
Ujung Kulon National Park is a national park at the westernmost tip of Java, located in Sumer District of Pandeglang Regency, part of Banten province of Indonesia. It once included the volcanic island group of Krakatoa in Lampung province, although current maps suggest the Krakatoa island group as its own protected area, the Pulau Anak Krakatau Marine Nature Reserve.

Satpura Tiger Reserve (STR) also known as Satpura National Park is located in the Hoshangabad district of Madhya Pradesh in India. Its name is derived from the Satpura range. It covers an area of 524 km2 (202 sq mi). Satpura National Park, along with the adjoining Bori and Pachmarhi wildlife sanctuaries, provides 2,200 km2 (850 sq mi) of unique central Indian highland ecosystem. It was set up in 1981.

Grass jelly, also known as leaf jelly or herb jelly, is a jelly-like dessert originating from China. It is commonly consumed in East Asia and Southeast Asia. It is created by using Chinese mesona and has a mild, slightly bitter taste. Grass jelly was invented by the Hakka people who historically used the food to alleviate heat stroke after long days working in the field. The dish was introduced to Southeast Asia by the Chinese diaspora. It is served chilled, with other toppings such as fruit, or in bubble tea or other drinks. Outside Asia, it is sold in Asian supermarkets.

Secondary succession is the secondary ecological succession of a plant's life. As opposed to the first, primary succession, secondary succession is a process started by an event that reduces an already established ecosystem to a smaller population of species, and as such secondary succession occurs on preexisting soil whereas primary succession usually occurs in a place lacking soil. Many factors can affect secondary succession, such as trophic interaction, initial composition, and competition-colonization trade-offs. The factors that control the increase in abundance of a species during succession may be determined mainly by seed production and dispersal, micro climate; landscape structure ; bulk density, pH, and soil texture.

Melastoma is a genus in the family Melastomataceae. It has over 100 species distributed around Southeast Asia, India, north to Japan, south to Australia and the Pacific Islands. The number of species should probably be reduced according to some sources. Many species have been planted around the world for the aesthetic value of their bright purple flowers.

Melastoma affine, also known by the common names blue tongue or native lassiandra, is a shrub of the family Melastomataceae. Distributed in tropical and sub-tropical forests of India, South-east Asia and Australia, it is a plant of rainforest margins. Bees are the principal pollinators of this species.

Kaeng Krachan National Park is the largest national park of Thailand. It is on the border with Burma, contiguous with the Tanintharyi Nature Reserve. It is a popular park owing to its proximity to the tourist town of Hua Hin. It was named a UNESCO World Heritage Site on 26 July 2021, despite concerns from the OHCHR around the human rights violations of the indigenous people that live in the park.

The yellow-breasted flowerpecker is a species of bird in the family Dicaeidae. It is found in Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar, Singapore, and Thailand. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forest and subtropical or tropical moist montane forest.
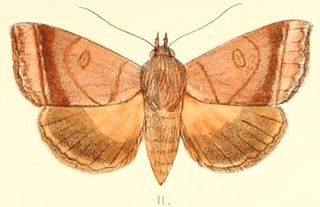
Ophiusa trapezium is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Achille Guenée in 1852. It is found from the Indo-Australian tropics of India, Sri Lanka to Queensland, the Bismarck Islands and New Caledonia. Adults are fruit piercers.
Melastoma denticulatum is a species of flowering plant in the family Melastomataceae, native from the Solomon Islands to the south Pacific.

Ategumia adipalis is a moth of the family Crambidae described by Julius Lederer in 1863. It is found from India to Australia and in Japan, Sri Lanka, Vietnam and China. It was introduced to Hawaii in 1965.

Agrotera basinotata is a moth of the family Crambidae described by George Hampson in 1891. It is native to Queensland, Thailand, Hong Kong and Japan, but was introduced to Hawaii for the control of Melastoma malabathricum.

Gatesclarkeana idia is a moth of the family Tortricidae. It is found in Japan, Taiwan, China, Indonesia, Thailand and Vietnam.
Phu Soi Dao National Park named after 2,120 metres (6,960 ft) high Phu Soi Dao mountain, is a protected area at the southern end of the Luang Prabang Range in the Thai/Lao border area, on the Thai side of the range. It is located in Ban Khok and Nam Pat Districts of Uttaradit Province and Chat Trakan District of Phitsanulok Province. The park was established as Thailand's 109th national park in 2008.

Melastoma malabathricum, known also as Malabar melastome, Indian rhododendron, Singapore rhododendron, planter's rhododendron and senduduk, is a flowering plant in the family Melastomataceae. Despite its common names, it does not have any connection to actual rhododendrons, and belongs to the Rosids clade as opposed to the Asterids clade. This plant is native to Indomalaya, Japan and Australia, and is usually found at elevations between 100 m and 2,800 m in grassland and sparse forest habitats. It has been used as a medicinal plant in certain parts of the world, but has been declared a noxious weed in the United States. M. malabathricum is a known hyperaccumulator of aluminium, and as such can be used for phytoremediation.
Homona eductana is a species of moth of the family Tortricidae. It is found in India, Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore and China.

Homona tabescens is a species of moth of the family Tortricidae. It is found in south-east Asia, where it has been recorded from Java, Sabah, China, Thailand, Malaysia, New Guinea and Vietnam.

Melastoma septemnervium are erect shrubs or small slender trees with 5 petal, medium-sized, pink flowers that have made them attractive for cultivation. The leaves have the 5 distinctive longitudinal veins (nerves) typical of plants in the family Melastomataceae.

Melastoma sanguineum is called red melastome or fox-tongued melastoma in English. They are erect shrubs or small slender trees with medium-sized violet-pink colored flowers with 6 petals that have made them attractive for cultivation. The leaves have the 5 distinctive longitudinal veins (nerves) typical of plants in the family Melastomataceae.
Melastoma malabituin is a species of shrubs in the plant family Melastomataceae. It is native to the island of Luzon in the Philippines. It was discovered by Filipino botanist John Michael Agcaoilli in 1997 and first described in 2020.















