Related Research Articles

The hoolock gibbons are three primate species of genus Hoolock in the gibbon family, Hylobatidae, native to eastern Bangladesh, Northeast India, Myanmar, and Southwest China.

The stump-tailed macaque, also called the bear macaque, is a species of macaque native to South Asia and Southeast Asia. In India, it occurs south of the Brahmaputra River, in the northeastern part of the country. Its range in India extends from Assam and Meghalaya to eastern Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram and Tripura.

Dibru-Saikhowa National Park is a national park located in Dibrugarh and Tinsukia districts, Assam, India. It was designated a Biosphere Reserve in July 1997 with an area of 765 km2 (295 sq mi), including a core area of 340 km2 (130 sq mi) and a buffer zone of 425 km2 (164 sq mi).

The Nokrek National Park, the core area of the Nokrek Biosphere Reserve, is a National park located approximately 2 km away from Tura Peak in West Garo Hills district of Meghalaya, India.The Nokrek Biosphere Reserve along with the Nokrek National Park was added by UNESCO to its list of Biosphere Reserves in May 2009. along with the Balpakram National Park in South Garo Hills. The Nokrek area is a hotspot of biodiversity in Meghalaya. Established in 1986, the National Park area comprising around 47.48 square kilometres is looked after by the Northern Nokrek Range and the Southern Nokrek Range under the East & West Garo Hills Wildlife Division of the Meghalaya State Forest Department under the administrative control of the Government of Meghalaya, India.

Balpakram National Park is a national park to the south of Garo Hills in Meghalaya, India, located at an altitude of about 910 m (3,000 ft) close to the international border with Bangladesh. It was inaugurated in December 1987 and provides habitat for barking deer, Asian golden cat, Bengal tiger, marbled cat, wild water buffalo, red panda and Indian elephant. Balpakram means "land of the eternal wind" according to the myth of the Garo people.

Namdapha National Park is a 1,985 km2 (766 sq mi) large protected area in Arunachal Pradesh of Northeast India. The park was established in 1983. With more than 1,000 floral and about 1,400 faunal species, it is a biodiversity hotspot in the Eastern Himalayas. The national park harbours the northernmost lowland evergreen rainforests in the world at 27°N latitude. It also harbours extensive dipterocarp forests, comprising the northwestern parts of the Mizoram-Manipur-Kachin rain forests ecoregion.
Endangered mammals of India are the mammal species in India that are listed as threatened in the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Animals

The northern pig-tailed macaque is a vulnerable species of macaque in the subfamily Cercopithecidae. It is found in Bangladesh, Cambodia, China, India, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand, and Vietnam. Traditionally, M. leonina was considered a subspecies of the southern pig-tailed macaque, but is now classified as an individual species. In the 21st century, the pig-tailed macaque was split into the northern pig-tailed macaque species Macaca leonina and the Sundaland pig-tailed macaque species M. nemestrina. This reclassification was aided by the observation of sexual swellings and basic attributes that distinguish the two. The northern pig-tailed macaque is frugivorous and their social grouping is matriarchal, where sexual dimorphic traits can distinguish males and females. Their adaptation to omnivorous diets occur in periods of fruit scarcity, munching on wild vegetation and crops, human foods, and small insects and mammals. Despite their adaptability, northern-pig tailed macaques experience viral threats such as the human immunodeficiency virus type 1, pathogenic simian immunodeficiency, and coronavirus. Human impacts are also present, such as agricultural expansions, aquaculture, transportation infrastructure, hunting and logging for meat and trophies, and the illegal pet trade; that result in habitat loss, forest fragmentation, and a reduced well-being.

The Hollongapar Gibbon Sanctuary, formerly known as the Gibbon Wildlife Sanctuary or Hollongapar Reserved Forest, is an isolated protected area of evergreen forest located in Assam, India. The sanctuary was officially constituted and renamed in 1997. Set aside initially in 1881, its forests used to extend to the foothills of the Patkai mountain range.
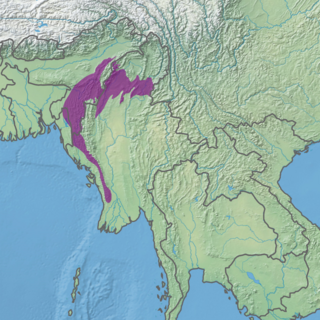
The Mizoram–Manipur–Kachin rain forests is a subtropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion which occupies the lower hillsides of the mountainous border region joining India, Bangladesh, and Burma (Myanmar) and China's Yunnan Province. The ecoregion covers an area of 135,600 square kilometres (52,400 sq mi). Located where the biotas of the Indian Subcontinent and Indochina meet, and in the transition between subtropical and tropical regions of Asia, the Mizoram–Manipur–Kachin rain forests are home to great biodiversity. The WWF rates the ecoregion as "Globally Outstanding" in biological distinctiveness.

