Related Research Articles

Emergency medicine is the medical speciality concerned with the care of illnesses or injuries requiring immediate medical attention. Emergency physicians specialize in providing care for unscheduled and undifferentiated patients of all ages. As first-line providers, in coordination with emergency medical services, they are primarily responsible for initiating resuscitation and stabilization and performing the initial investigations and interventions necessary to diagnose and treat illnesses or injuries in the acute phase. Emergency medical physicians generally practice in hospital emergency departments, pre-hospital settings via emergency medical services, and intensive care units. Still, they may also work in primary care settings such as urgent care clinics.
A Physician Assistant or Physician Associate (PA) is a type of healthcare professional. While these job titles are used internationally, there is significant variation in training and scope of practice from country to country, and sometimes between smaller jurisdictions such as states or provinces. Depending on location, PAs practice semi-autonomously under the supervision of a physician, or autonomously performing a subset of medical services classically provided by physicians.

Louis Wade Sullivan is an active health policy leader, minority health advocate, author, physician, and educator. He served as the Secretary of the United States Department of Health and Human Services during President George H. W. Bush's Administration and was Founding Dean of the Morehouse School of Medicine.

Primary care is the day-to-day healthcare given by a health care provider. Typically this provider acts as the first contact and principal point of continuing care for patients within a healthcare system, and coordinates other specialist care that the patient may need. Patients commonly receive primary care from professionals such as a primary care physician, a physician assistant, a physical therapist, or a nurse practitioner. In some localities, such a professional may be a registered nurse, a pharmacist, a clinical officer, or an Ayurvedic or other traditional medicine professional. Depending on the nature of the health condition, patients may then be referred for secondary or tertiary care.

The United States Public Health Service Commissioned Corps, also referred to as the Commissioned Corps of the United States Public Health Service, is the uniformed service branch of the United States Public Health Service (PHS) and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States alongside the United States Army, Navy, Marine Corps, Coast Guard, Air Force, and Space Force and the NOAA Commissioned Officer Corps. The commissioned corps' primary mission is the protection, promotion, and advancement of health and safety of the general public.
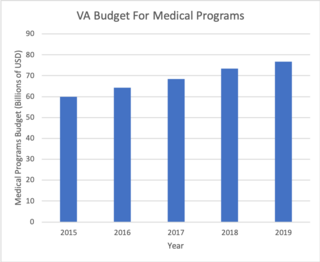
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is the component of the United States Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) led by the Under Secretary of Veterans Affairs for Health that implements the healthcare program of the VA through a nationalized healthcare service in the United States, providing healthcare and healthcare-adjacent services to veterans through the administration and operation of 146 VA Medical Centers (VAMC) with integrated outpatient clinics, 772 Community Based Outpatient Clinics (CBOC), and 134 VA Community Living Centers Programs. It is the largest division in the department, and second largest in the entire federal government, employing over 350,000 employees. All VA hospitals, clinics and medical centers are owned by and operated by the Department of Veterans Affairs, and all of the staff employed in VA hospitals are federal employees. Because of this, veterans that qualify for VHA healthcare do not pay premiums or deductibles for their healthcare but may have to make copayments depending on the medical procedure. VHA is not a part of the US Department of Defense Military Health System.

Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences (USU) is a health science university of the U.S. federal government. The primary mission of the school is to prepare graduates for service to the U.S. at home and abroad as uniformed health professionals, scientists and leaders; by conducting cutting-edge, military-relevant research; by leading the Military Health System in key functional and intellectual areas; and by providing operational support to units around the world.

The Army Medical Department of the U.S. Army (AMEDD), formerly known as the Army Medical Service (AMS), encompasses the Army's six medical Special Branches. It was established as the "Army Hospital" in July 1775 to coordinate the medical care required by the Continental Army during the Revolutionary War. The AMEDD is led by the Surgeon General of the U.S. Army, a lieutenant general.
Continuing medical education (CME) is continuing education (CE) that helps those in the medical field maintain competence and learn about new and developing areas of their field. These activities may take place as live events, written publications, online programs, audio, video, or other electronic media. Content for these programs is developed, reviewed, and delivered by faculty who are experts in their individual clinical areas. Similar to the process used in academic journals, any potentially conflicting financial relationships for faculty members must be both disclosed and resolved in a meaningful way. However, critics complain that drug and device manufacturers often use their financial sponsorship to bias CMEs towards marketing their own products.
A health professional, healthcare professional, or healthcare worker is a provider of health care treatment and advice based on formal training and experience. The field includes those who work as a nurse, physician, physician assistant, registered dietitian, veterinarian, veterinary technician, optometrist, pharmacist, pharmacy technician, medical assistant, physical therapist, occupational therapist, dentist, midwife, psychologist, audiologist, healthcare scientist, or who perform services in allied health professions. Experts in public health and community health are also health professionals.

