
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system or complex of genes on chromosome 6 in humans which encode cell-surface proteins responsible for regulation of the immune system. The HLA system is also known as the human version of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) found in many animals.

In genetics and bioinformatics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently large fraction of the population, many publications do not apply such a frequency threshold.

Complement receptor type 1 (CR1) also known as C3b/C4b receptor or CD35 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CR1 gene.
The term human blood group systems is defined by the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT) as systems in the human species where cell-surface antigens—in particular, those on blood cells—are "controlled at a single gene locus or by two or more very closely linked homologous genes with little or no observable recombination between them", and include the common ABO and Rh (Rhesus) antigen systems, as well as many others; 44 human systems are identified as of December 2022.
The Kell antigen system is a human blood group system, that is, a group of antigens on the human red blood cell surface which are important determinants of blood type and are targets for autoimmune or alloimmune diseases which destroy red blood cells. The Kell antigens are K, k, Kpa, Kpb, Jsa and Jsb. The Kell antigens are peptides found within the Kell protein, a 93-kilodalton transmembrane zinc-dependent endopeptidase which is responsible for cleaving endothelin-3.
XK is a protein found on human red blood cells and other tissues which is responsible for the Kx antigen which helps determine a person's blood type.

The Rh blood group system is a human blood group system. It contains proteins on the surface of red blood cells. After the ABO blood group system, it is the most likely to be involved in transfusion reactions. The Rh blood group system consisted of 49 defined blood group antigens in 2005. As of 2023, there are over 50 antigens among which the five antigens D, C, c, E, and e are the most important. There is no d antigen. Rh(D) status of an individual is normally described with a positive (+) or negative (−) suffix after the ABO type. The terms Rh factor, Rh positive, and Rh negative refer to the Rh(D) antigen only. Antibodies to Rh antigens can be involved in hemolytic transfusion reactions and antibodies to the Rh(D) and Rh antigens confer significant risk of hemolytic disease of the newborn.
The Yt antigen system is present on the membrane of red blood cells and helps determine a person's blood type. The antigens are found on the protein acetylcholinesterase, an enzyme which helps break down acetylcholine. The Yt system features two alleles, Yt(a) and Yt(b). Antibodies against the Yt system can lead to transfusion reactions such as hemolytic anemia.
hh, or the Bombay blood group, is a rare blood type. This blood phenotype was first discovered in Bombay by Dr. Y. M. Bhende in 1952. It is mostly found in the Indian sub-continent and Iran.
Animal erythrocytes have cell surface antigens that undergo polymorphism and give rise to blood types. Antigens from the human ABO blood group system are also found in apes and Old World monkeys, and the types trace back to the origin of humanoids. Other animal blood sometimes agglutinates with human blood group reagents, but the structure of the blood group antigens in animals is not always identical to those typically found in humans. The classification of most animal blood groups therefore uses different blood typing systems to those used for classification of human blood.
The MNS antigen system is a human blood group system based upon two genes on chromosome 4. There are currently 50 antigens in the system, but the five most important are called M, N, S, s, and U.
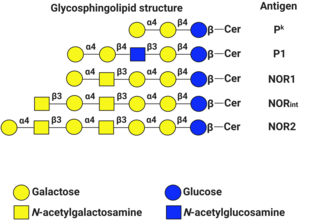
P1PK is a human blood group system based upon the A4GALT gene on chromosome 22. The P antigen was first described by Karl Landsteiner and Philip Levine in 1927. The P1PK blood group system consists of three glycosphingolipid antigens: Pk, P1 and NOR. In addition to glycosphingolipids, terminal Galα1→4Galβ structures are present on complex-type N-glycans. The GLOB antigen is now the member of the separate GLOB (globoside) blood group system.

The Ii antigen system is a human blood group system based upon a gene on chromosome 6 and consisting of the I antigen and the i antigen. The I antigen is normally present on the cell membrane of red blood cells in all adults, while the i antigen is present in fetuses and newborns.

The Diego antigen system is composed of 21 blood factors or antigens carried on the Band 3 glycoprotein, also known as Anion Exchanger 1 (AE1). The antigens are inherited through various alleles of the gene SLC4A1, located on human chromosome 17. The AE1 glycoprotein is expressed only in red blood cells and, in a shortened form, in some cells in the kidney. The Diegoa antigen is fairly common in Indigenous peoples of the Americas and East Asians, but very rare or absent in most other populations, supporting the theory that the two groups share common ancestry.

Glycophorin A (MNS blood group), also known as GYPA, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the GYPA gene. GYPA has also recently been designated CD235a (cluster of differentiation 235a).

Glycophorin B (MNS blood group) (gene designation GYPB) also known as sialoglycoprotein delta and SS-active sialoglycoprotein is a protein which in humans is encoded by the GYPB gene. GYPB has also recently been designated CD235b (cluster of differentiation 235b).

Ecto-ADP-ribosyltransferase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ART4 gene. ART4 has also been designated as CD297.

Erythroid membrane-associated protein is a protein that in humans is responsible for the Scianna blood group system, and is encoded by the ERMAP gene.

Glycophorin-E is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GYPE gene.

The Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Database (dbSNP) is a free public archive for genetic variation within and across different species developed and hosted by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) in collaboration with the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI). Although the name of the database implies a collection of one class of polymorphisms only, it in fact contains a range of molecular variation: (1) SNPs, (2) short deletion and insertion polymorphisms (indels/DIPs), (3) microsatellite markers or short tandem repeats (STRs), (4) multinucleotide polymorphisms (MNPs), (5) heterozygous sequences, and (6) named variants. The dbSNP accepts apparently neutral polymorphisms, polymorphisms corresponding to known phenotypes, and regions of no variation. It was created in September 1998 to supplement GenBank, NCBI’s collection of publicly available nucleic acid and protein sequences.












