Related Research Articles
In physics, the fundamental interactions, also known as fundamental forces, are the interactions that do not appear to be reducible to more basic interactions. There are four fundamental interactions known to exist: the gravitational and electromagnetic interactions, which produce significant long-range forces whose effects can be seen directly in everyday life, and the strong and weak interactions, which produce forces at minuscule, subatomic distances and govern nuclear interactions. Some scientists hypothesize that a fifth force might exist, but these hypotheses remain speculative.

General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity and Einstein's theory of gravity, is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physics. General relativity generalizes special relativity and refines Newton's law of universal gravitation, providing a unified description of gravity as a geometric property of space and time or four-dimensional spacetime. In particular, the curvature of spacetime is directly related to the energy and momentum of whatever matter and radiation are present. The relation is specified by the Einstein field equations, a system of second order partial differential equations.
In theories of quantum gravity, the graviton is the hypothetical quantum of gravity, an elementary particle that mediates the force of gravitational interaction. There is no complete quantum field theory of gravitons due to an outstanding mathematical problem with renormalization in general relativity. In string theory, believed by some to be a consistent theory of quantum gravity, the graviton is a massless state of a fundamental string.
Quantum gravity (QG) is a field of theoretical physics that seeks to describe gravity according to the principles of quantum mechanics. It deals with environments in which neither gravitational nor quantum effects can be ignored, such as in the vicinity of black holes or similar compact astrophysical objects, such as neutron stars.

A theory of everything, final theory, ultimate theory, unified field theory or master theory is a hypothetical, singular, all-encompassing, coherent theoretical framework of physics that fully explains and links together all aspects of the universe. Finding a theory of everything is one of the major unsolved problems in physics. String theory and M-theory have been proposed as theories of everything.

In physics, gravity (from Latin gravitas 'weight') is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the strong interaction, 1036 times weaker than the electromagnetic force and 1029 times weaker than the weak interaction. As a result, it has no significant influence at the level of subatomic particles. However, gravity is the most significant interaction between objects at the macroscopic scale, and it determines the motion of planets, stars, galaxies, and even light.
In physics, there are four observed fundamental interactions that form the basis of all known interactions in nature: gravitational, electromagnetic, strong nuclear, and weak nuclear forces. Some speculative theories have proposed a fifth force to explain various anomalous observations that do not fit existing theories. The characteristics of this fifth force depend on the hypothesis being advanced. Many postulate a force roughly the strength of gravity with a range of anywhere from less than a millimeter to cosmological scales. Another proposal is a new weak force mediated by W′ and Z′ bosons.

Kip Stephen Thorne is an American theoretical physicist known for his contributions in gravitational physics and astrophysics. A longtime friend and colleague of Stephen Hawking and Carl Sagan, he was the Richard P. Feynman Professor of Theoretical Physics at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) until 2009 and is one of the world's leading experts on the astrophysical implications of Einstein's general theory of relativity. He continues to do scientific research and scientific consulting, most notably for the Christopher Nolan film Interstellar. Thorne was awarded the 2017 Nobel Prize in Physics along with Rainer Weiss and Barry C. Barish "for decisive contributions to the LIGO detector and the observation of gravitational waves".

Sergei Kopeikin is a USSR-born theoretical physicist and astronomer presently living and working in the United States, where he holds the position of Professor of Physics at the University of Missouri in Columbia, Missouri. He specializes in the theoretical and experimental study of gravity and general relativity. He is also an expert in the field of the astronomical reference frames and time metrology. His general relativistic theory of the Post-Newtonian reference frames which he had worked out along with Victor A. Brumberg, was adopted in 2000 by the resolutions of the International Astronomical Union as a standard for reduction of ground-based astronomical observation. A computer program Tempo2 used to analyze radio observations of pulsars, includes several effects predicted by S. Kopeikin that are important for measuring parameters of the binary pulsars, for testing general relativity, and for detection of gravitational waves of ultra-low frequency. Sergei Kopeikin has worked out a complete post-Newtonian theory of equations of motion of N extended bodies in scalar-tensor theory of gravity with all mass and spin multipole moments of arbitrary order and derived the Lagrangian of the relativistic N-body problem.