Gale S. Pollock is a retired United States Army major general who served as the Deputy Surgeon General of the United States Army from October 2006 to March 2007, and also as chief of the Army Nurse Corps. She became acting Surgeon General of the United States Army for nine months following the 20 March 2007 retirement of her predecessor, Kevin C. Kiley, due to fallout from the Walter Reed Army Medical Center neglect scandal. She was the first woman and the first non-physician to hold the position.
Health services research (HSR) became a burgeoning field in North America in the 1960s, when scientific information and policy deliberation began to coalesce. Sometimes also referred to as health systems research or health policy and systems research (HPSR), HSR is a multidisciplinary scientific field that examines how people get access to health care practitioners and health care services, how much care costs, and what happens to patients as a result of this care. HSR utilizes all qualitative and quantitative methods across the board to ask questions of the healthcare system. It focuses on performance, quality, effectiveness and efficiency of health care services as they relate to health problems of individuals and populations, as well as health care systems and addresses wide-ranging topics of structure, processes, and organization of health care services; their use and people's access to services; efficiency and effectiveness of health care services; the quality of healthcare services and its relationship to health status, and; the uses of medical knowledge.

The term military medicine has a number of potential connotations. It may mean:

Disaster medicine is the area of medical specialization serving the dual areas of providing health care to disaster survivors and providing medically related disaster preparation, disaster planning, disaster response and disaster recovery leadership throughout the disaster life cycle. Disaster medicine specialists provide insight, guidance and expertise on the principles and practice of medicine both in the disaster impact area and healthcare evacuation receiving facilities to emergency management professionals, hospitals, healthcare facilities, communities and governments. The disaster medicine specialist is the liaison between and partner to the medical contingency planner, the emergency management professional, the incident command system, government and policy makers.

Steven Kenneth Galson is an American public health physician. He is currently Senior Vice President for Global Regulatory Affairs & Strategy at Amgen, the California-based biopharmaceutical company. He is also Professor-at-Large at the Keck Graduate Institute for Applied Life Sciences in Claremont, California. He is a retired rear admiral in the United States Public Health Service Commissioned Corps and public health administrator who served as the acting Surgeon General of the United States from October 1, 2007 – October 1, 2009. He served concurrently as acting Assistant Secretary for Health from January 22, 2009 to June 25, 2009, and as the Deputy Director and Director of the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) at the Food and Drug Administration from 2001 to 2007. As the Acting Surgeon General, he was the commander of the United States Public Health Service Commissioned Corps and, while serving as the Assistant Secretary for Health, was the operational head of the Public Health Service.

A hospital is a healthcare institution providing patient treatment with specialized health science and auxiliary healthcare staff and medical equipment. The best-known type of hospital is the general hospital, which typically has an emergency department to treat urgent health problems ranging from fire and accident victims to a sudden illness. A district hospital typically is the major health care facility in its region, with many beds for intensive care and additional beds for patients who need long-term care. Specialized hospitals include trauma centers, rehabilitation hospitals, children's hospitals, seniors' (geriatric) hospitals, and hospitals for dealing with specific medical needs such as psychiatric treatment and certain disease categories. Specialized hospitals can help reduce health care costs compared to general hospitals. Hospitals are classified as general, specialty, or government depending on the sources of income received.
Clinical peer review, also known as medical peer review is the process by which health care professionals, including those in nursing and pharmacy, evaluate each other's clinical performance. A discipline-specific process may be referenced accordingly.
The International Society of Travel Medicine (ISTM) is an international society of physicians, pharmacists, nurses, and other medical professionals based in Dunwoody, United States to promote travel health initiatives. Founded as an organization in 1991, ISTM has built a global network that is committed to the advancement of travel medicine - currently the largest organization of this type. The ISTM fosters research, facilitates the rapid exchange of information, and provides educational programming to serve the travel medicine community. Promoting the development and evaluation of safe, effective, preventive and curative interventions for patients prior to travel, during travel and post travel is an important aspect of supporting the travel medicine community.

Cultural competence in healthcare refers to the ability for healthcare professionals to demonstrate cultural competence toward patients with diverse values, beliefs, and feelings. This process includes consideration of the individual social, cultural, and psychological needs of patients for effective cross-cultural communication with their health care providers. The goal of cultural competence in health care is to reduce health disparities and to provide optimal care to patients regardless of their race, gender, ethnic background, native languages spoken, and religious or cultural beliefs. Cultural competency training is important in health care fields where human interaction is common, including medicine, nursing, allied health, mental health, social work, pharmacy, oral health, and public health fields.

The Gorgas Medal was originally established as an annual award in 1915 by the Medical Reserve Corps Association of New York in honor of Surgeon General William C. Gorgas, U.S. Army. The award was based on a writing competition open to members of the U.S. Army Medical Corps, the U.S. Army Medical Reserve Corps, and to Medical Corps members of other “organized militia”. Surgeon General Gorgas appointed Colonel Charles Richard, Lieutenant Colonel Champe C. McCulloch, Jr., and Major Eugene R. Whitmore, Medical Corps, to form a review board and act as judge and jury for the writing competition. These officers were members of the Army Medical School faculty.
References
- ↑ United States Congress (1903). . United States Statutes at Large, Volume 32– via Wikisource. [ scan
 ]
] - ↑ Military Medicine, AMSUS, The Society of Federal Health Professionals, (2022)