
Banaskantha district is one of the thirty-three districts of the Gujarat state of India. The administrative headquarters of the district is at Palanpur which is also its largest city. The district is located in the Northeast of Gujarat and is presumably named after the West Banas River which runs through the valley between Mount Abu and Aravalli Range, flowing to the plains of Gujarat in this region and towards the Rann of Kutch. The district is famous for the Ambaji temple which draws many tourists. It covers an area of 12703 km2 and is the second largest district in the state.

Palanpur is a city and a municipality of Banaskantha district in the Indian state of Gujarat. Palanpur is the administrative headquarters of Banaskantha district. Palanpur is the ancestral home to an industry of Indian diamond merchants.
Radhanpur is a town and a municipality in Patan district in the Indian state of Gujarat.
Deesa is a city and a municipality in the Banaskantha district in the state of Gujarat, India.

Tharad is a town in Tharad taluka in the Banaskantha district of the state of Gujarat in India. It is the administrative center of Tharad taluka. Tharad is near the border of Gujarat, 40 km from the border with Pakistan and 15 km from the Indian state of Rajasthan. Majority of its population follow the religion of Hinduism. Its main industries are agriculture and diamond polishing. It is one of the first major towns in Gujarat on National Highway 15.
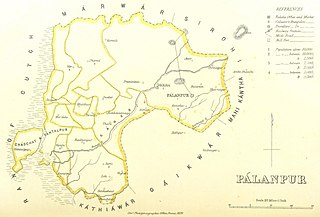
Palanpur Agency, also spelled Pahlunpore Agency, was a political agency or collection of princely states in British India, within the Gujarat Division of Bombay Presidency. In 1933, the native states of the Mahi Kantha Agency, except for Danta, were included in the Western India States Agency. The agency, headquartered at Palanpur, oversaw some 17 princely states and estates in the area, encompassing an area of 6393 square miles (16,558 km2) and a population, in 1901, of 467,271.
Kankrej thana or Kankrej Estates was a former collection of native states in what is now part of Banaskantha district of Gujarat, India.

Vav is a town and the headquarters of Vav Taluka in Banaskantha district in Gujarat state of India. Vav is the largest taluka of the district.
Dhanera is one of the 182 Legislative Assembly constituencies of Gujarat state in India. It is part of Banaskantha district. It is numbered as 9-Dhanera.
Vadgam is one of the 182 Legislative Assembly constituencies of Gujarat state in India. It is part of Banaskantha district, numbered as 11-Vadgam and is reserved for candidates belonging to the Scheduled Castes. It falls under the Patan Lok Sabha constituency.
Palanpur is one of the 182 Legislative Assembly constituencies of Gujarat state in India. It is part of Banaskantha district.It is numbered as 12-Palanpur.

Kumbhariya is a village of historical, archaeological and religious importance with cultural heritage in Danta Taluka of Banaskantha district, Gujarat, India.

Banas Dairy is a division of Gujarat Cooperative Milk Marketing Federation which is under the ownership of Ministry of Cooperation, Government of Gujarat based in the Banaskantha district of Gujarat, India and is Asia's largest milk producer. It was founded in 1969, in accordance with the 1961 rule of the National Dairy Development Board under Operation Flood. Galbabhai Nanjibhai Patel played an important role in the foundation of the dairy. It is headquartered at Palanpur.
The history of Palanpur starts with its relation to the historic city of Chandravati ruled by Paramara dynasty. The town was re-peopled and ruled by Chauhans around thirteenth century. At the start of the seventeenth century, the Palanpur State was taken over by Jhalori dynasty of Pashtun Lohani (Bihari-Pathan) tribe which was founded in 1373 and ruled from Jhalor. The dynasty came into historical prominence during the period of instability that followed the demise of Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb in the early 18th century. It was overrun soon afterwards by the Marathas; the Lohanis followed the trend of seeking recourse in the British East India Company against them and finally entered the subsidiary alliance system in 1817, along with all other neighbouring states, becoming a British protectorate governed by Palanpur Agency. After independence of India in 1947, Palanpur State was dissolved in 1949 and merged with India as a part of Bombay State. Subsequently, Palanpur became the capital of Banaskantha district of Gujarat.(Hebatpur) Currently Maximum Jagirdar Families Living In Hebatpur Village:12 Km Away From Palanpur. In Addition:5 Villages Lohani Family. 42 Villages Bihari Families. Also Pathan & Ghori Families.

Balaram Ambaji Wildlife Sanctuary is located at Banaskantha, Gujarat, India. It covers 542 km2, and falls in the catchment area of Banas and Sabarmati rivers, and is a part of the Khathiar-Gir dry deciduous forests' ecoregion. The sanctuary borders Rajasthan and close to mount abu. The period from October to May is considered to be the best time to visit.

Radhanpur is a town and a municipality in Patan district in the Indian state of Gujarat. Radhanpur belonged to the Vaghelas in early years and later it was held as a fief under the Gujarat Sultanate by Fateh Khan Baloch. During Mughal period, the descendants of Babi dynasty were appointed as the governor of Radhanpur and other villages of North Gujarat. After decline of Mughal, they became free and established themselves as independent rulers. In 1743, Babi descendant Jawan Mard Khan II took over viceroyalty of Ahmedabad and controlled several villages in North Gujarat. He was defeated by Maratha Gaekwads in 1753 at Ahmedabad and Gaekwads agreed to his demand of control of villages in North Gujarat headquartered at Radhanpur State. His descendants lost some of these villages to Gaekwads subsequently. In 1813, Sher Khan made a treaty with the Gaekwar and British and became British protectorate. His descendants ruled the state until independence of India in 1947.
Diyodar, also spelled Diodar or Deodar, is a town and former princely state in Diyodar Taluka of Banaskantha district in Gujarat, western India.
Tervada is a village in Kankrej Taluka of Banaskantha district in Gujarat, India.

Balaram River is a river in Banaskantha district of Gujarat, India. It flows entirely in Banaskantha district and merges into Banas River at 14 km before Dantiwada Dam.
Jagana is a village in the Palanpur taluka of Banaskantha district in northern Gujarat, India. The villages Vasna, Bhagal, Sedrasana are located near to Jagana and it is just 6 km away from the district headquarters, Palanpur.