Jacob David Bekenstein was an American and Israeli theoretical physicist who made fundamental contributions to the foundation of black hole thermodynamics and to other aspects of the connections between information and gravitation.
In theoretical physics, particularly fringe physics, polarizable vacuum (PV) and its associated theory refers to proposals by Harold Puthoff, Robert H. Dicke, and others to develop an analogue of general relativity to describe gravity and its relationship to electromagnetism.

Robert M. Wald is an American theoretical physicist and professor at the University of Chicago. He studies general relativity, black holes, and quantum gravity and has written textbooks on these subjects.
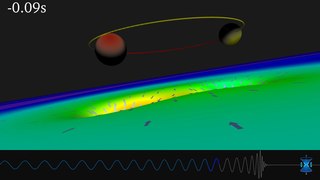
Gravitational waves are waves of the intensity of gravity generated by the accelerated masses of an orbital binary system that propagate as waves outward from their source at the speed of light. They were first proposed by Oliver Heaviside in 1893 and then later by Henri Poincaré in 1905 as waves similar to electromagnetic waves but the gravitational equivalent. Gravitational waves were later predicted in 1916 by Albert Einstein on the basis of his general theory of relativity as ripples in spacetime. Later he refused to accept gravitational waves. Gravitational waves transport energy as gravitational radiation, a form of radiant energy similar to electromagnetic radiation. Newton's law of universal gravitation, part of classical mechanics, does not provide for their existence, since that law is predicated on the assumption that physical interactions propagate instantaneously – showing one of the ways the methods of Newtonian physics are unable to explain phenomena associated with relativity.

Gravitoelectromagnetism, abbreviated GEM, refers to a set of formal analogies between the equations for electromagnetism and relativistic gravitation; specifically: between Maxwell's field equations and an approximation, valid under certain conditions, to the Einstein field equations for general relativity. Gravitomagnetism is a widely used term referring specifically to the kinetic effects of gravity, in analogy to the magnetic effects of moving electric charge. The most common version of GEM is valid only far from isolated sources, and for slowly moving test particles.
Anna Maria Nobili is an Italian physicist active in the field of gravitational physics. Her institution is Pisa University. She authored a number of papers on satellite dynamics and co-authored a book with Andrea Milani and Paolo Farinella on the orbital perturbations induced by non-gravitational forces. After having published several papers on celestial mechanics, also in collaboration with Clifford Will and E. Myles Standish, Nobili is now Principal Investigator of the Galileo Galilei (GG) experiment aimed to improve the accuracy of the equivalence principle lying at the foundation of general relativity and of other metric theories of gravity. Asteroid 552746 Annanobili, discovered by Yuri Ivascenko at the Andrushivka Astronomical Observatory in 2010, was named in her honor. The official naming citation was published by IAU's WGSBN on 20 September 2021.

C. W. Francis Everitt is a US-based English physicist working on experimental testing of general relativity.

Transformation optics is a branch of optics which applies metamaterials to produce spatial variations, derived from coordinate transformations, which can direct chosen bandwidths of electromagnetic radiation. This can allow for the construction of new composite artificial devices, which probably could not exist without metamaterials and coordinate transformation. Computing power that became available in the late 1990s enables prescribed quantitative values for the permittivity and permeability, the constitutive parameters, which produce localized spatial variations. The aggregate value of all the constitutive parameters produces an effective value, which yields the intended or desired results.
Lee Samuel Finn is an American astrophysicist, former Professor of Physics, Astronomy and Astrophysics and former Director of the Center for Gravitational Wave Physics at Pennsylvania State University. His research interests are in gravitational wave astronomy.

Ivor Robinson was a British-American mathematical physicist, born and educated in England, noted for his important contributions to the theory of relativity. He was a principal organizer of the Texas Symposium on Relativistic Astrophysics.
Valeria Ferrari is an Italian physicist whose research concerns the theoretical modeling of gravitational waves, and the oscillations in black holes and neutron stars that could cause them. She is a professor of theoretical physics at Sapienza University of Rome.
References
- ↑ Mashhoon, Bahram (1972). The gravitational and electromagnetic interactions of a black hole.
- 1 2 Pepe, Alberto; Kurtz, Michael J. (November 2012). "A Measure of Total Research Impact Independent of Time and Discipline". PLoS ONE . 7 (11): e46428. arXiv: 1209.2124 . Bibcode:2012PLoSO...746428P. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046428 . PMC 3492370 . PMID 23144782. e46428.