Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia is a subtype of pneumocytic hyperplasia in the lung. It can be a precursor lesion of in situ adenocarcinoma of the lung (bronchioloalveolar carcinoma). In prostate tissue biopsy, it can be confused for adenocarcinoma of the prostate. The needle biopsy rate is less than 1%.
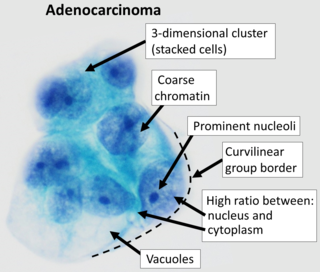
Adenocarcinoma is a type of cancerous tumor that can occur in several parts of the body. It is defined as neoplasia of epithelial tissue that has glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or both. Adenocarcinomas are part of the larger grouping of carcinomas, but are also sometimes called by more precise terms omitting the word, where these exist. Thus invasive ductal carcinoma, the most common form of breast cancer, is adenocarcinoma but does not use the term in its name—however, esophageal adenocarcinoma does to distinguish it from the other common type of esophageal cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Several of the most common forms of cancer are adenocarcinomas, and the various sorts of adenocarcinoma vary greatly in all their aspects, so that few useful generalizations can be made about them.
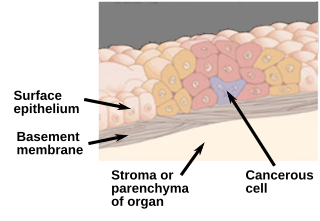
Carcinoma in situ (CIS) is a group of abnormal cells. While they are a form of neoplasm, there is disagreement over whether CIS should be classified as cancer. This controversy also depends on the exact CIS in question. Some authors do not classify them as cancer, however, recognizing that they can potentially become cancer. Others classify certain types as a non-invasive form of cancer. The term "pre-cancer" has also been used.

Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) is a rare, progressive and systemic disease that typically results in cystic lung destruction. It predominantly affects women, especially during childbearing years. The term sporadic LAM is used for patients with LAM not associated with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC), while TSC-LAM refers to LAM that is associated with TSC.
The International Classification of Diseases for Oncology (ICD-O) is a domain-specific extension of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems for tumor diseases. This classification is widely used by cancer registries.

Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) of the lung —previously included in the category of "bronchioloalveolar carcinoma" (BAC)—is a subtype of lung adenocarcinoma. It tends to arise in the distal bronchioles or alveoli and is defined by a non-invasive growth pattern. This small solitary tumor exhibits pure alveolar distribution and lacks any invasion of the surrounding normal lung. If completely removed by surgery, the prognosis is excellent with up to 100% 5-year survival.

Endometrial hyperplasia is a condition of excessive proliferation of the cells of the endometrium, or inner lining of the uterus.

Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) is an incidental microscopic finding with characteristic cellular morphology and multifocal tissue patterns. The condition is a laboratory diagnosis and refers to unusual cells in the lobules of the breast. The lobules and acini of the terminal duct-lobular unit (TDLU), the basic functional unit of the breast, may become distorted and undergo expansion due to the abnormal proliferation of cells comprising the structure. These changes represent a spectrum of atypical epithelial lesions that are broadly referred to as lobular neoplasia (LN).
In urologic pathology, atypical small acinar proliferation, is a collection of small prostatic glands, on prostate biopsy, whose significance is uncertain and cannot be determined to be benign or malignant.

High-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (HGPIN) is an abnormality of prostatic glands and believed to precede the development of prostate adenocarcinoma.
The Bethesda system (TBS), officially called The Bethesda System for Reporting Cervical Cytology, is a system for reporting cervical or vaginal cytologic diagnoses, used for reporting Pap smear results. It was introduced in 1988 and revised in 1991, 2001, and 2014. The name comes from the location of the conference, sponsored by the National Institutes of Health, that established the system.

Atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) is the term used for a benign lesion of the breast that indicates an increased risk of breast cancer.
Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma of the lung (MCACL) is a very rare malignant mucus-producing neoplasm arising from the uncontrolled growth of transformed epithelial cells originating in lung tissue.

Adenocarcinoma of the lung is the most common type of lung cancer, and like other forms of lung cancer, it is characterized by distinct cellular and molecular features. It is classified as one of several non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC), to distinguish it from small cell lung cancer which has a different behavior and prognosis. Lung adenocarcinoma is further classified into several subtypes and variants. The signs and symptoms of this specific type of lung cancer are similar to other forms of lung cancer, and patients most commonly complain of persistent cough and shortness of breath.
Acinar adenocarcinoma is a histological subtype of gland-forming cancer that is diagnosed when cuboidal and/or columnar shaped malignant cells in the neoplastic tissue form acini and tubules. It is a common form of cancer occurring in the lung and prostate gland.
Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (AAH) is a hyperplastic lesion of the epithelial lining of pulmonary alveoli.
Pneumocytic hyperplasia is an hyperplasia of pneumocytes lining pulmonary alveoli.

Multifocal micronodular pneumocyte hyperplasia (MMPH) is a subtype of pneumocytic hyperplasia.
Minimally invasive adenocarcinoma of the lung (MIA) is defined as a small (≤3 cm), solitary tumour with predominant alveolar epithelial appearance, as in situ adenocarcinoma of the lung, with a zone of focal invasion of the stroma with a size inferior to 5 mm. For MIA—as with adenocarcinoma in situ—, the prognosis is near 100% survival.
Pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors are neuroendocrine tumors localized to the lung: bronchus or pulmonary parenchyma.
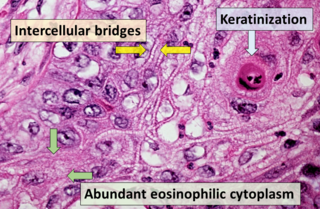
Squamous-cell carcinoma (SCC), also known as epidermoid carcinoma, comprises a number of different types of cancer that begin in squamous cells. These cells form on the surface of the skin, on the lining of hollow organs in the body, and on the lining of the respiratory and digestive tracts.