Anwaruddin Choudhury is an Indian naturalist, noted for his expertise on the fauna of North-East India.

Dehing Patkai National Park is located in the Dibrugarh and Tinsukia districts of Assam and covers an area of 231.65 km2 (89.44 sq mi) rainforest. It was declared a wildlife sanctuary on 13 June 2004. On 13 December 2020 Government of Assam upgraded it into a national park. On 9 June 2021 Forest Department of Assam officially notified it as a national park. It is located in the Dehing Patkai Landscape which is a dipterocarp-dominated lowland rainforest. The rainforest stretches for more than 575 km2 (222 sq mi) in the districts of Dibrugarh, Tinsukia and Charaideo. The forest further spreads over in the Tirap and Changlang districts of Arunachal Pradesh. Dehing Patkai National Park harbours the largest stretch of lowland rainforests in India. Dehing Patkai Wildlife Sanctuary was declared as Dehing Patkai Elephant Reserve under Project Elephant. Dehing-Patkai as a potential wildlife sanctuary was identified in late 1980s during a primate survey as "Upper Dehing Wildlife Sanctuary". Subsequently during a study on white-winged wood duck in early 1990s, it was discovered as a globally important site for this duck and recommended to be upgraded to "Upper Dehing National Park".
Nambor Wildlife Sanctuary is a protected area located in Karbi Anglong district of Assam in India. This wildlife sanctuary covers an area of 37 km2. The area was declared as a sanctuary on 27 July 2000. It is located 25 km from Golaghat district and 65 km from the Kaziranga National Park. Together with Garampani Wildlife Sanctuary of Karbi Anglong and Nambor-Doigrung Wildlife Sanctuary of Golaghat distrcit it forms a larger complex of wilderness. The proposal for this sanctuary was made in 1993.
Nambor - Doigrung Wildlife Sanctuary is a Morangi located in Golaghat district of Assam in India. This wildlife sanctuary covers an area of 97.15 km2. It is located 25 km from Golaghat town and about 318 km from Guwahati LGBI Airport. The forest type is tropical semi-evergreen with pockets of pure evergreen, interspersed with small forest marshes. The area was declared as a Wildlife sanctuary in 2003. The sanctuary along with Garampani Wildlife Sanctuary and Nambor Wildlife Sanctuary (37 km2) are a part of the Kaziranga-Karbi Anglong Elephant Reserve, which was declared on 17 April 2003, with an estimated area of 3,270 km2.
BARAIL Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the southern part of Assam, India, in Cachar district and lies between 24°55΄53΄΄-25°05΄52΄΄ N latitude and 92°27΄40΄΄-93°04΄30΄΄ E longitude. The Dima Hasao part of Barail is not part of this sanctuary. The altitude ranges between 55–1500 m above mean sea level. It spreads over 326.24 km2. The annual average rainfall and temperature range from 2500–4000 mm and 9.2 °C to 36.2 °C respectively; the Humidity varies from 62% to 83%. Field works in Barail area proposed as a national park/sanctuary in 1980s.

