Related Research Articles
Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop. Developmental biology also encompasses the biology of regeneration, asexual reproduction, metamorphosis, and the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism.

In biology, tissue is a historically derived biological organizational level between cells and a complete organ. A tissue is therefore often thought of as an assembly of similar cells and their extracellular matrix from the same embryonic origin that together carry out a specific function. Organs are then formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues.

Exponential growth is a process that increases quantity over time at an ever-increasing rate. It occurs when the instantaneous rate of change of a quantity with respect to time is proportional to the quantity itself. Described as a function, a quantity undergoing exponential growth is an exponential function of time, that is, the variable representing time is the exponent. Exponential growth is the inverse of logarithmic growth.

The vascular cambium is the main growth tissue in the stems and roots of many plants, specifically in dicots such as buttercups and oak trees, gymnosperms such as pine trees, as well as in certain other vascular plants. It produces secondary xylem inwards, towards the pith, and secondary phloem outwards, towards the bark.
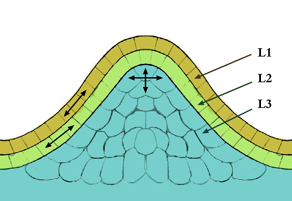
The meristem is a type of tissue found in plants. It consists of undifferentiated cells capable of cell division. Cells in the meristem can develop into all the other tissues and organs that occur in plants. These cells continue to divide until a time when they get differentiated and then lose the ability to divide.

In materials science and solid mechanics, Poisson's ratio (nu) is a measure of the Poisson effect, the deformation of a material in directions perpendicular to the specific direction of loading. The value of Poisson's ratio is the negative of the ratio of transverse strain to axial strain. For small values of these changes, is the amount of transversal elongation divided by the amount of axial compression. Most materials have Poisson's ratio values ranging between 0.0 and 0.5. For soft materials, such as rubber, where the bulk modulus is much higher than the shear modulus, Poisson's ratio is near 0.5. For open-cell polymer foams, Poisson's ratio is near zero, since the cells tend to collapse in compression. Many typical solids have Poisson's ratios in the range of 0.2–0.3. The ratio is named after the French mathematician and physicist Siméon Poisson.

Plant hormones are signal molecules, produced within plants, that occur in extremely low concentrations. Plant hormones control all aspects of plant growth and development, including embryogenesis, the regulation of organ size, pathogen defense, stress tolerance and reproductive development. Unlike in animals each plant cell is capable of producing hormones. Went and Thimann coined the term "phytohormone" and used it in the title of their 1937 book.

A pollen tube is a tubular structure produced by the male gametophyte of seed plants when it germinates. Pollen tube elongation is an integral stage in the plant life cycle. The pollen tube acts as a conduit to transport the male gamete cells from the pollen grain—either from the stigma to the ovules at the base of the pistil or directly through ovule tissue in some gymnosperms. In maize, this single cell can grow longer than 12 inches (30 cm) to traverse the length of the pistil.

Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds necessary for plant growth and reproduction, plant metabolism and their external supply. In its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle, or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite. This is in accordance with Justus von Liebig’s law of the minimum. The total essential plant nutrients include seventeen different elements: carbon, oxygen and hydrogen which are absorbed from the air, whereas other nutrients including nitrogen are typically obtained from the soil.

Auxins are a class of plant hormones with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essential for plant body development. The Dutch biologist Frits Warmolt Went first described auxins and their role in plant growth in the 1920s. Kenneth V. Thimann became the first to isolate one of these phytohormones and to determine its chemical structure as indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). Went and Thimann co-authored a book on plant hormones, Phytohormones, in 1937.
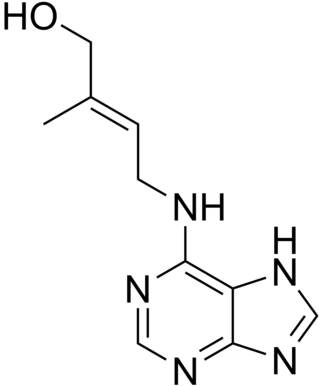
Cytokinins (CK) are a class of plant hormones that promote cell division, or cytokinesis, in plant roots and shoots. They are involved primarily in cell growth and differentiation, but also affect apical dominance, axillary bud growth, and leaf senescence.
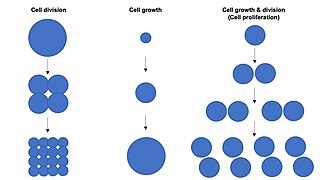
Cell growth refers to an increase in the total mass of a cell, including both cytoplasmic, nuclear and organelle volume. Cell growth occurs when the overall rate of cellular biosynthesis is greater than the overall rate of cellular degradation.
1-Triacontanol (n-triacontanol) is a fatty alcohol of the general formula C30H62O, also known as melissyl alcohol or myricyl alcohol. It is found in plant cuticle waxes and in beeswax. Triacontanol is a growth stimulant for many plants, most notably roses, in which it rapidly increases the number of basal breaks. 1-Triacontanol is a natural plant growth regulator. It has been widely used to enhance the yield of various crops around the world, mainly in Asia. Triacontanol has been reported to increase the growth of plants by enhancing the rates of photosynthesis, protein biosynthesis, the transport of nutrients in a plant and enzyme activity, reducing complex carbohydrates among many other purposes. The fatty alcohol appears to increase the physiological efficiency of plant cells and boost the potential of the cells responsible for the growth and maturity of a plant.

