
Hurricane Lane was the strongest Pacific hurricane to make landfall in Mexico since Hurricane Kenna of 2002. The thirteenth named storm, ninth hurricane, and sixth major hurricane of the 2006 Pacific hurricane season, Lane developed on September 13 from a tropical wave to the south of Mexico. It moved northwestward, parallel to the coast of Mexico, and steadily intensified in an area conducive to further strengthening. After turning to the northeast, Lane attained peak winds of 125 mph (205 km/h), and made landfall in the state of Sinaloa at peak strength. It rapidly weakened and dissipated on September 17, and later brought precipitation to southern part of the U.S. state of Texas.
The 1925 Pacific hurricane season ran through the summer and fall of 1925. Before the satellite age started in the 1960s, data on east Pacific hurricanes was extremely unreliable. Most east Pacific storms were of no threat to land. 1925 season was the first Pacific hurricane season that was covered in detail by Monthly Weather Review, and this season included the most intense November Pacific hurricane on record until beaten by Hurricane Kenneth in 2011.

Hurricane Tico is one of four major hurricanes to ever strike Mazatlan, and one of the strongest landfalling Pacific hurricanes on record. Tico was the twenty-third tropical cyclone, nineteenth named storm, eleventh hurricane, and eighth major hurricane of the 1983 Pacific hurricane season.The origins of Hurricane Tico were from a weak tropical disturbance that crossed Costa Rica into the Pacific Ocean on October 7, 1983. Over warm waters, the system was sufficiently organized to be declared Tropical Depression Twenty-One on October 11, about 575 mi (930 km) south of Acapulco. On October 12 it turned sharply northward; the depression was upgraded to Tropical Storm Tico on October 13. Tropical Storm Tico continued to intensify. Two days after becoming a tropical storm, Tico strengthened further to attain hurricane status. Early on October 19, it reached peak winds of 130 mph (215 km/h). It weakened slightly as it approached the coast, and at about 1500 UTC that day Tico made landfall near Mazatlán with winds of 125 mph (205 km/h). The remains were tracked into the Mid-Atlantic States for five more days.

Hurricane Bridget of June 1971 was one of the worst hurricanes to strike the Mexican city of Acapulco. It formed on June 14 as a tropical depression, which is a minimal tropical cyclone with winds less than gale force. However, it was soon upgraded to a tropical storm, and Bridget steadily intensified to become a hurricane on June 15. After peaking at Category 2 intensity, it weakened to a tropical storm on June 17, then made landfall in Mexico. Hours later, however, it turned offshore as a tropical depression. Bridget dissipated on June 20 after leaving heavy damage and 17 deaths in the Acapulco area.

Hurricane Virgil was a late season hurricane of the 1992 Pacific hurricane season that struck southwestern Mexico in October 1992. Forming from a tropical wave that left Africa on September 13, it slowly developed into a tropical depression. It soon strengthened into Tropical Storm Virgil, and rapidly intensified into a hurricane on October 2. Continuing to intensify, the hurricane attained major hurricane strength, and peaked as a Category 4 hurricane off the coast of Mexico. Shortly before landfall, it weakened to a Category 2 hurricane, and it dissipated on October 5. Damage was generally minimal, though one person was reported missing.

Hurricane Tina was the strongest and longest-lived storm of the 1992 Pacific hurricane season, which also threatened land for a brief period. The twenty-fourth tropical cyclone, twenty-second tropical storm, fourteenth hurricane, and eighth major hurricane of the record breaking season, Tina formed from a tropical wave on September 17. The storm moved towards the west and strengthened into a hurricane. A breakdown in a ridge and to the north and a trough then re-curved Tina to the northeast and towards land, still moving slowly and gradually slowing down. The trough broke down and was replaced by a strong ridge. Tina then changed direction again and headed out to sea. It intensified into a Category 4 storm with winds of 150 mph (240 km/h) and a central pressure of 932 millibars. Tina then slowly weakened as it turned to the north. Tropical Depression Tina dissipated on October 11, shortly after entering the Central Pacific Hurricane Center's area of responsibility. Although the tropical cyclone never made landfall, heavy rains were recorded across western Mexico. While at peak intensity, the storm also displayed annular characteristics.
Atoyac de Álvarez is a city and seat of the municipality of Atoyac de Álvarez, in the state of Guerrero, south-western Mexico. It was affected by Hurricane Manuel in 2013.

