A ligament is the fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones. It is also known as articular ligament, articular larua, fibrous ligament, or true ligament. Other ligaments in the body include the:
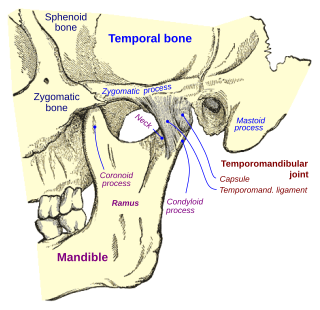
Temporomandibular joint dysfunction is an umbrella term covering pain and dysfunction of the muscles of mastication and the temporomandibular joints. The most important feature is pain, followed by restricted mandibular movement, and noises from the temporomandibular joints (TMJ) during jaw movement. Although TMD is not life-threatening, it can be detrimental to quality of life; this is because the symptoms can become chronic and difficult to manage.

The rib cage is an endoskeletal enclosure in the thorax of most vertebrate animals that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum, which protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and great vessels. The circumferential enclosure formed by left and right rib cages, together known as the thoracic cage, is a semi-rigid bony and cartilaginous structure which surrounds the thoracic cavity and supports the shoulder girdles to form the core part of the axial skeleton.

Osteopathy is a pseudoscientific system of alternative medicine that emphasizes physical manipulation of the body's muscle tissue and bones. In most countries, practitioners of osteopathy are not medically trained and are referred to as osteopaths.

In anatomy, the temporomandibular joints (TMJ) are the two joints connecting the jawbone to the skull. It is a bilateral synovial articulation between the temporal bone of the skull above and the mandible below; it is from these bones that its name is derived. This joint is unique in that it is a bilateral joint that functions as one unit. Since the TMJ is connected to the mandible, the right and left joints must function together and therefore are not independent of each other.
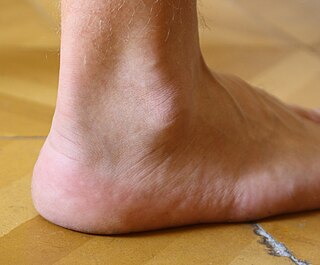
The ankle, or the talocrural region, or the jumping bone (informal) is the area where the foot and the leg meet. The ankle includes three joints: the ankle joint proper or talocrural joint, the subtalar joint, and the inferior tibiofibular joint. The movements produced at this joint are dorsiflexion and plantarflexion of the foot. In common usage, the term ankle refers exclusively to the ankle region. In medical terminology, "ankle" can refer broadly to the region or specifically to the talocrural joint.

Craniosacral therapy (CST) or cranial osteopathy is a form of alternative medicine that uses gentle touch to feel non-existent rhythmic movements of the skull's bones and supposedly adjust the immovable joints of the skull to achieve a therapeutic result. CST is a pseudoscience and its practice has been characterized as quackery. It is based on fundamental misconceptions about the anatomy and physiology of the human skull and is promoted as a cure-all for a variety of health conditions.

The human musculoskeletal system is an organ system that gives humans the ability to move using their muscular and skeletal systems. The musculoskeletal system provides form, support, stability, and movement to the body.

