood cells to engulf microorganisms. Human isoforms of the catalytic component of the complex include NOX1, NOX2, NOX3, NOX4, NOX5, DUOX1, and DUOX2.
Soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 is a tyrosine kinase protein with antiangiogenic properties. A non-membrane associated splice variant of VEGF receptor 1 (Flt-1), sFlt-1 binds the angiogenic factors VEGF and PlGF, reducing blood vessel growth through reduction of free VEGF and PlGF concentrations. In humans, sFlt-1 is important in the regulation of blood vessel formation in diverse tissues, including the kidneys, cornea, and uterus. Abnormally high levels of sFlt-1 have been implicated in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia.

Heme oxygenase, or haem oxygenase, is an enzyme that catalyzes the degradation of heme to produce biliverdin, ferrous iron, and carbon monoxide.

Intrauterine hypoxia occurs when the fetus is deprived of an adequate supply of oxygen. It may be due to a variety of reasons such as prolapse or occlusion of the umbilical cord, placental infarction, maternal diabetes and maternal smoking. Intrauterine growth restriction may cause or be the result of hypoxia. Intrauterine hypoxia can cause cellular damage that occurs within the central nervous system. This results in an increased mortality rate, including an increased risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). Oxygen deprivation in the fetus and neonate have been implicated as either a primary or as a contributing risk factor in numerous neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders such as epilepsy, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, eating disorders and cerebral palsy.

Biliverdin reductase (BVR) is an enzyme found in all tissues under normal conditions, but especially in reticulo-macrophages of the liver and spleen. BVR facilitates the conversion of biliverdin to bilirubin via the reduction of a double bond between the second and third pyrrole ring into a single bond.

Endothelial NOS (eNOS), also known as nitric oxide synthase 3 (NOS3) or constitutive NOS (cNOS), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NOS3 gene located in the 7q35-7q36 region of chromosome 7. This enzyme is one of three isoforms that synthesize nitric oxide (NO), a small gaseous and lipophilic molecule that participates in several biological processes. The other isoforms include neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS), which is constitutively expressed in specific neurons of the brain and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), whose expression is typically induced in inflammatory diseases. eNOS is primarily responsible for the generation of NO in the vascular endothelium, a monolayer of flat cells lining the interior surface of blood vessels, at the interface between circulating blood in the lumen and the remainder of the vessel wall. NO produced by eNOS in the vascular endothelium plays crucial roles in regulating vascular tone, cellular proliferation, leukocyte adhesion, and platelet aggregation. Therefore, a functional eNOS is essential for a healthy cardiovascular system.

Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FLT1 gene.

Placental growth factor(PlGF) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PGF gene.

Phosphatidylinositol-glycan biosynthesis class F protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PIGF gene.

Zinc protoporphyrin (ZPP) refers to coordination complexes of zinc and protoporphyrin IX. It is a red-purple solid that is soluble in water. The complex and related species are found in red blood cells when heme production is inhibited by lead and/or by lack of iron.
Central aortic blood pressure is the blood pressure at the root of aorta. Studies have shown the importance of central aortic pressure, especially as compared to peripheral blood pressure, and its implications in assessing the efficacy of antihypertensive treatment with respect to cardiovascular risk factors, kidney disease, and mortality. There is an emerging movement for clinicians to begin using central aortic blood pressure, instead of peripheral blood pressure, as a guide for clinical decisions.

A placental disease is any disease, disorder, or pathology of the placenta.
Roland Stocker is a Swiss Australian biochemist who discovered the antioxidant activity of bilirubin. He is a former Olympic rower and has represented Switzerland at the 1980 Summer Olympics.
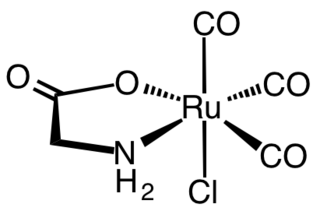
Carbon monoxide-releasing molecules (CORMs) are chemical compounds designed to release controlled amounts of carbon monoxide (CO). CORMs are being developed as potential therapeutic agents to locally deliver CO to cells and tissues, thus overcoming limitations of CO gas inhalation protocols.

Axel Haverich is a German cardiac surgeon.
Nehal N. Mehta, is an American cardiologist at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) in Bethesda, Maryland where he studies the role of innate immunity and inflammation in the development of cardiovascular and metabolic diseases.

Lucy Chappell is a British professor of obstetrics at King’s College London and the Chief Scientific Adviser (CSA) for the UK Department of Health and Social Care. As part of her CSA role, she oversees the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) as Chief Executive Officer. Her research areas include medical problems during pregnancy such as pre-eclampsia, and the safety of medicines in pregnancy.















