
Podoviridae is a family of bacteriophage in the order Caudovirales often associated with T-7 like phages. There are 130 species in this family, assigned to 3 subfamilies and 52 genera. This family is characterized by having very short, noncontractile tails. Podoviradae are largely understudied and most new isolates are of the phicbkviruses genus, a group of giant viruses that appear to be Caulobacter specific.
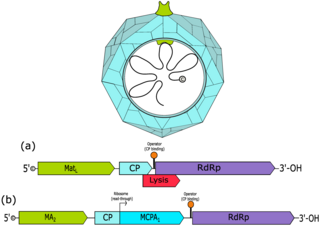
Fiersviridae is a family of positive-strand RNA viruses which infect prokaryotes. Bacteria serve as the natural host. They are small viruses with linear, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genomes that encode four proteins. All phages of this family require bacterial pili to attach to and infect cells. The family has 185 genera, most discovered by metagenomics. In 2020, the family was renamed from Leviviridae to its current name.

Potyviridae is a family of positive-strand RNA viruses that encompasses more than 30% of known plant viruses, many of which are of great agricultural significance. The family has 12 genera and 235 species, three of which are unassigned to a genus.
Furovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Virgaviridae. Graminae, winter wheat, wheat, triticale, oat, sorghum bicolor, and plants serve as natural hosts. There are six species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: (SBWMV): green and yellow mosaic.

Benyvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Benyviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: BNYVV: rhizomania.
Icerudivirus is a genus of viruses in the family Rudiviridae. These viruses are non-enveloped, stiff-rod-shaped viruses with linear dsDNA genomes, that infect hyperthermophilic archaea of the species Sulfolobus islandicus. There are three species in the genus.
Hordeivirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Virgaviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus.
Pecluvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Virgaviridae. Cereal crops and graminaceous weeds serve as natural hosts. There are two species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: (SBWMV): green and yellow mosaic. The name of the genus is derived from Peanut clump virus: Peanut clump virus, giving rise to Pecluvirus.
Pomovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Virgaviridae. Plants and dicotyledons serve as natural hosts. There are five species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: dwarfing of shoots (mop-top) and potato spraing disease. The name of the genus is derived from Potato mop-top virus, Potato mop-top virus, giving rise to Pomovirus.
Tobravirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Virgaviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are three species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: SBWMV: green and yellow mosaic.
Guttaviridae is a family of viruses. Archaea serve as natural hosts. There are two genera in this family, containing one species each. The name is derived from the Latin gutta, meaning 'droplet'.
Gammaflexiviridae is a family of viruses in the order Tymovirales. Fungi serve as natural hosts. There is only one genus in the family, Mycoflexivirus, which has one species: Botrytis virus F.

Bottigliavirus is the only genus in the family Ampullaviridae and contains 3 species. Ampullaviridae infect archaea of the genus Acidianus. The name of the family and genus is derived from the Latin word for bottle, ampulla, due to the virions having the shape of a bottle. The family was first described during an investigation of the microbial flora of hot springs in Italy.
Mason-Pfizer monkey virus (M-PMV), formerly Simian retrovirus (SRV), is a species of retroviruses that usually infect and cause a fatal immune deficiency in Asian macaques. The ssRNA virus appears sporadically in mammary carcinoma of captive macaques at breeding facilities which expected as the natural host, but the prevalence of this virus in feral macaques remains unknown. M-PMV was transmitted naturally by virus-containing body fluids, via biting, scratching, grooming, and fighting. Cross contaminated instruments or equipment (fomite) can also spread this virus among animals.
Tristromaviridae is a family of viruses. Archaea of the genera Thermoproteus and Pyrobaculum serve as natural hosts. Tristromaviridae is the sole family in the order Primavirales. There are two genera and three species in the family.
Deltalipothrixvirus is a genus of viruses in the family Lipothrixviridae. Archaea acidianus serve as natural hosts. Two species are assigned to the genus.
Acidianus rod-shaped virus 1 (ARV1), scientific name Itarudivurs ARV1, is an archaeal virus and the sole species in the genus Itarudivirus. Its only known host is Acidianus sp. Acii26.
Sulfolobus islandicus rod-shaped virus 1 (SIRV1) is a virus in the order Ligamenvirales. Its only known host is the Archaean Sulfolobus islandicus. The species was first documented from a hot spring sample in Yellowstone National Park.

Ribozyviria is a realm of satellite nucleic acids — infectious agents that resemble viruses, but cannot replicate without a helper virus. Established in ICTV TaxoProp 2020.012D, the realm is named after the presence of genomic and antigenomic ribozymes of the Deltavirus type. The agents in Ribozyviria are satellite nucleic acids, which are distinct from satellite viruses in that they do not encode all of their own structural proteins but require proteins from their helper viruses in order to assemble. Additional common features include a rod-like structure, an RNA-binding "delta antigen" encoded in the genome, and animal hosts. Furthermore, the size range of the genomes of these viruses is between around 1547–1735nt, they encode a hammerhead ribozyme or a hepatitis delta virus ribozyme, and their coding capacity only involves one conserved protein. Most lineages of this realm are poorly understood, the notable exception being the genus Deltavirus, comprising the causal agents of hepatitis D in humans.

Adnaviria is a realm of viruses that includes archaeal viruses that have a filamentous virion and a linear, double-stranded DNA genome. The genome exists in A-form (A-DNA) and encodes a dimeric major capsid protein (MCP) that contains the SIRV2 fold, a type of alpha-helix bundle containing four helices. The virion consists of the genome encased in capsid proteins to form a helical nucleoprotein complex. For some viruses, this helix is surrounded by a lipid membrane called an envelope. Some contain an additional protein layer between the nucleoprotein helix and the envelope. Complete virions are long and thin and may be flexible or a stiff like a rod.






