Related Research Articles
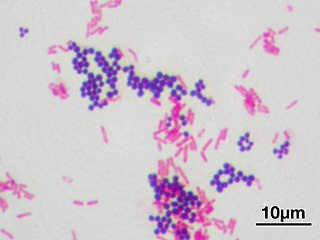
In microbiology and bacteriology, Gram stain, is a method of staining used to classify bacterial species into two large groups: gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria. The name comes from the Danish bacteriologist Hans Christian Gram, who developed the technique in 1884.

In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall.

Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner cytoplasmic cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane.
Peptidoglycan or murein is a unique large macromolecule, a polysaccharide, consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like peptidoglycan layer outside the plasma membrane, the rigid cell wall characteristic of most bacteria. The sugar component consists of alternating residues of β-(1,4) linked N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM). Attached to the N-acetylmuramic acid is a oligopeptide chain made of three to five amino acids. The peptide chain can be cross-linked to the peptide chain of another strand forming the 3D mesh-like layer. Peptidoglycan serves a structural role in the bacterial cell wall, giving structural strength, as well as counteracting the osmotic pressure of the cytoplasm. This repetitive linking results in a dense peptidoglycan layer which is critical for maintaining cell form and withstanding high osmotic pressures, and it is regularly replaced by peptidoglycan production. Peptidoglycan hydrolysis and synthesis are two processes that must occur in order for cells to grow and multiply, a technique carried out in three stages: clipping of current material, insertion of new material, and re-crosslinking of existing material to new material.

Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severity of the condition is variable.

Mycoplasma is a genus of bacteria that, like the other members of the class Mollicutes, lack a cell wall around their cell membranes. Peptidoglycan (murein) is absent. This characteristic makes them naturally resistant to antibiotics that target cell wall synthesis. They can be parasitic or saprotrophic. Several species are pathogenic in humans, including M. pneumoniae, which is an important cause of "walking" pneumonia and other respiratory disorders, and M. genitalium, which is believed to be involved in pelvic inflammatory diseases. Mycoplasma species are among the smallest organisms yet discovered, can survive without oxygen, and come in various shapes. For example, M. genitalium is flask-shaped, while M. pneumoniae is more elongated, many Mycoplasma species are coccoid. Hundreds of Mycoplasma species infect animals.
Atypical pneumonia, also known as walking pneumonia, is any type of pneumonia not caused by one of the pathogens most commonly associated with the disease. Its clinical presentation contrasts to that of "typical" pneumonia. A variety of microorganisms can cause it. When it develops independently from another disease, it is called primary atypical pneumonia (PAP).
Mycoplasma pneumoniae is a very small bacterium in the class Mollicutes. It is a human pathogen that causes the disease mycoplasma pneumonia, a form of atypical bacterial pneumonia related to cold agglutinin disease. M. pneumoniae is characterized by the absence of a peptidoglycan cell wall and resulting resistance to many antibacterial agents. The persistence of M. pneumoniae infections even after treatment is associated with its ability to mimic host cell surface composition.

The periplasm is a concentrated gel-like matrix in the space between the inner cytoplasmic membrane and the bacterial outer membrane called the periplasmic space in gram-negative bacteria. Using cryo-electron microscopy it has been found that a much smaller periplasmic space is also present in gram-positive bacteria.
The cell envelope comprises the inner cell membrane and the cell wall of a bacterium. In gram-negative bacteria an outer membrane is also included. This envelope is not present in the Mollicutes where the cell wall is absent.
Coinfection is the simultaneous infection of a host by multiple pathogen species. In virology, coinfection includes simultaneous infection of a single cell by two or more virus particles. An example is the coinfection of liver cells with hepatitis B virus and hepatitis D virus, which can arise incrementally by initial infection followed by superinfection.

Bacterial pneumonia is a type of pneumonia caused by bacterial infection.
Mycoplasma pneumonia is a form of bacterial pneumonia caused by the bacterial species Mycoplasma pneumoniae. It is also known as PPLO, which is an acronym for Pleuro Pneumonia Like Organism.