Hurricane Olivia was considered the worst hurricane to hit Mazatlán, Sinaloa since 1943, in addition to being the strongest landfalling and costliest hurricane of the 1975 Pacific hurricane season. Olivia formed on October 22 to the south of Mexico, quickly intensifying into a tropical storm. The storm moved northwestward initially, followed by a northeast turn. On October 23, Olivia attained hurricane status, and the next day reached Category 3 intensity on the Saffir-Simpson scale just before moving ashore Mazatlán in northwest Mexico. Olivia destroyed 7,000 houses in the region, leaving 30,000 people homeless, and damage totaled $20 million. The hurricane killed 30 people, 20 of them from drowning in shrimp boats.
The Atoyac River is a river in Oaxaca, Mexico. The Atoyac flows into the Rio Verde which empties into the Pacific near Laguna Chacahua, in Lagunas de Chacahua National Park, 90 km west of Puerto Escondido. The mountainous terrain of the region it occupies allows for no navigable rivers; instead, there are a large number of smaller ones, which often change name from area to area. The continental divide passes through the state, meaning that there is drainage towards both the Gulf of Mexico and the Pacific Ocean. Most of the drainage towards the Gulf is represented by the Papaloapan and Coatzacoalcos Rivers and their tributaries such as the Grande and Salado Rivers. Three rivers account for most of the water headed for the Pacific: the Mixteco River, Tehuantepec River, and the Atoyac, with their tributaries.

Tropical Storm Andres is one out of two tropical cyclones on record to strike El Salvador. The first named storm of the active 1997 Pacific hurricane season, Andres formed on June 1 off the coast of Mexico. It initially moved toward the coast, although a change in steering winds turned the storm toward Mexico and Guatemala. After passing just offshore, Andres again changed direction toward the southeast, gradually weakening in the process. On June 7, it turned toward and hit El Salvador before dissipating. The storm brought rainfall to coastlines along much of its path, destroying some houses and inflicted damage. Two fishermen were reported missing in Nicaragua due to high seas, and there were four deaths in El Salvador.
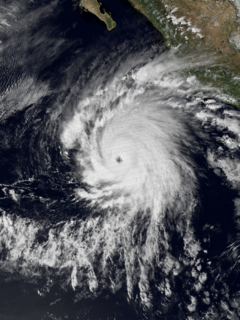
Hurricane Roslyn was the strongest hurricane in the 1986 Pacific hurricane season. The 17th and final named storm of the season, Roslyn developed on October 15 to the south of Mexico. Its movement was initially guided by a ridge to its north, and it became a tropical storm on October 16 and a hurricane a day later. The hurricane reached peak winds of 145 mph (233 km/h) on October 19 before weakening and turning to the northeast. Roslyn ultimately moved ashore near Mazatlán, Sinaloa as a minimal hurricane, where it caused minimal damage due to the light population affected. It rapidly dissipated, although the remnants brought precipitation to Texas and other portions of the central and southern United States. There were no fatalities, and reported damage was minor.

Hurricane Madeline was the second landfalling major hurricane along the Pacific coast of Mexico in a week. Madeline formed on September 29, not far from Central America. The next day, the circulation dissipated, and as a result weakened to a remnant low. Four days later, on October 3, the low regenerated into a tropical depression. The system remained weak for three days as it drifted west-northwest. When it began to recurve towards Mexico on October 6, the cyclone rapidly intensified and eventually made landfall at peak intensity as a Category 4. Shortly after landfall, the cyclone rapidly dissipated.

Hurricane Dolores was regarded as the worst hurricane to strike Acapulco since 1938. Developing on June 13, 1974, the system rapidly organized into a tropical storm the next day off the southern coast of Mexico. Over the following day, Dolores developed an eye-like feature and attained hurricane status. With peak winds of 80 mph (130 km/h), the storm made landfall near Acapulco. Once onshore, Dolores rapidly dissipated and was last noted on June 17.

Hurricane Odile was the second of three tropical storms to make landfall in Mexico during the 1984 Pacific hurricane season. The fifteenth named storm and twelfth hurricane of the active season, it developed from a tropical disturbance about 185 miles (300 km) south of Acapulco on September 17. Curving towards the northwest, Odile became a Category 1 hurricane on September 19. The tropical cyclone reached its peak intensity with winds of 105 mph (165 km/h) two days later; however, Hurricane Odile began to weaken as moved erratically it encountered less favorable conditions and was downgraded to a tropical storm shortly before making landfall northwest of Zihuatanejo. Over land, the storm rapidly weakened, and dissipated on September 23. The storm caused significant rainfall accumulations of 24.73 inches (628.1 mm) in Southern Mexico, resulting in severe damage to tourism resorts. Flooding from Odile resulted in the evacuation of 7,000 people, 21 deaths, and the damage of about 900 homes.
The 1942–48 Pacific hurricane seasons all began during late spring in the northeast Pacific Ocean and the central Pacific. They ended in late fall.











