
The Book of Joshua is the sixth book in the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament, and is the first book of the Deuteronomistic history, the story of Israel from the conquest of Canaan to the Babylonian exile. It tells of the campaigns of the Israelites in central, southern and northern Canaan, the destruction of their enemies, and the division of the land among the Twelve Tribes, framed by two set-piece speeches, the first by God commanding the conquest of the land, and, at the end, the second by Joshua warning of the need for faithful observance of the Law (torah) revealed to Moses.

Hernán Cortés de Monroy y Pizarro Altamirano, 1st Marquess of the Valley of Oaxaca was a Spanish conquistador who led an expedition that caused the fall of the Aztec Empire and brought large portions of what is now mainland Mexico under the rule of the King of Castile in the early 16th century. Cortés was part of the generation of Spanish explorers and conquistadors who began the first phase of the Spanish colonization of the Americas.

Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1922 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (1922–1952) and Chairman of the Council of Ministers of the Soviet Union (1941–1953). Initially governing the country as part of a collective leadership, he consolidated power to become a dictator by the 1930s. Ideologically adhering to the Leninist interpretation of Marxism, he formalised these ideas as Marxism–Leninism, while his own policies are called Stalinism.
William I, usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England, reigning from 1066 until his death in 1087. A descendant of Rollo, he was Duke of Normandy from 1035 onward. By 1060, following a long struggle to establish his throne, his hold on Normandy was secure. In 1066, following the death of Edward the Confessor, William invaded England, leading an army of Normans to victory over the Anglo-Saxon forces of Harold Godwinson at the Battle of Hastings, and suppressed subsequent English revolts in what has become known as the Norman Conquest. The rest of his life was marked by struggles to consolidate his hold over England and his continental lands, and by difficulties with his eldest son, Robert Curthose.

The Battle of Hastings was fought on 14 October 1066 between the Norman-French army of William, the Duke of Normandy, and an English army under the Anglo-Saxon King Harold Godwinson, beginning the Norman conquest of England. It took place approximately 7 mi (11 km) northwest of Hastings, close to the present-day town of Battle, East Sussex, and was a decisive Norman victory.

Spain began colonizing the Americas under the Crown of Castile and was spearheaded by the Spanish conquistadors. The Americas were invaded and incorporated into the Spanish Empire, with the exception of Brazil, British America, and some small regions of South America and the Caribbean. The crown created civil and religious structures to administer the vast territory. The main motivations for colonial expansion were profit through resource extraction and the spread of Catholicism through indigenous conversions.

Francisco Pizarro González was a Spanish conquistador, best known for his expeditions that led to the Spanish conquest of Peru.
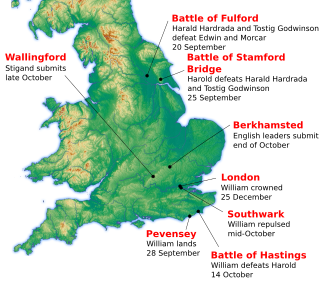
The Norman Conquest was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Normans, Bretons, Flemish, and French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Conqueror.

George Robert Acworth Conquest was a British historian and poet.
The right of conquest is a right of ownership to land after immediate possession via force of arms. It was recognized as a principle of international law that gradually deteriorated in significance until its proscription in the aftermath of World War II following the concept of crimes against peace introduced in the Nuremberg Principles. The interdiction of territorial conquests was confirmed and broadened by the UN Charter, which provides in article 2, paragraph 4, that "All Members shall refrain in their international relations from the threat or use of force against the territorial integrity or political independence of any state, or in any other manner inconsistent with the purposes of the United Nations." Although civil wars continued, wars between established states have been rare since 1945. Nations that have resorted to the use of force since the Charter came into effect have typically invoked self-defense or the right of collective defense.

The Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire, also known as the Conquest of Peru, was one of the most important campaigns in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. After years of preliminary exploration and military skirmishes, 168 Spanish soldiers under conquistador Francisco Pizarro, his brothers, and their indigenous allies captured the Sapa Inca Atahualpa in the 1532 Battle of Cajamarca. It was the first step in a long campaign that took decades of fighting but ended in Spanish victory in 1572 and colonization of the region as the Viceroyalty of Peru. The conquest of the Inca Empire, led to spin-off campaigns into present-day Chile and Colombia, as well as expeditions towards the Amazon Basin.

The Muslim conquest of Persia, also known as the Arab conquest of Iran, was carried out by the Rashidun Caliphate from 633 to 654 AD and led to the fall of the Sassanid Empire as well as the eventual decline of the Zoroastrian religion.

The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire: the Mongol Empire, which by 1300 covered large parts of Eurasia. Historians regard the Mongol devastation as one of the deadliest episodes in history. In addition, Mongol expeditions may have spread the bubonic plague across much of Eurasia, helping to spark the Black Death of the 14th century.

The Umayyadconquest of Hispania, also known as the Umayyad conquest of the Visigothic Kingdom, was the initial expansion of the Umayyad Caliphate over Hispania from 711 to 718. The conquest resulted in the destruction of the Visigothic Kingdom and the establishment of the Umayyad Wilayah of Al-Andalus.

The early Muslim conquests, also referred to as the Arab conquests and the early Islamic conquests began with the Islamic prophet Muhammad in the 7th century. He established a new unified polity in the Arabian Peninsula which under the subsequent Rashidun and Umayyad Caliphates saw a century of rapid expansion.

The Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, also known as the Conquest of Mexico or the Spanish-Aztec War (1519–21), was one of the primary events in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. There are multiple 16th-century narratives of the events by Spanish conquistadors, their indigenous allies, and the defeated Aztecs. It was not solely a contest between a small contingent of Spaniards defeating the Aztec Empire but rather the creation of a coalition of Spanish invaders with tributaries to the Aztecs, and most especially the Aztecs' indigenous enemies and rivals. They combined forces to defeat the Mexica of Tenochtitlan over a two-year period. For the Spanish, the expedition to Mexico was part of a project of Spanish colonization of the New World after twenty-five years of permanent Spanish settlement and further exploration in the Caribbean.

The siege of Cusco was the siege of the city of Cusco by the army of Sapa Inca Manco Inca Yupanqui against a garrison of Spanish conquistadors and Indian auxiliaries led by Hernando Pizarro in the hope to restore the Inca Empire (1438–1533). The siege lasted ten months and was ultimately unsuccessful.

Conquest is the act of military subjugation of an enemy by force of arms.

Transoxiana or Transoxania is the Latin name for a region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to modern-day eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Turkmenistan and southern Kyrgyzstan. Geographically, it is the region between the rivers Amu Darya to its south and the Syr Darya to its north.

Conquest Hospital is a National Health Service hospital in St Leonards-on-Sea in Hastings in East Sussex, England. It is managed by the East Sussex Healthcare NHS Trust.

