The Kamlang Wildlife Sanctuary, established in 1989, is the 50th Tiger reserve in India. The Sanctuary is rich with floral and faunal diversity. It is situated in the Lohit District of the northeastern Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh. The park is named after the Kamlang River which flows through it. The Mishmi, Digaro Mishmi, and Miju Mishmi people tribal people who reside around the periphery of the sanctuary claim their descent from the King Rukmo of the epic Mahabharata. They believe in a myth of an invisible god known as Suto Phenkhenynon jamalu. An important body of water in the sanctuary is the Glow Lake. Located in tropical and sub-tropical climatic zones, the sanctuary is the habitat of the four big cat species of India: tiger, leopard, clouded leopard and snow leopard.
The Amchang Wildlife Sanctuary is a wildlife sanctuary located on the eastern fringe of Guwahati, Assam, India. The sanctuary is known for hosting rare and endangered birds and animals. Amchang's habitat is dominated by tropical moist deciduous forest with semi-evergreen forest in depressions and river-valleys. It is known for its elephants which have become isolated with no movement with other elephant-populations. The first published information of these elephants was found in 1985 There were depredations in the fringe areas, which are part of Guwahati city, the capital of Assam. It was acute as the pachyderms were confined to an isolated forest not very large. Hence, a protected area was mooted. The wild elephants from Amchang often enter parts of Guwahati City but on a few occasions they travelled to the heart of the city. The sanctuary has other mammals such as Chinese pangolin, slow loris, Assamese macaque, rhesus monkey, hoolock gibbon, leopard, leopard cat, jungle cat, sambar, barking deer, red serow, Malayan giant squirrel, crestless Himalayan porcupine. However, it is the presence of an isolated population of gaur or Indian "bison" that has added significance to Amchang. This bovid is also confined to this sanctuary with no links to other areas. Amchang is an Important Bird & Biodiversity Area. The sanctuary has a diverse birdlife. Some noteworthy species found includes White-backed vulture, Slender-billed vulture, White-cheeked hill partridges, Grey peacock pheasant, Kaleej pheasant, Greater adjutant stork mostly in flight, Great pied hornbill, Oriental pied hornbill and Green imperial pigeon among many others. Prior to 2004, the area was made up of three individual reserved forests, the Amchang reserved forest, South Amchang reserved forest and Khanapara reserved forest. These three forests were combined in 2004 by the Assam government to form the sanctuary as it exists today. It is spread over in an area of 78.64 square kilometre
Dehing Patkai Landscape, located in the Upper Assam, stretches for over roughly 600 square kilometres and comprises three large blocks of forests and several forest fragments. The forest is classified as a lowland Tropical Wet Evergreen Forest (Dipterocarpus-Mesua). It falls under Indo-Burma Biodiversity Hotspot. Due to its biodiversity and significance for elephant habitat, parts of the landscape are recognised as Dehing Patkai Elephant Reserve and 111 km2 is protected as the Dehing Patkai Wildlife Sanctuary since 2004.

Raimona National Park is located in extreme western part of Assam, India. It is spread across Gossaigaon and Kokrajhar subdivisions of Kokrajhar district of Bodoland Territorial Region.
References
- 1 2 Choudhury, A.U. (2009). Balpakram –Meghalaya’s heritage IBA. Mistnet 10 (4): 11-13.
- ↑ "Balphakram National Park". world-wildlife-adventures.com.[ dead link ]
- ↑ Choudhury, A.U. (2003). Meghalaya's vanishing wilderness. Sanctuary Asia 23(5): 30-35.
- ↑ Choudhury, A.U. (1994). The decline of Wild water buffalo in Northeastern India. Oryx 28(1): 70-73.
- ↑ Choudhury, A.U. (2010). The vanishing herds : wild water buffalo. Gibbon Books & The Rhino Foundation for Nature in NE India, Guwahati, India. 184pp. [Supported by CEPF & Taiwan Forestry Bureau].
- ↑ Choudhury, A.U. (1996). Red panda in Garo Hills. Environ IV(I): 21.
- ↑ Choudhury, A.U. (2001). An overview of the status and conservation of the red panda Ailurus fulgens in India, with reference to its global status. Oryx 35(3):250-259.
- ↑ Choudhury, A.U. (1999). Status and conservation of the Asian elephant Elephas maximus in north-eastern India. Mammal Review 29(3): 141-173.
- ↑ Choudhury, A.U. (2002). Distribution and Conservation of the Gaur Bos gaurus in the Indian Subcontinent. Mammal Review 32(3): 199-226.
- ↑ Choudhury, A.U. (2003). The cats in North East India. Cat News 39:15-19.
- ↑ Choudhury, A.U. (2002). Status and conservation of the stump-tailed macaque Macaca arctoides in India. Primate Report. 63: 63-72.
- ↑ Choudhury, A.U. (2003). The pig-tailed macaque Macaca nemestrina in India - status and conservation. Primate Conservation 19:91-94.
- ↑ Choudhury, A.U. (2006). The distribution and status of hoolock gibbon, Hoolock hoolock, in Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram and Nagaland in Northeast India. Primate Conservation 20: 79-87.
- ↑ Islam, Z. & rahmani, A. (2004). IBAs in India. BNHS & BirdLife Int., Mumbai & Cambridge