Related Research Articles

The IBM 704 is the model name of a large digital mainframe computer introduced by IBM in 1954. Designed by John Backus and Gene Amdahl, it was the first mass-produced computer with hardware for floating-point arithmetic. The IBM 704 Manual of operation states:
The type 704 Electronic Data-Processing Machine is a large-scale, high-speed electronic calculator controlled by an internally stored program of the single address type.

The IBM 1620 was announced by IBM on October 21, 1959, and marketed as an inexpensive scientific computer. After a total production of about two thousand machines, it was withdrawn on November 19, 1970. Modified versions of the 1620 were used as the CPU of the IBM 1710 and IBM 1720 Industrial Process Control Systems.

The IBM 650 Magnetic Drum Data-Processing Machine is an early digital computer produced by IBM in the mid-1950s. It was the first mass-produced computer in the world. Almost 2,000 systems were produced, the last in 1962, and it was the first computer to make a meaningful profit. The first one was installed in late 1954 and it was the most popular computer of the 1950s.

The JOHNNIAC was an early computer built by the RAND Corporation and based on the von Neumann architecture that had been pioneered on the IAS machine. It was named in honor of von Neumann, short for John von NeumannNumerical Integrator and Automatic Computer.
The Cyclone is a vacuum-tube computer, built by Iowa State College at Ames, Iowa. The computer was commissioned in July 1959. It was based on the IAS architecture developed by John von Neumann. The Cyclone was based on ILLIAC, the University of Illinois Automatic Computer. The Cyclone used 40-bit words, used two 20-bit instructions per word, and each instruction had an eight-bit op-code and a 12-bit operand or address field. In general IAS-based computers were not code compatible with each other, although originally math routines which ran on the ILLIAC would also run on the Cyclone.

The UNIVAC 1100/2200 series is a series of compatible 36-bit computer systems, beginning with the UNIVAC 1107 in 1962, initially made by Sperry Rand. The series continues to be supported today by Unisys Corporation as the ClearPath Dorado Series. The solid-state 1107 model number was in the same sequence as the earlier vacuum-tube computers, but the early computers were not compatible with their solid-state successors.

The UNIVAC 1103 or ERA 1103, a successor to the UNIVAC 1101, is a computer system designed by Engineering Research Associates and built by the Remington Rand corporation in October 1953. It was the first computer for which Seymour Cray was credited with design work.

The IBM 709 is a computer system that was initially announced by IBM in January 1957 and first installed during August 1958. The 709 was an improved version of its predecessor, the IBM 704, and was the third of the IBM 700/7000 series of scientific computers. The improvements included overlapped input/output, indirect addressing, and three "convert" instructions which provided support for decimal arithmetic, leading zero suppression, and several other operations. The 709 had 32,768 words of 36-bit magnetic core memory and could execute 42,000 add or subtract instructions per second. It could multiply two 36-bit integers at a rate of 5000 per second.

The IBM 700/7000 series is a series of large-scale (mainframe) computer systems that were made by IBM through the 1950s and early 1960s. The series includes several different, incompatible processor architectures. The 700s use vacuum-tube logic and were made obsolete by the introduction of the transistorized 7000s. The 7000s, in turn, were eventually replaced with System/360, which was announced in 1964. However the 360/65, the first 360 powerful enough to replace 7000s, did not become available until November 1965. Early problems with OS/360 and the high cost of converting software kept many 7000s in service for years afterward.

The HP 2100 is a series of 16-bit minicomputers that were produced by Hewlett-Packard (HP) from the mid-1960s to early 1990s. Tens of thousands of machines in the series were sold over its twenty-five year lifetime, making HP the fourth largest minicomputer vendor during the 1970s.
In computing, a word is the natural unit of data used by a particular processor design. A word is a fixed-sized datum handled as a unit by the instruction set or the hardware of the processor. The number of bits or digits in a word is an important characteristic of any specific processor design or computer architecture.

The LGP-30, standing for Librascope General Purpose and then Librascope General Precision, is an early off-the-shelf computer. It was manufactured by the Librascope company of Glendale, California, and sold and serviced by the Royal Precision Electronic Computer Company, a joint venture with the Royal McBee division of the Royal Typewriter Company. The LGP-30 was first manufactured in 1956, at a retail price of $47,000, equivalent to $530,000 in 2023.

IBM 7070 is a decimal-architecture intermediate data-processing system that was introduced by IBM in 1958. It was part of the IBM 700/7000 series, and was based on discrete transistors rather than the vacuum tubes of the 1950s. It was the company's first transistorized stored-program computer.

The CDC 6000 series is a discontinued family of mainframe computers manufactured by Control Data Corporation in the 1960s. It consisted of the CDC 6200, CDC 6300, CDC 6400, CDC 6500, CDC 6600 and CDC 6700 computers, which were all extremely rapid and efficient for their time. Each is a large, solid-state, general-purpose, digital computer that performs scientific and business data processing as well as multiprogramming, multiprocessing, Remote Job Entry, time-sharing, and data management tasks under the control of the operating system called SCOPE. By 1970 there also was a time-sharing oriented operating system named KRONOS. They were part of the first generation of supercomputers. The 6600 was the flagship of Control Data's 6000 series.

The Elliott 803 is a small, medium-speed transistor digital computer which was manufactured by the British company Elliott Brothers in the 1960s. About 211 were built.
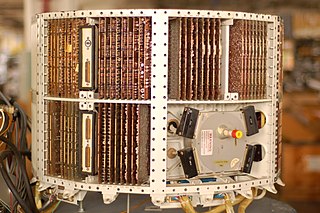
The D-17B (D17B) computer was used in the Minuteman I NS-1OQ missile guidance system. The complete guidance system contained a D-17B computer, the associated stable platform, and power supplies.
The D-37C (D37C) is the computer component of the all-inertial NS-17 Missile Guidance Set (MGS) for accurately navigating to its target thousands of miles away. The NS-17 MGS was used in the Minuteman II (LGM-30F) ICBM. The MGS, originally designed and produced by the Autonetics Division of North American Aviation, could store multiple preprogrammed targets in its internal memory.

The SDS 9 Series computers are a backward compatible line of transistorized computers produced by Scientific Data Systems in the 1960s and 1970s. This line includes the SDS 910, SDS 920, SDS 925, SDS 930, SDS 940, and the SDS 945. The SDS 9300 is an extension of the 9xx architecture. The 1965 SDS 92 is an incompatible 12-bit system built using monolithic integrated circuits.

The Monroe Calculating Machine Mark XI was a general-purpose stored-program electronic digital computer introduced in 1960 by the Monroe Calculating Machine Division of Litton Industries. The system was marketed for "primarily for billing, and invoice writing", but could also be used for low-end scientific computing.
Philco was one of the pioneers of transistorized computers, also known as second generation computers. After the company developed the surface barrier transistor, which was much faster than previous point-contact types, it was awarded contracts for military and government computers. Commercialized derivatives of some of these designs became successful business and scientific computers. The TRANSAC Model S-1000 was released as a scientific computer. The TRANSAC S-2000 mainframe computer system was first produced in 1958, and a family of compatible machines, with increasing performance, was released over the next several years.
References
- ↑ D, Goldstein, Gordon (January 1958). "COMPUTERS AND DATA PROCESSORS. NORTH AMERICA - Autonetics, RECOMP II, Downey, California". Digital Computer Newsletter. 10 (1): 1.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)[ dead link ] - ↑ Weik, Martin H. (Mar 1961). "RECOMP II". ed-thelen.org. A Third Survey of Domestic Electronic Digital Computing Systems.
- ↑ Autonetics Recomp Theory of Operation