The Segond fracture is a type of avulsion fracture from the lateral tibial plateau of the knee, immediately below the articular surface of the tibia.
Reciprocal inhibition describes the relaxation of muscles on one side of a joint to accommodate contraction on the other side. In some allied health disciplines, this is known as reflexive antagonism. The central nervous system sends a message to the agonist muscle to contract. The tension in the antagonist muscle is activated by impulses from motor neurons, causing it to relax.
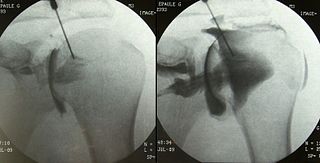
An arthrogram is a series of images of a joint after injection of a contrast medium, usually done by fluoroscopy or MRI. The injection is normally done under a local anesthetic such as Novocain or lidocaine. The radiologist or radiographer performs the study using fluoroscopy or x-ray to guide the placement of the needle into the joint and then injects around 10 ml of contrast based on age. There is some burning pain from the anesthetic and a painful bubbling feeling in the joint after the contrast is injected. This only lasts 20 – 30 hours until the Contrast is absorbed. During this time, while it is allowed, it is painful to use the limb for around 10 hours. After that the radiologist can more clearly see what is going on under your skin and can get results out within 24 to 48 hours.
Muscle Energy Techniques (METs) describes a broad class of manual therapy techniques directed at improving musculoskeletal function or joint function, and improving pain. METs are commonly used by manual therapists, physical therapists, occupational therapist, chiropractors, athletic trainers, osteopathic physicians, and massage therapists. Muscle energy requires the patient to actively use his or her muscles on request to aid in treatment. Muscle energy techniques are used to treat somatic dysfunction, especially decreased range of motion, muscular hypertonicity, and pain.
Counterstrain is a technique used in osteopathic medicine, osteopathy, physical therapy, massage therapy, and chiropractic to treat somatic dysfunction. It is a system of diagnosis and treatment that uses tender points, which are produced by trauma, inflammation, postural strain, or disease, to identify structures to manipulate. The manipulation uses light pressure to decompress the local nociceptors and mechanoreceptors responsible for the sensation of pain, returning central sensitization to its normal state. This technique extends Strain-counterstrain, a technique inhibits the reflexes by putting the tissues in a position of ease directly opposite to that of the reflex. Strain-counterstrain is also known as the Jones technique,, and spontaneous release by position. Counterstrain was developed by Lawrence Jones in 1955 and was originally called “Spontaneous Release by Positioning,” before being termed “strain-counterstrain.”

The distal radioulnar articulation is a synovial pivot joint between the two bones in the forearm; the radius and ulna. It is one of two joints between the radius and ulna, the other being the proximal radioulnar articulation. The joint features an articular disc, and is reinforced by the palmar and dorsal radioulnar ligaments.

The plantar calcaneonavicular ligament is a complex of three ligaments on the underside of the foot that connect the calcaneus with the navicular bone.

The midcarpal joint is formed by the scaphoid, lunate, and triquetral bones in the proximal row, and the trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate bones in the distal row. The distal pole of the scaphoid articulates with two trapezial bones as a gliding type of joint. The proximal end of the scaphoid combines with the lunate and triquetrum to form a deep concavity that articulates with the convexity of the combined capitate and hamate in a form of diarthrodial, almost condyloid joint.
William Garner Sutherland, D.O. (1873–1954) was an American osteopathic physician and important figure in American osteopathic medicine. Several of his manual therapy techniques are still practiced today by practitioners of osteopathy, although craniosacral therapy is regarded as pseudoscience by the medical community. Sutherland was the first osteopathic physician to conceptualize the cranial approach and teach it systematically. However, Sutherland acknowledged Andrew Taylor Still as the developer of all osteopathy, including the cranial approach. Sutherland was the first person to claim to feel a rhythmic shape change in the bones of the cranium. He later applied this movement to all body tissues and this movement is the agent of change in dysfunctional tissues. He later named this motion the body's "Primary Respiration."

Bennett fracture is a type of partial broken finger involving the base of the thumb, and extends into the carpometacarpal (CMC) joint.
Myotherapy is a form of muscle therapy which focuses on the assessment, treatment and rehabilitation of musculoskeletal pain and associated pathologies. The term myotherapy was originally coined by Bonnie Prudden to describe a specific type of trigger point therapy which she developed in the 1970s based on the earlier work of Travell and Simons who researched the cause and treatment of pain arising from myofascial trigger points. While based on rational principles, there is little scientific research regarding the efficacy of this therapy, so it remains controversial within the medical and academic disciplines.

The term sacroiliac joint dysfunction refers to abnormal motion in the sacroiliac joint, either too much motion or too little motion, that causes pain in this region.