Gravitropism is a coordinated process of differential growth by a plant in response to gravity pulling on it. It also occurs in fungi. Gravity can be either "artificial gravity" or natural gravity. It is a general feature of all higher and many lower plants as well as other organisms. Charles Darwin was one of the first to scientifically document that roots show positive gravitropism and stems show negative gravitropism. That is, roots grow in the direction of gravitational pull and stems grow in the opposite direction. This behavior can be easily demonstrated with any potted plant. When laid onto its side, the growing parts of the stem begin to display negative gravitropism, growing upwards. Herbaceous (non-woody) stems are capable of a degree of actual bending, but most of the redirected movement occurs as a consequence of root or stem growth outside. The mechanism is based on the Cholodny–Went model which was proposed in 1927, and has since been modified. Although the model has been criticized and continues to be refined, it has largely stood the test of time.

Vascular tissue is a complex conducting tissue, formed of more than one cell type, found in vascular plants. The primary components of vascular tissue are the xylem and phloem. These two tissues transport fluid and nutrients internally. There are also two meristems associated with vascular tissue: the vascular cambium and the cork cambium. All the vascular tissues within a particular plant together constitute the vascular tissue system of that plant.

In botany, secondary growth is the growth that results from cell division in the cambia or lateral meristems and that causes the stems and roots to thicken, while primary growth is growth that occurs as a result of cell division at the tips of stems and roots, causing them to elongate, and gives rise to primary tissue. Secondary growth occurs in most seed plants, but monocots usually lack secondary growth. If they do have secondary growth, it differs from the typical pattern of other seed plants.

A primordium in embryology, is an organ or tissue in its earliest recognizable stage of development. Cells of the primordium are called primordial cells. A primordium is the simplest set of cells capable of triggering growth of the would-be organ and the initial foundation from which an organ is able to grow. In flowering plants, a floral primordium gives rise to a flower.
Turgor pressure is the force within the cell that pushes the plasma membrane against the cell wall.
Acid growth refers to the ability of plant cells and plant cell walls to elongate or expand quickly at low (acidic) pH. The cell wall needs to be modified in order to maintain the turgor pressure. This modification is controlled by plant hormones like auxin. Auxin also controls the expression of some cell wall genes. This form of growth does not involve an increase in cell number. During acid growth, plant cells enlarge rapidly because the cell walls are made more extensible by expansin, a pH-dependent wall-loosening protein. Expansin loosens the network-like connections between cellulose microfibrils within the cell wall, which allows the cell volume to increase by turgor and osmosis. A typical sequence leading up to this would involve the introduction of a plant hormone (auxin, for example) that causes protons (H+ ions) to be pumped out of the cell into the cell wall. As a result, the cell wall solution becomes more acidic. It was suggested by different scientist that the epidermis is a unique target of the auxin but this theory has been disapproved over time. This activates expansin activity, causing the wall to become more extensible and to undergo wall stress relaxation, which enables the cell to take up water and to expand. The acid growth theory has been very controversial in the past.

In biology, phototropism is the growth of an organism in response to a light stimulus. Phototropism is most often observed in plants, but can also occur in other organisms such as fungi. The cells on the plant that are farthest from the light contain a hormone called auxin that reacts when phototropism occurs. This causes the plant to have elongated cells on the furthest side from the light. Phototropism is one of the many plant tropisms, or movements, which respond to external stimuli. Growth towards a light source is called positive phototropism, while growth away from light is called negative phototropism. Negative phototropism is not to be confused with skototropism, which is defined as the growth towards darkness, whereas negative phototropism can refer to either the growth away from a light source or towards the darkness. Most plant shoots exhibit positive phototropism, and rearrange their chloroplasts in the leaves to maximize photosynthetic energy and promote growth. Some vine shoot tips exhibit negative phototropism, which allows them to grow towards dark, solid objects and climb them. The combination of phototropism and gravitropism allow plants to grow in the correct direction.
References
- ↑ Types of Growth: Auxetic Growth, Tutor Vista
- ↑ Juo, Pei-show (21 December 2001). Concise Dictionary of Biomedicine and Molecular Biology. CRC Press. p. 130. ISBN 9781420041309.