The bacteria capsule is a large structure common to many bacteria. It is a polysaccharide layer that lies outside the cell envelope, and is thus deemed part of the outer envelope of a bacterial cell. It is a well-organized layer, not easily washed off, and it can be the cause of various diseases.
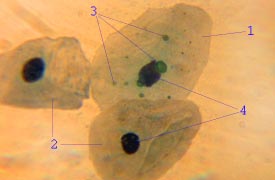
Chlamydia pneumoniae is a species of Chlamydia, an obligate intracellular bacterium that infects humans and is a major cause of pneumonia. It was known as the Taiwan acute respiratory agent (TWAR) from the names of the two original isolates – Taiwan (TW-183) and an acute respiratory isolate designated AR-39. Briefly, it was known as Chlamydophila pneumoniae, and that name is used as an alternate in some sources. In some cases, to avoid confusion, both names are given.
Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) refers to pneumonia contracted by a person outside of the healthcare system. In contrast, hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) is seen in patients who have recently visited a hospital or who live in long-term care facilities. CAP is common, affecting people of all ages, and its symptoms occur as a result of oxygen-absorbing areas of the lung (alveoli) filling with fluid. This inhibits lung function, causing dyspnea, fever, chest pains and cough.
Pneumococcal pneumonia is a type of bacterial pneumonia that is caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus). It is the most common bacterial pneumonia found in adults, the most common type of community-acquired pneumonia, and one of the common types of pneumococcal infection. The estimated number of Americans with pneumococcal pneumonia is 900,000 annually, with almost 400,000 cases hospitalized and fatalities accounting for 5-7% of these cases.
Differential staining is a staining process which uses more than one chemical stain. Using multiple stains can better differentiate between different microorganisms or structures/cellular components of a single organism.
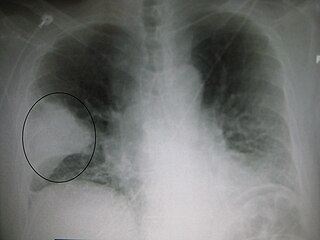
Pneumonia can be classified in several ways, most commonly by where it was acquired, but may also by the area of lung affected or by the causative organism. There is also a combined clinical classification, which combines factors such as age, risk factors for certain microorganisms, the presence of underlying lung disease or systemic disease and whether the person has recently been hospitalized.
Chronic Mycoplasma pneumonia and Chlamydia pneumonia infections are associated with the onset and exacerbation of asthma. These microbial infections result in chronic lower airway inflammation, impaired mucociliary clearance, an increase in mucous production and eventually asthma. Furthermore, children who experience severe viral respiratory infections early in life have a high possibility of having asthma later in their childhood. These viral respiratory infections are mostly caused by respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and human rhinovirus (HRV). Although RSV infections increase the risk of asthma in early childhood, the association between asthma and RSV decreases with increasing age. HRV on the other hand is an important cause of bronchiolitis and is strongly associated with asthma development. In children and adults with established asthma, viral upper respiratory tract infections (URIs), especially HRVs infections, can produce acute exacerbations of asthma. Thus, Chlamydia pneumoniae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae and human rhinoviruses are microbes that play a major role in non-atopic asthma.
References
- ↑ de Souza Luna, Luciano Kleber; Panning, Marcus; Grywna, Klaus; Pfefferle, Susanne; Drosten, Christian (March 2007). "Spectrum of Viruses and Atypical Bacteria in Intercontinental Air Travelers with Symptoms of Acute Respiratory Infection". Journal of Infectious Diseases. 195 (5): 675–679. doi: 10.1086/511432 . PMC 7199876 . PMID 17262708.
- ↑ Liechti, George (February 27, 2014). "A new metabolic cell-wall labelling method reveals peptidoglycan in Chlamydia trachomatis". Nature. 506 (7489): 507–510. doi:10.1038/nature12892. PMC 3997218 . PMID 24336210.
- ↑ Mina, M; Burke, R; Klugman, K (May 1, 2014). "Estimating the prevalence of coinfection with influenza virus and the atypical bacteria Bordetella pertussis, Chlamydophila pneumoniae, and Mycoplasma pneumoniae". European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases. BrowZine Library. 33 (9): 1585–1589. doi:10.1007/s10096-014-2120-0. PMC 4835343 . PMID 24789653.